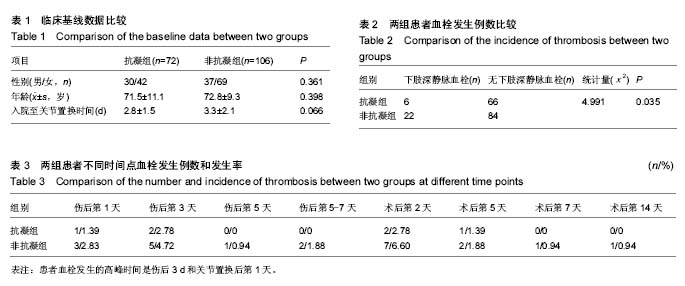
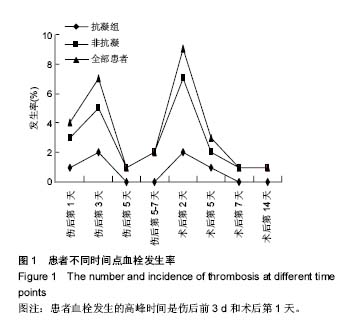
| [1] 魏俊强,王新宇,金宇,等.利伐沙班对股骨转子间骨折术后失血风险和深静脉血栓形成效果及安全性研究[J].解放军医药杂志, 2015,27(10):95-98.[2] Della Valle CJ,Mirzabeigi E, Zuckerman JD,et al. Thromboembolic prophylaxis for patients with a fracture of the proximal femur.Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2002;31(1): 16-24.[3] 张辉良,梁俊生,张洪斌.不同药物对预防骨折围手术期下肢深静脉血栓形成的对比[J]. 实用医学杂志,2012,28(2):293-294.[4] Bjørnarå BT, Gudmundsen TE, Dahl OE. Frequency and timing of clinical venous thromboembolism after major joint surgery.Bone Joint J.2006;88(3): 386-391.[5] 唐颖,郭庆山,赵玉峰,等.创伤骨折并发下肢深静脉血栓的危险因素分析[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2010,26(12):1122-1125.[6] 中华医学会骨科学分会.中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,36(2):65-71.[7] Chang X, Qian WW, Weng XS. Case-control study on influence of femoral neck fracture on deep venous thrombosis in patients undergoing prosthetic hip surgery. Zhongguo Gu Shang.2012;25(5):389-92.[8] 卢绍燊,丁玲,余海波,等.利伐沙班预防高龄股骨颈骨折患者髋关节置换术前血液高凝状态及深静脉血栓形成的效果[J].广东医学, 2015,36(9):1426-1429.[9] 王强,盛伟斌,姜曙祥,等.老年髋关节周围骨折应用低分子肝素预防下肢深静脉血栓的研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015, 25(2):164-165.[10] 张时文,李宣明.全髋关节置换术和人工股骨头置换术治疗高龄股骨颈骨折的疗效比较[J].中华创伤杂志,2014,20(7):692-694.[11] 李春根,陈江,牟明威,等.人工股骨头置换术治疗高龄股骨颈骨折的疗效分析[J]. 中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2011,5(4):509-512.[12] 彭志平,林云.彩超对下肢深静脉血栓筛查的意义[J].中国超声医学杂志,2013,29(2):167-169.[13] 何文.下肢深静脉血栓形成的超声检查[J].中华医学杂志,2003, 83(7)615-616.[14] 张姝江.实施概要:抗血栓治疗及血栓预防骨科手术病人的静脉血栓预防部分美国胸科医师协会循证临床实践指南(ACCP第9版)[J]. 中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2012,6(4):641-642.[15] 中华医学会外科学分会血管外科学组.深静脉血栓形成的诊断和治疗指南(第2版)[J].中华外科杂志,2012,50(7):611-614.[16] 王琦,孙辉,张先龙. 老年股骨颈骨折患者关节置换术前深静脉血栓形成的发生率[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(12): 1119-1122.[17] Hull RD, Pineo GF, Stein PD,et al.Timing of initial administration of low-molecular-weight heparin prophylaxis against deep vein thrombosis in patients following elective hip arthroplasty: a systematic review. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161 (16):1952-1960[18] Sikorski JM,Hampson WG, Staddon GE.The natural history and aetiology of deep vein thrombosis after total hip replacement. Bone Joint J.1981;63(2): 171-177.[19] Yamaguchi T, Hasegawa M, Niimi R, et al. Incidence and time course of asymptomatic deep vein thrombosis with fondaparinux in patients undergoing total joint arthroplasty. Thrombosis Res.2010;126(4): e323-e326.[20] Smith EB, Parvizi J, Purtill JJ.Delayed surgery for patients with femur and hip fractures-risk of deep venous thrombosis. 2011;70(6):113-116.[21] Hill J, Treasure T.Guideline Development Group. Reducing the risk of venous thromboembolism (deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism) in patients admitted to hospital: summary of the NICE guideline. Heart.2010;96(11):879-882.[22] Eriksson BI,Borris LC,Friedman RJ,et al.Rivaroxaban versus enoxaparin for thrombprophylaxis after hip athroplasty.N Engl J Med.2008;358:2765-2775.[23] Dietch ZC, Petroze RT, Thames MT et al.The "high-risk" deep venous thrombosis screening protocol for trauma patients: Is it practical?.Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015;79(6):970-975.[24] Gornik HL,Sbarma AM.Duplex ultrasound in the diagnosis of lower-extremity deep venous thrombosis. Circulation. 2014; 129(8):917-921.[25] 李涛,吕明,李庆涛.综合防治法预防老年人股骨近端骨折下肢深静脉血栓形成的比较研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2008, 22(4):453-455.[26] Smith EB, Parvizi J, Purtill JJ.Delayed surgery for patients with femur and hip fractures-risk of deep venous thrombosis. 2011;70(6):113-116.[27] 肖湘,冯凯强,袁宇.老年骨质疏松性髋部骨折患者术前下肢深静脉血栓患病率及危险因素分析[J].中华骨科杂志, 2015,35(11): 1084-1090.[28] Yamaguchi T, Hasegawa M, Niimi R, et al. Incidence and time course of asymptomatic deep vein thrombosis with fondaparinux in patients undergoing total joint arthroplasty. Thrombosis Res.2010;126(4): e323-e326.[29] Warwick D,Rosencher N.The ‘‘critical thrombosis period’’in major orthopedic surgery: when to start and when to stop prophylaxis.Clinical and Applied Thrombosis/Hemostasis. 2010;16(4): 394-405. |
.jpg)
.jpg)