中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (15): 2406-2409.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.15.020
• 骨与关节图像与影像 bone and joint imaging • 上一篇 下一篇
坐骨股骨撞击综合征的MRI诊断标准
张德洲,李东明,易雪冰,罗 铧
- 四川省骨科医院,四川省成都市 610041
MRI diagnostic criteria for ischiofemoral impingement syndrome
Zhang De-zhou, Li Dong-ming, Yi Xue-bing, Luo Hua
- Sichuan Provincial Orthopedic Hospital, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
坐骨股骨撞击综合征:是指坐骨结节与股骨小转子间隙变窄相关的髋部疼痛,股方肌出现形态学异常和(或) MRI信号异常。当坐骨结节和股骨小转子间隙变窄,走行于其中的股方肌受到反复摩擦和损伤,出现股方肌及其邻近肌群的水肿或撕裂,水肿的软组织(以股方肌为主)对邻近坐骨神经的刺激,成为髋部疼痛的诱发因素或直接原因。患者常有髋部、臀部及腹股沟区的非特异性疼痛,疼痛可向下肢远端放射,还可同时伴有髋部弹响、捻发音或髋关节交锁症状,疼痛时间可持续数月甚至数年。
脂肪抑制技术:由于人体内脂肪组织中的氢质子和其他组织中的氢质子所处的分子环境不同,使得它们的共振频率不相同;当脂肪和其他组织的氢质子同时受到射频脉冲激励后,它们的弛豫时间也不一样。在不同的回波时间采集信号,脂肪组织和非脂肪组织表现出不同的信号强度。利用人体内不同组织的上述特性,可以使用相关技术使脂肪组织的信号强度减低或消除而非脂肪组织信号几乎不受任何影响。该技术可以抑制脂肪组织信号,增加图像的组织对比,鉴别病灶内是否含有脂肪,为病灶的出血、水肿的鉴别诊断提供信息。
摘要
背景:坐骨股骨撞击综合征越来越引起人们的重视,但因其发病率较低,国内外相关研究较少,部分影像科医生对该病的影像学表现认识不够深刻。
目的:探讨坐骨股骨撞击综合征的MRI诊断标准,以提高对坐骨股骨撞击综合征MRI表现的认识。
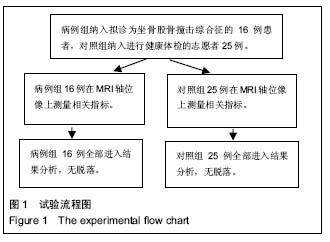
方法:选择拟诊断为坐骨股骨撞击综合征的病例16例21髋作为病例组,25例健康志愿者作为对照组,在MRI轴位像上分别测量双侧坐骨股骨间距(即坐骨结节与股骨小转子间的最短距离)与股方肌间距(股骨小转子与腘绳肌腱止点的距离),并观察股方肌的信号及形态。对比分析2组坐骨股骨间隙和股方肌间隙的差异。
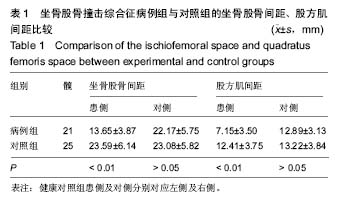
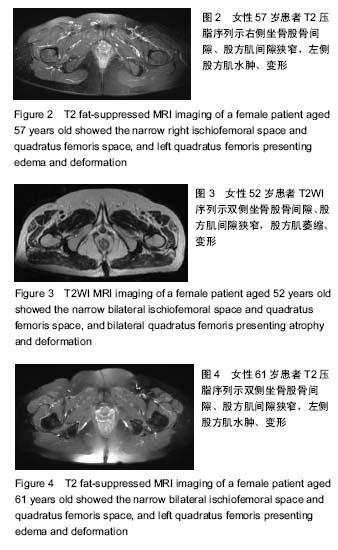
结果与结论:①16例患者中女13例,男3例;双髋发病5例,均为女性;②病例组患侧坐骨股骨间距为(13.65±3.87) mm,对侧为(22.17±5.75)mm,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01);患侧股方肌间距为(7.15±3.50) mm,对侧为(12.89±3.13) mm,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01);③对照组左侧坐骨股骨间距为(23.59±6.14) mm,右侧为(23.08±5.82) mm,双侧对比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);对照组左侧股方肌间距为(12.41±3.75) mm,右侧为(13.22±3.84) mm,双侧对比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);④病例组患侧坐骨股骨间距、股方肌间距与对照组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01),病例组对侧坐骨股骨间距、股方肌间隙与对照组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);⑤病例组股方肌有不同程度变形、水肿及萎缩;⑥综上,女性坐骨股骨撞击综合征的发病率明显高于男性,双侧发病常见。患侧坐骨股骨间距≤11.46 mm,股方肌间距≤5.53 mm,患侧股方肌水肿和形态异常,为坐骨股骨撞击综合征的MRI诊断标准。MRI轴位压脂图像是诊断坐骨股骨撞击综合征的敏感序列。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-1785-0688(张德洲)
中图分类号:
.jpg)