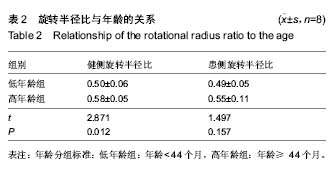
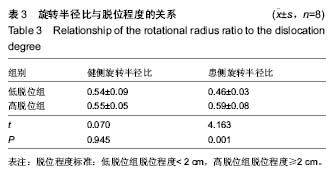
| [1] Cooper AP, Doddabasappa SN, Mulpuri K. Evidence-based management of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Orthop Clin North Am. 2014;45(3):341-354.[2] Thomas SR, Wedge JH, Salter RB. Outcome at forty-five years after open reduction and innominate osteotomy for late-presenting developmental dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(11):2341-2350.[3] Graf R. The diagnosis of congenital hip-joint dislocation by the ultrasonic Combound treatment. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1980;97(2):117-133.[4] Harcke HT. Screening newborns for developmental dysplasia of the hip: the role of sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994;162(2):395-397.[5] Omero?lu H. Use of ultrasonography in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Child Orthop. 2014;8(2):105-113.[6] Vedantam R, Bell MJ. Dynamic ultrasound assessment for monitoring of treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop. 1995;15(6):725-728.[7] Sink EL, Ricciardi BF, Torre KD, et al. Selective ultrasound screening is inadequate to identify patients who present with symptomatic adult acetabular dysplasia. J Child Orthop. 2014;8(6):451-455.[8] White KK, Sucato DJ, Agrawal S, et al. Ultrasonographic findings in hips with a positive Ortolani sign and their relationship to Pavlik harness failure. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(1):113-120.[9] White KK, Sucato DJ, Agrawal S, et al. Ultrasonographic findings in hips with a positive Ortolani sign and their relationship to Pavlik harness failure. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(1):113-120.[10] Chin MS, Betz BW, Halanski MA. Comparison of hip reduction using magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography in hip dysplasia. J Pediatr Orthop. 2011;31(5):525-529.[11] Kotlarsky P, Haber R, Bialik V, et al. Developmental dysplasia of the hip: What has changed in the last 20 years. World J Orthop. 2015;6(11):886-901.[12] Schwend RM, Shaw BA, Segal LS. Evaluation and treatment of developmental hip dysplasia in the newborn and infant. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2014;61(6):1095-1107.[13] Bin K, Laville JM, Salmeron F. Developmental dysplasia of the hip in neonates: evolution of acetabular dysplasia after hip stabilization by brief Pavlik harness treatment. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(4):357-361.[14] Jia J, Li L, Zhang L, et al. Can excessive lateral rotation of the ischium result in increased acetabular anteversion? A 3D-CT quantitative analysis of acetabular anteversion in children with unilateral developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop. 2011;31(8):864-869.[15] Kothari A, Grammatopoulos G, Hopewell S, et al. How Does Bony Surgery Affect Results of Anterior Open Reduction in Walking-age Children With Developmental Hip Dysplasia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(5):1199-1208.[16] Sankar WN, Neubuerger CO, Moseley CF. Femoral head sphericity in untreated developmental dislocation of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop. 2010;30(6):558-561.[17] 何金鹏,郝运,王小林,等.数字化模板联合骨性参数测量辅助髋关节假体型号选择的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2015, 29(6): 688-692.[18] Stanton RP, Capecci R. Computed tomography for early evaluation of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop. 1992;12(6):727-730.[19] Mandel DM, Loder RT, Hensinger RN. The predictive value of computed tomography in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop. 1998;18(6):794-798.[20] Argenson JN, Ryembault E, Flecher X, et al. Three-dimensional anatomy of the hip in osteoarthritis after developmental dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(9): 1192-1196.[21] 郝运,何金鹏.计算机辅助膝关节内外翻畸形个体化矫形[J].CT 理论与应用研究,2016,25(4): 393-401. [22] Zhao X, Yan YB, Cao PC, et al. Surgical results of developmental dysplasia of the hip in older children based on using three-dimensional computed tomography. J Surg Res. 2014;189(2):268-273.[23] Franceschi JP, Sbihi A,Computer Assisted Orthopedic Surgery-France (CAOS-France). 3D templating and patient-specific cutting guides (Knee-Plan) in total knee arthroplasty: postoperative CT-based assessment of implant positioning. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(6 Suppl): S281-286.[24] Chin KR, Mills MV, Seale J, et al. Ideal starting point and trajectory for C2 pedicle screw placement: a 3D computed tomography analysis using perioperative measurements. Spine J. 2014;14(4):615-618.[25] Fukunishi S, Okahisa S, Fukui T, et al. Significance of preoperative 3D-CT angiography for localization of the femoral artery in complicated THA. J Orthop Sci. 2014;19(3): 457-464.[26] Shang C, Liu T, Xie H, et al. Spatial changes of the peri-acetabular pelvic in developmental dysplasia of the hip---a combined 3-dimentional computed tomography (3D-CT) study in patients and experimental study in rats.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014;7(12):4983-4989.[27] Jia J, Li L, Zhang L, et al. Can excessive lateral rotation of the ischium result in increased acetabular anteversion? A 3D-CT quantitative analysis of acetabular anteversion in children with unilateral developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop. 2011;31(8):864-869.[28] Li X, Viceconti M, Cohen MC, et al. Developing CT based computational models of pediatric femurs. J Biomech. 2015; 48(10):2034-2040.[29] Chan HH, Siewerdsen JH, Vescan A, et al. 3D Rapid Prototyping for Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery: Applications in Image-Guidance, Surgical Simulation and Patient-Specific Modeling. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0136370.[30] 何金鹏. 3D重建与 3D打印技术在恶性骨与软组织肿瘤治疗中的应用研究[D]. 武汉:华中科技大学,2014:1-120.[31] Liu XZ, Shu DL, Ran W, et al. Digital surgical templates for managing high-energy zygomaticomaxillary complex injuries associated with orbital volume change: a quantitative assessment. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;71(10):1712-1723. |
.jpg)

.jpg)