中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (53): 7998-8003.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.53.014
• 骨与关节临床实践 clinical practice of the bone and joint • 上一篇 下一篇
X射线联合磁共振成像评估踝关节损伤分型:自身对照、3个月随访临床试验研究方案
刘国彬,张国平,任庆云,雷立存,赵 峰,高宏阳,朱超华,李亚光
- 河北医科大学第一医院,河北省石家庄市 050031
Classification of ankle injury on radiography and magnetic resonance imaging: study protocol for a self-controlled, clinical trial with 3-month follow-up
Liu Guo-bin, Zhang Guo-ping, Ren Qing-yun, Lei Li-cun, Zhao Feng, Gao Hong-yang, Zhu Chao-hua, Li Ya-guang
- First Hospital, Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050031, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
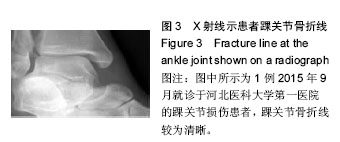
踝关节骨折:踝关节由胫腓骨下端与距骨组成。其骨折、脱位是骨科常见的损伤,多由间接暴力引起踝部扭伤后发生。根据暴力方向、大小及受伤时足的位置的不同可引起各种不同类型的骨折。
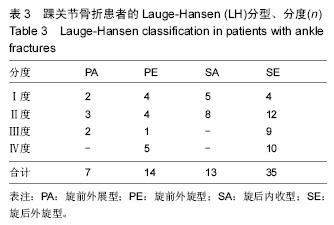
Lange-Hansen分型:于1950年提出,根据足在受伤时的位置和暴力的方向将骨折分为旋后/内收型、旋后/外旋型、旋前/外展型和旋前/外旋型4类,每1类又根据骨折程度及是否伴有韧带软组织损伤而分为不同的亚类。
摘要
背景:X射线是检测踝关节损伤常用的方法,但其对部分踝关节骨折以及踝关节周围韧带损伤情况较难诊断清楚,从而不能进行准确的骨折分型及制定治疗方案。磁共振成像检查可清晰显示隐匿性骨折以及踝关节周围韧带的损伤情况,可用于诊断踝关节骨折的韧带损伤。试验假设X射线联合磁共振成像可对踝关节骨折患者进行正确的骨折分型及术后评估。
目的:观察踝关节损伤分型及术后评估中X射线联合磁共振成像的应用情况。
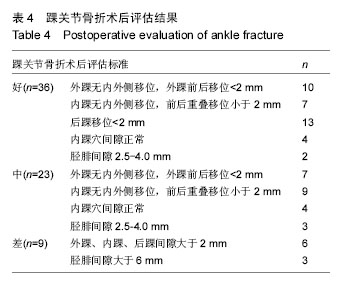
方法:研究为回顾性、单中心、自身前后对照临床试验,在中国河北省,河北医科大学第一医院完成。纳入试验的踝关节损伤患者68例,均进行踝关节骨折内固定及周围韧带损伤修复,对患者骨折部位进行X射线和磁共振成像检查,术前根据Lauge-Hansen分型标准进行骨折分型,并采用课题组自拟的踝关节骨折评估标准进行术后评估。试验的主要观察指标为术后3个月踝关节骨折术后评估标准为好的患者例数的百分率;试验的次要观察指标为患者术前Lauge-Hansen分型结果,术前、术后3个月踝关节X射线和磁共振成像检查结果评估患者骨折的修复情况;试验的其他观察指标为术后3个月患者不良反应的发生率。结果显示,术后3个月,踝关节骨折术后评估标准为好的患者例数的百分率为53%;踝关节骨折术后评估标准为好、良、差的患者分别有36,23,9例;术前根据Lauge-Hansen分型:旋前外展型有7例,旋前外旋型有14例,旋后内收型有13例,旋后外旋型有35例;术后3个月患者不良反应发生率为17%。试验于试验于2016年11月16日在北美临床试验注册中心做回顾性注册(NCT02964754);研究符合世界医学会制定的《赫尔辛基宣言》的要求;参与试验的患者对治疗方案和治疗过程均知情同意,并签署知情同意书,2015年7月研究对象已入组,研究预期2年结束。
讨论:试验旨在证实采用X射线及磁共振成像检查联合应用可对踝关节骨折患者进行正确的骨折分型及术后评估,为踝关节损伤修复提供准确的临床依据。
ORCID: 0000-0003-0018-5212(刘国彬)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)