| [1] Oryan A, Alidadi S, Moshiri A, et al. Bone regenerative medicine: classic options, novel strategies, and future directions. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014; 9(1):18.[2] Ciarelli TE, Tjhia C, Rao DS, et al. Trabecular packet-level lamellar density patterns differ by fracture status and bone formation rate in white females. Bone. 2009; 45(5): 903-908.[3] 刘海波,孙海飚,韩晓强,等.不同浓度的血清素对体外培养大鼠成骨细胞分化的影响[J].世界复合医学. 2015, (3): 227-230.[4] Ottewell PD .The role of osteoblasts in bone metastasis. J Bone Oncol. 2016; 5(3):124-127.[5] Brandao-Burch A, Utting JC, Orriss IR, et al. Acidosis inhibits bone formation by osteoblasts in vitro by preventing mineralization. Calcif Tissue Int. 2005; 77(3): 167-174.[6] Utting JC, Robins SP, Brandao-Burch A, et al. Hypoxia inhibits the growth, differentiation and bone-forming capacity of rat osteoblasts. Exp Cell Res. 2006; 312(10): 1693-1702.[7] Jayakumar P, Di Silvio L. Osteoblasts in bone tissue engineering. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2010; 224(12): 1415-1440.[8] Costa R, Ribeiro C, Lopes AC, et al. Osteoblast, fibroblast and in vivo biological response to poly(vinylidene fluoride) based composite materials. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013; 24(2):395-403.[9] Beloti MM, Martins W Jr, Xavier SP, et al. In vitro osteogenesis induced by cells derived from sites submitted to sinus grafting with anorganic bovine bone. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008; 19(1): 48-54.[10] 司徒镇强,吴军正.细胞培养[M]. 西安:世界图书出版公司西安公司, 1996. [11] 孟国林.骨科实验技术[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2012.[12] 薛庆善.体外培养的原理与技术[M].北京:科学出版社,2001.[13] Peck WA, Birge SJ Jr, Fedak SA. Bone cells: biochemical and biological studies after enzymatic isolation. Science. 1964; 146(3650): 1476-1477.[14] Washington JT, Schneiderman E, Spears R, et al. Biocompatibility and osteogenic potential of new generation endodontic materials established by using primary osteoblasts. J Endod. 2011; 37(8): 1166-1170.[15] Hayes JS, Khan IM, Archer CW, et al. The role of surface microtopography in the modulation of osteoblast differentiation. Eur Cell Mater. 2010; (20): 98-108.[16] Boskey AL ,Roy R. Cell culture systems for studies of bone and tooth mineralization. Chem Rev. 2008; 108(11): 4716-4733.[17] Kartsogiannis V, Ng KW. Cell lines and primary cell cultures in the study of bone cell biology. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2004; 228(1-2): 79-102.[18] Czekanska EM, Stoddart MJ, Richards RG, et al. In search of an osteoblast cell model for in vitro research. Eur Cell Mater. 2012; (24): 1-17.[19] Orriss IR, Taylor SE ,Arnett TR. Rat osteoblast cultures. Methods Mol Biol. 2012; (816): 31-41.[20] Wang D, Christensen K, Chawla K, et al. Isolation and characterization of MC3T3-E1 preosteoblast subclones with distinct in vitro and in vivo differentiation/mineralization potential. J Bone Miner Res. 1999; 14(6): 893-903.[21] Taylor SE, Shah M ,Orriss IR .Generation of rodent and human osteoblasts. Bonekey Rep. 2014; (3): 585.[22] Renaud M, Farkasdi S, Pons C, et al. A New Rat Model for Translational Research in Bone Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2016;22(2):125-131.[23] Morriss-Kay GM ,Wilkie AO .Growth of the normal skull vault and its alteration in craniosynostosis: insights from human genetics and experimental studies. J Anat. 2005; 207(5): 637-653.[24] Ishii M, Sun J, Ting MC, et al. The Development of the Calvarial Bones and Sutures and the Pathophysiology of Craniosynostosis. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015; (115): 131-156.[25] Bakker AD ,Klein-Nulend J. Osteoblast isolation from murine calvaria and long bones. Methods Mol Biol. 2012; (816): 19-29.[26] 胡泽兵,王冰,曹新生,等.骨质疏松动物及细胞学研究模型的建立与评价[J]. 解放军医学院学报,2013,34(7): 789-791.[27] Irie K, Zalzal S, Ozawa H, et al. Morphological and immunocytochemical characterization of primary osteogenic cell cultures derived from fetal rat cranial tissue. Anat Rec. 1998; 252(4): 554-567.[28] Hashemibeni B, Jafary F, Esmaeil N, et al. Comparison of Phenotypic Characterization between Differentiated Osteoblasts from Stem Cells and Calvaria Osteoblasts In vitro. Int J Prev Med. 2013; 4(2): 180-186.[29] 胡孝丽,王佳宇,余和东,等.大鼠胎鼠成骨细胞的培养及初步鉴定[J]. 临床口腔医学杂志,2016,32(4): 207-210.[30] 康银辉,魏波,祝兆波,等.皮质酮浓度对SD大鼠成骨细胞成骨基因表达的影响[J]. 海南医学, 2015, 26(18): 2661-2664.[31] 鄂玲玲,刘洪臣,王东胜.贴壁组织块反复消化法培养新生大鼠下颌骨成骨细胞及鉴定[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志,2009, 27(2): 130-134. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
组织块法:在成骨细胞原代培养中,组织块法是最简捷和经常使用的方法。将组织块剪成小碎块后逐依接种于培养瓶,细胞会从贴壁的组织碎块的边缘缓慢爬出,直至爬满整个培养瓶。
酶消化法:另外一种提取原代成骨细胞的常用方法是酶消化法。采用胰酶或胶原酶对组织块进行消化分离细胞,但是胰酶或胶原酶的用量和浓度较难控制,浓度过大或过小都不合适。
文题释义:
组织块法:在成骨细胞原代培养中,组织块法是最简捷和经常使用的方法。将组织块剪成小碎块后逐依接种于培养瓶,细胞会从贴壁的组织碎块的边缘缓慢爬出,直至爬满整个培养瓶。
酶消化法:另外一种提取原代成骨细胞的常用方法是酶消化法。采用胰酶或胶原酶对组织块进行消化分离细胞,但是胰酶或胶原酶的用量和浓度较难控制,浓度过大或过小都不合适。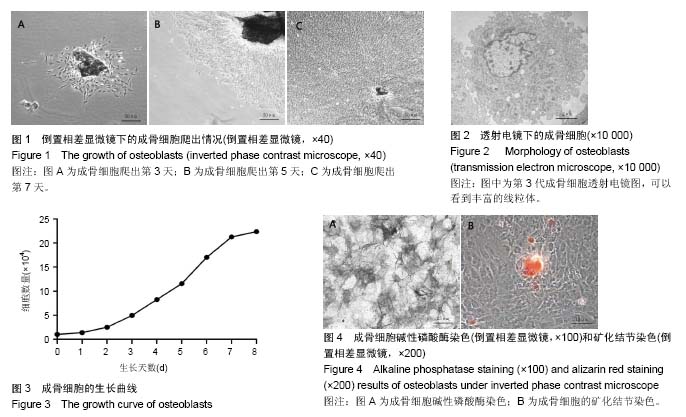
.jpg) 文题释义:
组织块法:在成骨细胞原代培养中,组织块法是最简捷和经常使用的方法。将组织块剪成小碎块后逐依接种于培养瓶,细胞会从贴壁的组织碎块的边缘缓慢爬出,直至爬满整个培养瓶。
酶消化法:另外一种提取原代成骨细胞的常用方法是酶消化法。采用胰酶或胶原酶对组织块进行消化分离细胞,但是胰酶或胶原酶的用量和浓度较难控制,浓度过大或过小都不合适。
文题释义:
组织块法:在成骨细胞原代培养中,组织块法是最简捷和经常使用的方法。将组织块剪成小碎块后逐依接种于培养瓶,细胞会从贴壁的组织碎块的边缘缓慢爬出,直至爬满整个培养瓶。
酶消化法:另外一种提取原代成骨细胞的常用方法是酶消化法。采用胰酶或胶原酶对组织块进行消化分离细胞,但是胰酶或胶原酶的用量和浓度较难控制,浓度过大或过小都不合适。