| [1] 杜莉,付钢,沈颉飞.牙体缺损程度对后牙桩核冠修复牙本质应力影响的三维有限元分析[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2005,21(12):738-740.[2] 李冰,刘斐,王健,武秀萍.不同桩核材料修复对牙本质应力分布规律影响的三维有限元分析[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2013,6(7): 413-416.[3] Liu S,Liu Y,Xu J,et al.Influence of occlusal contact and cusp inclination on the biomechanical character of a maxillary premolar: A finite element analysis.J Prosthet Dent.2014; 112(5):1238-1245.[4] 宋亮,徐斌,陈慧娟,等.桩核冠修复不同程度缺损下颌前磨牙的三维有限元分析[J].口腔医学研究,2015,31(10): 1013-1016.[5] 魏刘佳,洪小科,柳茜,等.不同咬合形式及不同长度螺纹根管固位钉修复大面积牙冠缺损的应力分析[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2008, 26(4):378-382.[6] 易新竹.牙合学(供口腔医学类专业用)[M].4版.北京:人民卫生,2008.[7] Wang M,Mehta N.A possible biomechanical role of occlusal cusp-fossa contact relationships.J Oral Rehabil.2013; 40(1): 69-79.[8] 王惠芸.我国人牙的测量和统计[J].中华口腔科杂志, 1959,7(3): 149.[9] Staninec M,Marshall GW,Hilton JF,et al.Ultimate tensile strength of dentin:evidence for a damage mechanics approach to dentinfailure.J Biomed Mater Res.2002;63: 342-345.[10] Asmussen E,Peutzfeldt A,Sahafi A.Finite element analysis of stress in endodontically treated dowel restored teeth.J Dent Res.2005;94:321-329.[11] Chen D,Wang N,Gao Y,et al.A 3-dimensional finite element analysis of the restoration of the maxillary canine with a complex zirconia post system.J Prosthet Dent.2014;112(6): 1406-1415.[12] 王文亚,傅波,罗华,等.不同桩核冠修复上颌中切牙的三维有限元模型建立及应力分析[J].医用生物力学, 2014,29(1):25-30.[13] 吴艳玲,鲁成林,张东升,等.下颌第一磨牙全瓷冠三维有限元建模及力学分析[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2009,10(2): 98-100. [14] Anna Karina FC,Thaty Aparecida X,Oswaldo Daniel AF,et al.Influence of occlusal contact area on cusp defection and stress distribution.J Contemp Dent Pract.2014;15(6):699-704.[15] 黄楠楠.不同磨牙关系下颌第一磨牙咬合接触类型分析及有限元受力研究[D].重庆医科大学, 2014. [16] 王美青,Noshir Mehta.上下牙尖窝接触关系的生物力特征[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2013, 29(1):112-120.[17] Jager ND,Pallav P,Feilzer AJ.The influence of design parameters on the FEA-determined stress distribution in CAD-CAM produced all-ceramic dental crowns.Dent Mater. 2005;21(3):242-251. [18] Wayne JS,Ruchi C,Christian P,et al.Effect of restoration volume on stresses in a mandibular molar: a finite element study.J Prosthet Dent.2014;112(4):925-931.[19] Okada D,Miura H,Suzuki C,et al.Stress Distribution in Roots Restored with Different Types of Post Systems with Composite Resin.Dent Mater J.2008;27(4):605-611.[20] Durmu? G,Oyar P.Effects of post core materials on stress distribution in the restoration of mandibular second premolars: A finite element analysis.J Prosthet Dent.2014;112(3): 547-554.[21] Da Silva FM,Septímio Lanza MD,Landre Júnior J,et al. Influence of Increase of the Occlusal Contact Area on the Tension Generation on Natural Teeth and Adjacent Structures by Finite Element Analysis(FEA).Dentistry.2014;4:244. [22] Yi YJ,Kelly JR.Effect of occlusal contact size on interfacial stresses and failure of a bonded ceramic: FEA and monotonic loading analyses.Dent Mater.2008;24(3):403-409.[23] 林川,杜莉.面载荷工况条件下三维有限元分析下颌第一磨牙的应力情况[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2015,31(3):393-396.[24] Croci CS,Caria PHF,Croci CS,et al.Rotation axis of the maxillary molar and maximum tooth movement according to force direction.Braz J Oral Sci.2015;14(2):130-134.[25] Abuelenain DA,Ajaj R,El-Bab EI,et al.Comparison of Stresses Generated within the Supporting Structures of Mandibular Second Molars Restored with Different Crown Materials: 3-D Finite Element Analysis (FEA).J Prosthodont.2014;24(6): 484-493.[26] Wang MQ,Zhang M,Zhang JH.Photoelastic study of the effects of occlusal surface morphology on tooth apical stress from vertical bite forces.J Contemp Dent Pract.2004;5(1): 74-93.[27] Benazzi S,Kullmer O,Grosse IR,et al.Using occlusal wear information and finite element analysis to investigate stress distributions in human molars.J Anat.2011;219(3):259-272.[28] Abduo J.Influence of fixed prosthodontic treatment on occlusal contacts in centric occlusion: a preliminary study.Br J Med Med Res.2015;5(12):1580-1589.[29] Lund JP.Mastication and its control by the brain stem.Crit Rev Oral Biol Med.1991;2(1):33-64.[30] Hützen D,Proff P,Gedrange T,et al.Occlusal contact patterns- Population-based data.Ann Anat.2007;189(4): 407-411.[31] 徐军.后牙冠桥的合接触[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2010.[32] Morris JB.Functional Occlusion: From TMJ to Smile Design.J Prosthod.2008;17(3):251. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
稳定咬合接触:健康牙的咬合在牙间交错位时可达到3区稳定接触,以获得正中稳定,即ABC 3区接触,A区为下后牙颊尖颊斜面与上后牙颊尖舌斜面的接触区,B区为下后牙颊尖舌斜面与上后牙舌尖颊斜面的接触区,C区为下后牙舌尖颊斜面与上后牙舌尖舌斜面的接触区,ABC接触是生理条件下磨牙颌面典型接触形式,有利于达到正中稳定,分散颌力,减少咬合力对牙的创伤,有研究表明B区接触有特殊的重要性。
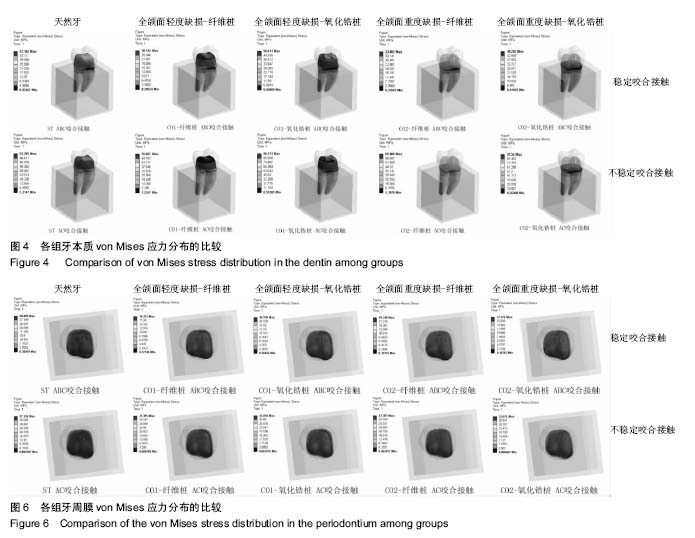
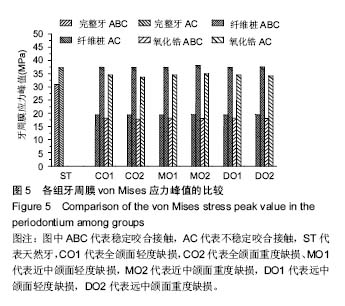
不同咬合接触对不同程度牙体缺损经不同桩核冠系统修复后牙体牙周组织应力分布的影响:相对于稳定咬合接触(ABC),不稳定咬合接触(AC)提高了牙体和牙周组织应力水平;采用高弹性模量的桩材料修复时,牙体组织应力更高,且缺损越大应力越高;纤维桩修复后牙周组织应力略高于氧化锆桩,和缺损形式关系不明显。研究结果提示临床修复体咬合调整需精确恢复,尤其是不能缺少B区接触。
文题释义:
稳定咬合接触:健康牙的咬合在牙间交错位时可达到3区稳定接触,以获得正中稳定,即ABC 3区接触,A区为下后牙颊尖颊斜面与上后牙颊尖舌斜面的接触区,B区为下后牙颊尖舌斜面与上后牙舌尖颊斜面的接触区,C区为下后牙舌尖颊斜面与上后牙舌尖舌斜面的接触区,ABC接触是生理条件下磨牙颌面典型接触形式,有利于达到正中稳定,分散颌力,减少咬合力对牙的创伤,有研究表明B区接触有特殊的重要性。
不同咬合接触对不同程度牙体缺损经不同桩核冠系统修复后牙体牙周组织应力分布的影响:相对于稳定咬合接触(ABC),不稳定咬合接触(AC)提高了牙体和牙周组织应力水平;采用高弹性模量的桩材料修复时,牙体组织应力更高,且缺损越大应力越高;纤维桩修复后牙周组织应力略高于氧化锆桩,和缺损形式关系不明显。研究结果提示临床修复体咬合调整需精确恢复,尤其是不能缺少B区接触。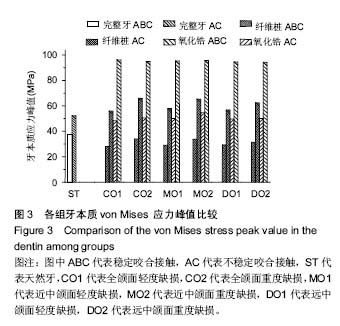
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
稳定咬合接触:健康牙的咬合在牙间交错位时可达到3区稳定接触,以获得正中稳定,即ABC 3区接触,A区为下后牙颊尖颊斜面与上后牙颊尖舌斜面的接触区,B区为下后牙颊尖舌斜面与上后牙舌尖颊斜面的接触区,C区为下后牙舌尖颊斜面与上后牙舌尖舌斜面的接触区,ABC接触是生理条件下磨牙颌面典型接触形式,有利于达到正中稳定,分散颌力,减少咬合力对牙的创伤,有研究表明B区接触有特殊的重要性。
不同咬合接触对不同程度牙体缺损经不同桩核冠系统修复后牙体牙周组织应力分布的影响:相对于稳定咬合接触(ABC),不稳定咬合接触(AC)提高了牙体和牙周组织应力水平;采用高弹性模量的桩材料修复时,牙体组织应力更高,且缺损越大应力越高;纤维桩修复后牙周组织应力略高于氧化锆桩,和缺损形式关系不明显。研究结果提示临床修复体咬合调整需精确恢复,尤其是不能缺少B区接触。
文题释义:
稳定咬合接触:健康牙的咬合在牙间交错位时可达到3区稳定接触,以获得正中稳定,即ABC 3区接触,A区为下后牙颊尖颊斜面与上后牙颊尖舌斜面的接触区,B区为下后牙颊尖舌斜面与上后牙舌尖颊斜面的接触区,C区为下后牙舌尖颊斜面与上后牙舌尖舌斜面的接触区,ABC接触是生理条件下磨牙颌面典型接触形式,有利于达到正中稳定,分散颌力,减少咬合力对牙的创伤,有研究表明B区接触有特殊的重要性。
不同咬合接触对不同程度牙体缺损经不同桩核冠系统修复后牙体牙周组织应力分布的影响:相对于稳定咬合接触(ABC),不稳定咬合接触(AC)提高了牙体和牙周组织应力水平;采用高弹性模量的桩材料修复时,牙体组织应力更高,且缺损越大应力越高;纤维桩修复后牙周组织应力略高于氧化锆桩,和缺损形式关系不明显。研究结果提示临床修复体咬合调整需精确恢复,尤其是不能缺少B区接触。