| [1]张燕,陈岩,李庆民,等.血小板纤维蛋白支架对心肌梗死的治疗作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(34):5129-5135.[2]Barkagan M, Steinvil A, Berchenko Y, et al. Impact of routine manual aspiration thrombectomy on outcomes of patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention for acute myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol. 2015,204:189-195.[3]Barchielli A, Profili F, Balzi D, et al. Trends in occurrence, treatment, and outcomes of acute myocardial infarction in Tuscany Region (Central Italy), 1997-2010. Epidemiol Prev. 2015;39(3):167-175.[4]Dai G, Xu Q, Luo R, et al. Atorvastatin treatment improves effects of implanted mesenchymal stem cells: meta-analysis of animal models with acute myocardial infarction. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2015;15(1):170.[5]Bajaj NS, Kalra R, Aggarwal H, et al. Comparison of approaches to revascularization in patients with multivessel coronary artery disease presenting with st-segment elevation myocardial infarction: meta-analyses of randomized control trials. J Am Heart Assoc. 2015;4(12):e002540.[6]杨世茂,王明国,李静,等.富血小板纤维蛋白与富血小板血浆体外释放生长因子的比较及其对脂肪干细胞增殖分化的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2012,30(6):641-644.[7]张红梅,张利鹏.可降解血管支架材料的表面性能及生物相容性[J],中国组织工程研究,2016,20(43):6445-6450.[8]于晓羽,代倩,程淑群,等.溶栓前肝素治疗对急性心肌梗死溶栓疗效的系统评价[J].中国循证医学杂志,2014,14(3):277-286.[9]王云飞,华琦,李静.急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死溶栓治疗的疗效与安全性[J].临床药物治疗杂志,2013,11(4):47-51.[10]吕俊远,王磊,李晰,等.胺碘酮治疗急性心肌梗死溶栓术后再灌注心律失常的Meta分析[J].中国循证医学杂志, 2013,13(9): 1110-1115.[11]Jeong YH, Bliden KP, Shuldiner AR, et al. Thrombin-induced platelet-fibrin clot strength: relation to high on-clopidogrel platelet reactivity, genotype, and post-percutaneous coronary intervention outcomes. Thromb Haemost. 2014;111(4): 713-724.[12]章晓波,毛琳,袁广银,等.心血管支架用Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr生物可降解镁合金的性能研究[J].稀有金属材料与工程, 2013,42(6): 1300-1305.[13]Zhang XB, Yuan GY, Fang XX, et al. Effects of solution treatment on yield ratio and biocorrosion behaviour of as-extruded Mg-2.7Nd-0.2Zn-0.4Zr alloy for cardiovascular stent application. Mater Technol. 2013;28(3):155-158.[14]Nguyen TY, Cipriano AF, Guan RG, et al. In vitro interactions of blood, platelet, and fibroblast with biodegradable magnesium-zinc-strontium alloys. Biomed Mater Res A. 2015; 103(9):2974-2986.[15]闫现政,韩东明,杨瑞民,等.可降解镁合金覆膜支架治疗兔颈总动脉侧壁型动脉瘤的可行性[J].中华放射学杂志, 2015,49(2): 138-142.[16]王汝朋,杨水祥.可吸收镁合金支架置入后犬冠状动脉C-反应蛋白、基质金属蛋白酶9和血管性血友病因子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(8):1216-1222.[17]李轩,石春来,王雪艳,等.心血管支架材料生物相容性:国际发展态势的文献计量学分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(8): 1267-1271.[18]Rathore A, Cleary M, Naito Y, et al. Development of tissue engineered vascular grafts and application of nanomedicine. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2012;4(3): 257-272.[19]Koens MJ, Krasznai AG, Hanssen AE, et al. Vascular replacement using a layered elastin-collagen vascular graft in a porcine model: one week patency versus one month occlusion. Organogenesis. 2015;11(3):105-121.[20]汪川,李京倖,辛毅,等.人脱细胞脐动脉支架与兔骨髓内皮祖细胞构建组织工程血管的实验研究[J].心肺血管病杂志,2014,33(4): 586-591.[21]Brougham CM, Levingstone TJ, Jockenhoevel S, et al. Incorporation of fibrin into a collagenglycosaminoglycan matrix results in a scaffold with improved mechanical properties and enhanced capacity to resist cell-mediated contraction. Acta Biomater. 2015;26:205-214.[22]Wang W, Hu J, He C, et al. Heparinized PLLA/PLCL nanofibrous scaffold for potential engineering of small-diameter blood vessel: tunable elasticity and anticoagulation property. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(5): 1784-1797.[23]Romanova OA, Grigor Ev TE, Goncharov ME, et al. Chitosan as a modifying component of artificial scaffold for human skin tissue engineering. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2015;159(4):557-566.[24]Xu C, Nakata T, Qiao XG, et al. Ageing behavior of extruded Mg-8.2Gd-3.8Y-1.0Zn-0.4Zr (wt.%) alloy containing LPSO phase and γ' precipitates. Sci Rep. 2017;7:43391. [25]Tsao YT, Shih YY, Liu YA, et al. Knockdown of SLC41A1 magnesium transporter promotes mineralization and attenuates magnesium inhibition during osteogenesis of mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017; 8(1):39. [26]Sonnow L, Könneker S, Vogt PM, et al. Biodegradable magnesium Herbert screw-image quality and artifacts with radiography, CT and MRI. BMC Med Imaging. 2017;17(1):16. [27]Wong HM, Zhao Y, Leung FK, et al. Functionalized polymeric membrane with enhanced mechanical and biological properties to control the degradation of magnesium alloy. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017 doi: 10.1002/adhm.201601269.[28]Minárik P, Jablonská E, Král R, et al. Effect of equal channel angular pressing on in vitro degradation of LAE442 magnesium alloy. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;73: 736-742. [29]Hiromoto S, Yamazaki T. Micromorphological effect of calcium phosphate coating on compatibility of magnesium alloy with osteoblast. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2017;18(1):96-109.[30]Yoshida T, Fukumoto T, Urade T, et al. Development of a new biodegradable operative clip made of a magnesium alloy: Evaluation of its safety and tolerability for canine cholecystectomy. Surgery. 2017 doi: 10.1016/j.surg. 2016.12.023. [31]Xu C, Nakata T, Qiao X, et al. Effect of LPSO and SFs on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Zr alloy. Sci Rep. 2017;7:40846. [32]Brooks EK, Ahn R, Tobias ME, et al. Magnesium alloy AZ91 exhibits antimicrobial properties in vitro but not in vivo. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017 doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.33839. [33]Cui HK, Li FB, Guo YC, et al. Intermediate analysis of magnesium alloy covered stent for a lateral aneurysm model in the rabbit common carotid artery. Eur Radiol. 2017 doi: 10.1007/s00330-016-4715-6.[34]Draxler J, Martinelli E, Weinberg AM, et al. The potential of isotopically enriched magnesium to study bone implant degradation in vivo. Acta Biomater. 2017 doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.01.054. [35]Lei D, Benson J, Magasinski A, et al. Transformation of bulk alloys to oxide nanowires.Science. 2017;355(6322):267-271. [36]Li X, Gao P, Wan P, et al. Novel Bio-functional Magnesium Coating on Porous Ti6Al4V Orthopaedic Implants: In vitro and In vivo Study. Sci Rep. 2017;7:40755.[37]Ibrahim H, Klarner AD, Poorganji B, et al. Microstructural, mechanical and corrosion characteristics of heat-treated Mg-1.2Zn-0.5Ca (wt%) alloy for use as resorbable bone fixation material. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;69: 203-212. [38]Liu Y, Xue J, Luo D, et al. One-step fabrication of biomimetic superhydrophobic surface by electrodeposition on magnesium alloy and its corrosion inhibition. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017;491:313-320. |
.jpg)

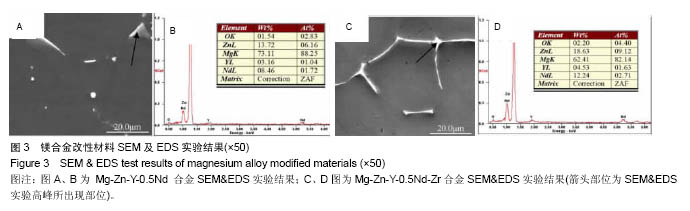
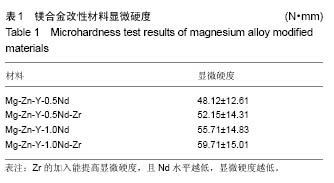
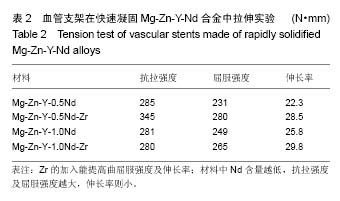
.jpg)
.jpg)