中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (22): 3547-3554.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.22.018
• 材料生物相容性 material biocompatibility • 上一篇 下一篇
纳米羟基磷灰石/聚苯硫醚复合材料在体内的生物相容性
范珂夏1,马 原1,杨为中2,余思逊1,孙志勇1,夏 勋1,杨立斌1,郭 恒1,匡永勤1,顾建文3
- 1解放军成都军区总医院,四川省成都市 610083;2四川大学材料科学与工程学院,四川省成都市 610064;3解放军306医院,北京市 100101
In vivo biocompatibility of nano-hydroxyapatite/polyphenylene sulfide composites
Fan Ke-xia1, Ma Yuan1, Yang Wei-zhong2, Yu Si-xun1, Sun Zhi-yong1, Xia Xun1, Yang Li-bin1, Guo Heng1, Kuang Yong-qin1, Gu Jian-wen3
- 1General Hospital of Chengdu Military Region of Chinese PLA, Chengdu 610083, Sichuan Province, China; 2College of Materials Science and Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610064, Sichuan Province, China; 3the 306th Hospital of PLA, Beijing 100101, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
生物相容性:还称作生物可接受性或生物适应性,指的是材料植入宿主体内,与特定部位相接触后,能够在机体正常活动中维持其功能稳定性,材料自身及其降解物应该体现出无毒无害、无致畸、无致癌及致突变效应,不会导致机体出现排斥反应及炎症效应,是决定材料是否能够植入机体的主要指标。因此生物材料研究和发展面临的一个主要难题就是改善材料具有的生物相容性特征。
材料生物相容性评价:目前依据GB/T 16886医疗器械生物学评价标准,主要要从两方面去评价生物材料具有的相容性:动物体外实验和体内实验,前一种指的是通过材料或者材料浸提液分析其对组织生长、增殖及代谢等产生的影响作用,研究方法主要有:血液相容性实验、亲水性实验及体外细胞毒性实验等;后一种指的是将材料植入活体动物体内后,观察动物生存情况、局部反应、材料及周围组织病理变化,主要研究方法包括全身毒性研究、超敏反应实验、植入后局部反应实验等。
背景:目前缺少纳米羟基磷灰石/聚苯硫醚复合材料生物相容性的相关研究。
目的:在已完成的体外生物相容性研究基础上,评价纳米羟基磷灰石/聚苯硫醚复合材料的体内生物相容性。
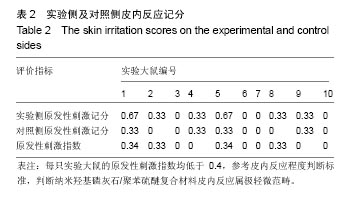
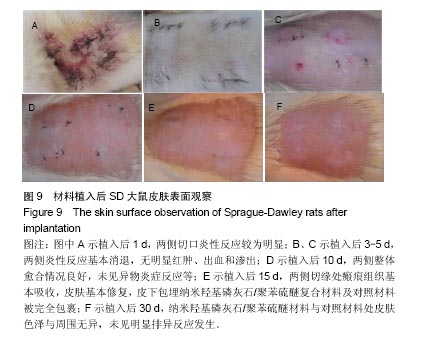
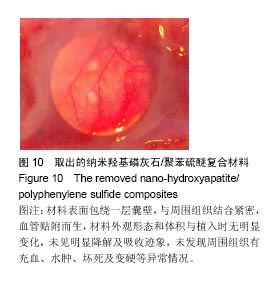
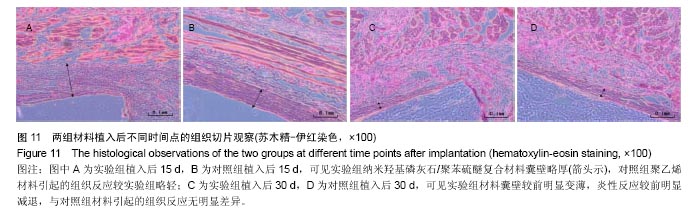
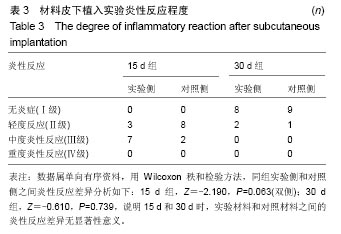
方法:①全身毒性实验:分别在SD大鼠腹腔注射纳米羟基磷灰石/聚苯硫醚复合材料浸提液与生理盐水,注射72 h后,观察大鼠一般情况、体质量及肝肾组织学变化;②迟发型超敏反应实验:在SD大鼠背部皮内分别注射纳米羟基磷灰石/聚苯硫醚复合材料浸提液与生理盐水,注射72 h内,观察皮肤刺激症状;③局部反应实验:在SD大鼠背部皮内分别植入纳米羟基磷灰石/聚苯硫醚复合材料与聚乙烯材料,植入15,30 d后,观察植入材料及其周围组织病理变化。
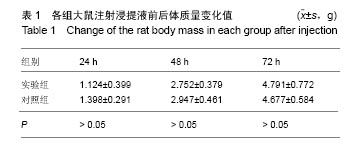
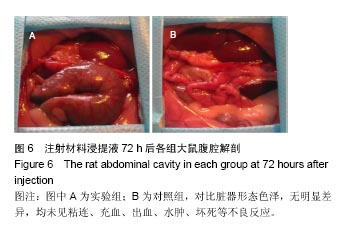
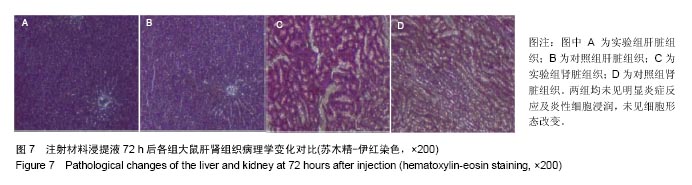
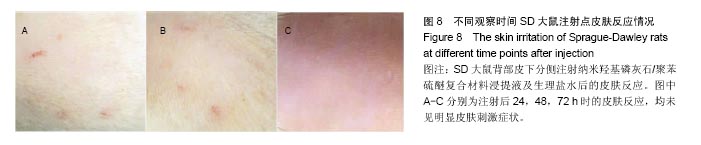
结果与结论:①腹腔注射纳米羟基磷灰石/聚苯硫醚复合材料浸提液后,大鼠一般情况良好,体质量稳步增长,与对照组无差异(P < 0.05),肝肾脏器形态、色泽均正常,参照毒性程度分级,判定复合材料全身毒性分级属正常级别;②大鼠背部皮下注射纳米羟基磷灰石/聚苯硫醚复合材料浸提液后,未见明显皮肤刺激症状,原发性刺激指数< 0.4,提示复合材料超敏反应程度属极轻微范畴;③纳米羟基磷灰石/聚苯硫醚复合材料植入大鼠背部皮下后,未见明显降解吸收及排异反应发生,接触面组织炎性反应程度(15 d≤Ⅲ级,30 d≤Ⅱ级)及纤维囊厚度(15 d≤Ⅲ级,30 d≤Ⅱ级)均提示材料与周围组织相容性良好;④结果表明,纳米羟基磷灰石/聚苯硫醚复合材料具有良好的体内生物相容性。
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)