| [1] Suri P,Morgenroth DC,Hunter DJ.Epidemiology of Osteoarthritis and Associated Comorbidities.PMR. 2012;4(5):S10-19.
[2] Chopin F, Biver E, Funck-Brentano T,et al.Prognostic interest of bone turnover markers in the management of postmenopausal osteoporosis.Joint Bone Spine. 2012;79(1):26-31.
[3] Castañeda S, Roman-Blas JA, Largo R, et al.Subchondral bone as a key target for osteoarthritis treatment. Biochemical Pharmacology.2012;83(3): 315-323.
[4] Cox G,Einhorn TA,Tzioupis C,et al.Bone-turnover markers in fracture healing.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2010; 92(3):329-334.
[5] Ramonda R,Lorenzin M,Modesti V.Serological markers of erosive hand osteoarthritis.Eur J Intl Med. 2013; 24(1): 11-15.
[6] 刘忠厚,杨定焯,朱汉民,等.中国人骨质疏松症建议诊断标准(第2稿)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2000,6(1):1-3.
[7] Rousseau JCH,Garnero P.Biological markers in osteoarthritis.Bone.2012;51(2):265-277.
[8] Zhang Y,Joanne M.Epidemiology of Osteoarthritis.Clin Geriatr Med N Am.2010;26(3): 355-369.
[9] Patra D,Sandell LJ.Recent advances in biomarkers in osteoarthritis.Curr Opin Rheumatol.2011;23(5): 465-470.
[10] White HD, Ahmad AM, Durham BH, et al. Effect of oral phosphate and alendronate on bone mineral density when given as adjunctive therapy to growth hormone replacement in adult growth hormone deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96(3):726-736.
[11] Karsdal MA,Byrjalsen I,Bay-Jensen AC,et al. Biochemical markers identify influences on bone and cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis-the effect of sex, Kellgren-Lawrence(KL)score,Body Mass Index(BMI),oral salmon calcitonin(sCT) treatment and diurnal variation.BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2010;11:125.
[12] Fait T, Donat J, Jenicek J, et al. Recommendation for hormone replacement therapy in postmenopause. Ceska gynekologie. 2010;75(2):109-110.
[13] Patra D,Sandell LJ.Recent advances in biomarkers in osteoarthritis.Curr Opin Rheumatol.2011;23(5): 465-470.
[14] Martínez J,Olmos JM,Hernández JL,et al.Bone turnover markers in Spanish postmenopausal women: The Camargo cohort study.Clin Chim Acta.2009; 409(1-2):70-74.
[15] Cortes-Prieto J, Vicente-Hernanz ML, Cortes-Garcia A, et al. Hormone replacement therapy: evolution of body mass index, bone mineral density, and lipid profile. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2013;13(2):19-40.
[16] Bay-Jensen AC,Slagboom E,Chen-An P,et al.Role of hormones in cartilage and joint metabolism: understanding an unhealthy metabolic phenotype in osteoarthritis.Menopause.2013; 20(5):578-586.
[17] Eriksen EF. Hormone replacement therapy or SERMS in the long term treatment of osteoporosis. Minerva ginecologica. 2012;64(3):207-221.
[18] 杨辉,唐三元,詹鹏.骨密度结合singh指数预测老年髋部骨折风险的意义[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,10: 900-902.
[19] Ragnar Agnarsson H, Johannsson G, Ragnarsson O. The impact of glucocorticoid replacement on bone mineral density in patients with hypopituitarism before and after 2 years of growth hormone replacement therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2014;99(4): 1479-1485.
[20] Stewart A,Black A,Robins SP,et al.Bone density and bone turnover in patients with osteoarthritis and osteoporosis.J Rheumatol.1999;26(3):622-626.
[21] Maichuk E, Voevodina IV, Mitrokhina TV, et al. The risk of atherosclerosis and osteoporosis development in post-ovariectomy syndrome women during hormone replacement therapy. Terapevticheskii arkhiv. 2014; 86(8):75-79.
[22] Karsdal MA,Byrjalsen I,Bay-Jensen AC,et al. Biochemical markers identify influences on bone and cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis-the effect of sex, Kellgren-Lawrence(KL)score,Body Mass Index(BMI),oral salmon calcitonin(sCT) treatment and diurnal variation.BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2010; 11:125.
[23] Cartwright B, Robinson J, Seed PT,et al. Hormone Replacement Therapy Versus the Combined Oral Contraceptive Pill in Premature Ovarian Failure: A Randomized Controlled Trial of the Effects on Bone Mineral Density. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016; 101(9):3497-3505.
[24] Puntus T,Schneider B,Meran J,et al.Influence of age and gender on associations of body mass index with bone mineral density,bone turnover markers and circulating calcium-regulating and bone-active sex hormones.Bone.2011;49(4):824-829.
[25] Evola G, Novo G, Amoroso G, et al. Modification of the lipidic and coagulative pattern in postmenopause women: effect of hormone replacement therapy. International angiology. 2010;29(4):355-361.
[26] Chopin F,Biver E,Funck-Brentano T.Prognostic interest of bone turnover markers in the management of postmenopausal osteoporosis.Joint Bone Spine. 2012; 79(1):26-31.
[27] Gambacciani M, Levancini M. Hormone replacement therapy and the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Przeglad Menopauzalny. 2014;13(4): 213-220. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
激素替代疗法(hormone replacement therapy,HRT):是指通过补充激素来治疗激素分泌减退或者缺乏所引起的疾病的治疗方法。广义上的HRT涵盖所有的激素。狭义上的HRT多是针对女性激素,特别是指雌激素替代疗法(estrogen replacement therapy,ERT)。美国公布的研究结果显示,虽然激素替代疗法能帮助中老年妇女改善更年期不适症状,但这种疗法也会增加女性患痴呆症的风险。新结果再次表明需要对激素替代疗法的利弊进行重新评估。
骨质疏松症:是由于多种原因导致的骨密度和骨质量下降,骨微结构破坏,造成骨脆性增加,从而容易发生骨折的全身性骨病。绝经后骨质疏松症一般发生在妇女绝经后5-10年内。
文题释义:
激素替代疗法(hormone replacement therapy,HRT):是指通过补充激素来治疗激素分泌减退或者缺乏所引起的疾病的治疗方法。广义上的HRT涵盖所有的激素。狭义上的HRT多是针对女性激素,特别是指雌激素替代疗法(estrogen replacement therapy,ERT)。美国公布的研究结果显示,虽然激素替代疗法能帮助中老年妇女改善更年期不适症状,但这种疗法也会增加女性患痴呆症的风险。新结果再次表明需要对激素替代疗法的利弊进行重新评估。
骨质疏松症:是由于多种原因导致的骨密度和骨质量下降,骨微结构破坏,造成骨脆性增加,从而容易发生骨折的全身性骨病。绝经后骨质疏松症一般发生在妇女绝经后5-10年内。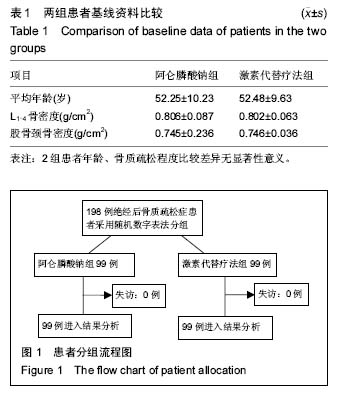

.jpg) 文题释义:
激素替代疗法(hormone replacement therapy,HRT):是指通过补充激素来治疗激素分泌减退或者缺乏所引起的疾病的治疗方法。广义上的HRT涵盖所有的激素。狭义上的HRT多是针对女性激素,特别是指雌激素替代疗法(estrogen replacement therapy,ERT)。美国公布的研究结果显示,虽然激素替代疗法能帮助中老年妇女改善更年期不适症状,但这种疗法也会增加女性患痴呆症的风险。新结果再次表明需要对激素替代疗法的利弊进行重新评估。
骨质疏松症:是由于多种原因导致的骨密度和骨质量下降,骨微结构破坏,造成骨脆性增加,从而容易发生骨折的全身性骨病。绝经后骨质疏松症一般发生在妇女绝经后5-10年内。
文题释义:
激素替代疗法(hormone replacement therapy,HRT):是指通过补充激素来治疗激素分泌减退或者缺乏所引起的疾病的治疗方法。广义上的HRT涵盖所有的激素。狭义上的HRT多是针对女性激素,特别是指雌激素替代疗法(estrogen replacement therapy,ERT)。美国公布的研究结果显示,虽然激素替代疗法能帮助中老年妇女改善更年期不适症状,但这种疗法也会增加女性患痴呆症的风险。新结果再次表明需要对激素替代疗法的利弊进行重新评估。
骨质疏松症:是由于多种原因导致的骨密度和骨质量下降,骨微结构破坏,造成骨脆性增加,从而容易发生骨折的全身性骨病。绝经后骨质疏松症一般发生在妇女绝经后5-10年内。