| [1]戈朝晖,王自立,魏敏吉,等.脊柱结核病灶中抗痨药物浓度的测定[J].中华骨科杂志,2005,25(2):97-101.[2]戈朝晖,王自立,魏敏吉.利福平在脊柱结核患者不同组织分布的实验研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2004,14(12):33-36.[3]Wang Z,Ge Z,Jin W,et al.Treatment of spinal tuberculosis with ultrashort- course chemotherapy in conjunction with partial excision of pathologic vertebrae.Spine J.2007;7(6):671-681.[4]Diacon AH,Donald PR.The early bactericidal activity of antituberculosis drugs.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther.2014;12(2): 223-237. [5]Vora C,Patadia R,Mittal K,et al.Recent patents and advances on anti-tuberculosis drug delivery and formulations.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul.2013;7(2):138-149.[6]罗翼,邹昌,张帅,等.注射型可吸收氨基酸聚合物/硫酸钙复合材料动物体内降解吸收及促成骨作用实验研究[J].华西医学, 2015,20(12):2224-2228.[7]Turner TM,Urban RM,Gitelis S,et al.Resorption evaluation of a large bolus of calcium sulfate in a canine medullary defect.Orthopedics.2003;26(5 Suppl):s577-579.[8]赵增辉,蒋电明,苏保,等.复合骨修复材料——聚氨基酸/硫酸钙的生物相容性研究[J].功能材料,2011,5(42):807-811.[9]德向研,施建党,王自立,等.载三联抗结核药硫酸钙/氨基酸聚合物人工骨体内缓释实验研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013, 23(6): 531-536.[10]刘海涛,施建党,王骞,等.硫酸钙/聚氨基酸复合三联抗痨药人工缓释材料的制备及物理性能测定[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015, 23(21):1984-1988.[11]刘海涛,王自立,施建党.人工骨载三联抗痨药物含量对其抗机械压缩强度的影响[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2013,35(7):759-762.[12]刘海涛,施建党,王骞,等.载三联抗结核药物硫酸钙/聚氨基酸人工材料体外缓释性能的观察[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(3): 239-244.[13]张峻山,王自立,施建党,等.复合三联抗结核药人工缓释材料体外抗结核性能[J].脊柱外科杂志,2014,12(6):380-384.[14]耿广起,王骞,王自立,等.构建新西兰兔脊柱结核模型的对比研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2014,34(2):216-223.[15]Geng G,Wang Q,Shi J,et al.Establishment of a new zealand rabbit model of spinal tuberculosis.J Spinal Disord Tech.2015; 28(3):E140-145.[16]曹烨,宋言峥,李垒,等.经典病灶清除手术治疗复杂复合性脊柱结核104例临床分析[J].中国抗痨杂志,2012,34(7):437-440. [17]Song SH,Jun SH,Park KU,et al.Simultaneous determination of first-line anti-tuberculosis drugs and their major metabolic ratios by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectr ometry.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrum.2008;21(7):1331-1338.[18]张立群,李华,巩维进.结核病的化学治疗[J].中国临床医生,2009, 37(21):165-166.[19]周林.抗结核药物研究进展[J].中国临床医生,2013,41(3):14-17.[20]王自立.病灶清除单节段融合固定治疗脊柱结核[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2009,19(11):807.[21]Khuhawar MY,Rind FM.Liquid chromatographic determination of isoniazid, pyrazinamide and rifampicin from pharmaceutical preparations and blood.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.2002;766(2):357-363.[22]李群力,蒋晓萌,施存元.高效液相色谱法测定复方利福平片中利福平、异烟肼及吡嗪酰胺的含量[J].中国抗生素杂志, 2002, 27(9):570-571.[23]Buchholz HW,Engelbrecht H.Depot effects of various antibiotics mixed with Palacos resins.Chirurg. 1970;41(11): 511-515.[24]Pang QY,Lu Y,Yu L,et al.Analytical separation of rifampicin, isoniazid and pyrazinamide in compound rifampicin tablets by RP-HPLC.Chin J Pharma Anal.1998;18(4):259.[25]胡咏梅,徐新华,徐建明.HPLC法测定血清中异烟肼、利福平和吡嗪酰胺浓度[J].安徽医科大学学报,2002,37(5):372-374.[26]金卫东,王骞,王自立,等.彻底与非彻底病灶清除术治疗脊柱结核的比较[J].中华骨科杂志,2014,34(2):196-203.[27]Guo H,Wei J,Liu CS.Development of a degradable cement of calcium phosphate and calcium sulfate composite for bone reconstruction.Biomed Mater.2006;1(4):193-197.[28]Urban RM,Turner TM,Hall DJ,et al.Increased bone formation using calcium sulfate-calcium phosphate composite graft.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2008;459:110-117.[29]Civinini R,De B,Carulli C,et al.The use of an injectable calcium sulphate/calcium phosphate bioceramic in the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head.Int Orthop. 2012; 36(8):1583-1588.[30]Liu P,Jiang H,Li S,et al.Determination of anti-tuberculosis drug concentration and distribution from sustained release microspheres in the vertebrae of a spinal tuberculosis rabbit model.J Orthop Res.2017;35(1):200-208. [31]Dong J,Zhang S,Liu H,et al.Novel alternative therapy for spinal tuberculosis during surgery: reconstructing with anti-tuberculosis bioactivity implants.Expert Opin Drug Deliv.2014;11(3):299-305. [32]Xi YH,Xue MT,Ye XJ,et al.Osteogenetic capacity of cross-linked adjustable anti-tuberculosis drug sustained-release artificial composite.Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.2013;93(19):1494-1498. [33]Wang P,Liu P,Peng H,et al.Biocompatibility evaluation of dicalcium phosphate/calcium sulfate/poly (amino acid) composite for orthopedic tissue engineering in vitro and in vivo.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2016;27(11):1170-1186.[34]Xue Y,Song Y,Liu L,et al.Experimental study on poly-amino acid/nano-hydroxyapatite/calcium sulfate cage for lumbar intervody fusion in goats.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2015;29(8):972-977. [35]Fan X,Ren H,Luo X,et al.Mechanics, degradability, bioactivity, in vitro, and in vivo biocompatibility evaluation of poly(amino acid)/hydroxyapatite/calcium sulfate composite for potential load-bearing bone repair.J Biomater Appl.2016;30(8): 1261-1272. [36]Mine Y,Zhang H.Anti-inflammatory Effects of Poly-L-lysine in Intestinal Mucosal System Mediated by Calcium-Sensing Receptor Activation.J Agric Food Chem.2015;63(48): 10437-10447. [37]Nayunigari MK,Gupta SK,Kokkarachedu V,et al.Development of anti-scale poly(aspartic acid-citric acid) dual polymer systems for water treatment.Environ Technol. 2014;35(21-24): 2903-2909. [38]Tan V,Evaniew N,Finlay K,et al.Chronology of the Radiographic Appearances of the Calcium Sulfate-Calcium Phosphate Synthetic Bone Graft Composite Following Resection of Bone Tumors: A Follow-up Study of Postoperative Appearances.Can Assoc Radiol J. 2016;67(1): 21-27. [39]Evaniew N,Tan V,Parasu N,et al.Use of a calcium sulfate-calcium phosphate synthetic bone graft composite in the surgical management of primary bone tumors. Orthopedics. 2013;36(2):e216-222. [40]Mistry S,Roy S,Maitra NJ,et al.A novel, multi-barrier, drug eluting calcium sulfate/biphasic calcium phosphate biodegradable composite bone cement for treatment of experimental MRSA osteomyelitis in rabbit model.J Control Release. 2016;239:169-181.[41]Wu CC,Hsu LH,Tsai YF,et al.Enhancement of biodegradation and osseointegration of poly(ε-caprolactone)/calcium phosphate ceramic composite screws for osteofixation using calcium sulfate.Biomed Mater.2016;11(2):025012. [42]Zhou Z,Buchanan F,Mitchell C,et al.Printability of calcium phosphate: calcium sulfate powders for the application of tissue engineered bone scaffolds using the 3D printing technique.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2014;38:1-10. [43]Al Khudairy A,Phelan JP.Letter to the editor: in vitro elution characteristics of vancomycin in a composite calcium phosphate/ calcium sulfate bone substitute.HSS J. 2014;10(1):98. [44]Yang X,Osagie L,Bostrom MP.In vitro elution characteristics of vancomycin in a composite calcium phosphate/calcium sulfate bone substitute.HSS J.2012;8(2):129-32. [45]Cai S,Zhai Y,Xu G,et al.Preparation and properties of calcium phosphate cements incorporated gelatin microspheres and calcium sulfate dihydrate as controlled local drug delivery system.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2011;22(11):2487-2496. |
.jpg)
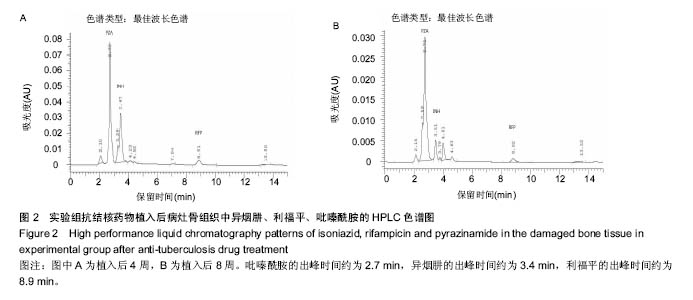
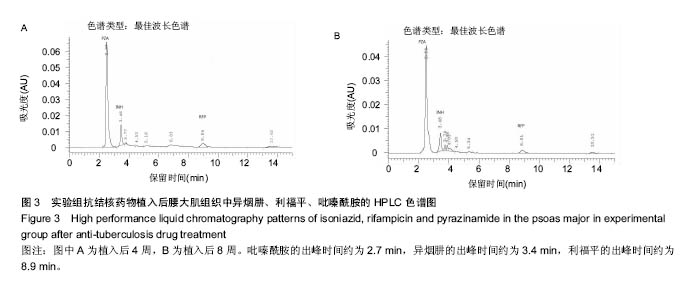
.jpg)