| [1] Sun Q,Xu J,Zou XQ,et al.The efficacy of percutaneous kyphoplasty in relieving painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Chin J Osteoporos.2009;15: 820-824.
[2] Werner CM,Osterhoff G,Schlickeiser J,et al.Vertebral body stenting versus kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a randomized trial.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2013;95: 577-584.
[3] Pitton MB,Herber S,Koch U,et al.CT-guided vertebroplasty:analysis of technical results, extraosseous cement leakages,and complications in 500 procedures.Eur Radiol.2008;18(11):2568-2578.
[4] Spiegl UJ,Beisse R,Hauck S,et al.Value of MRI imaging prior to a kyphoplasty for osteoporotic insufficiency fractures.Eur Spine J.2009;18(9): 1287-1292.
[5] Papathanassion D,Bnma-Muraille C,Jouannaud C. Single-photon emission computer tomography combined with computer tomography(SPECT/CT) in bone diseases.Joint Bone Spine.2009;76(5): 474-480.
[6] Hirschmann MT,Iranpour F,Davda K,et al. Combined single-photon emission computerized tomography and conventional computerized tomography (SPECT/CT): clinical value for the knee surgeons? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2010;18: 341-345.
[7] Husarik DB,Steinert HC.Single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography for sentinel node mapping in breast cancer.Semin Nucl Med.2007;37:29-33.
[8] Do HM.Magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of patients for percutaneous vertebroplasty.Top Magn Reson Imaging.2000;11:235-244.
[9] Baur A,Stäbler A,Arbogast S,et al.Acute osteoporotic and neoplastic vertebral compression fractures: fluid sign at MR imaging.Radiology.2002;225(3):730-735.
[10] Netter F,Journo A,Mayer JC,et al.Apport de la TEMP-TDM en complément de la scintigraphie osseuse planaire dans la pratique courante du service de médecine nucléaire.Med Nucl.2008; 32: 76-84.
[11] Bunyaviroch T,Aggarwal A,Oates ME.Optimized scintigraphic evaluation of infection and inflammation: role of single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography fusion imaging. Semin Nucl Med.2006;36(4):295-311.
[12] Gaitanis IN,Hadjipavlou AG,Katonis PG,et al.Balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of pathological vertebral compressive fractures.Eur Spine J.2005;14(3): 250-260.
[13] van Dijk WA,Poeze M,van Helden SH,et al.Ten-year mortality among hospitalised patients with fractures of the pubic rami.Injury.2009;41:411-414.
[14] Parmar R,Redfern DR,Hill JC. Comments on: role of bone scintigraphy.Ann R Coll Surg Engl.2006;88: 516-517.
[15] Langdon J,Way A,Heaton S,et al.Vertebral compression fractures new clinical signs to aid diagnosis.Arm R Coll Surg Enngl.2010;92(2): 163-166.
[16] Horger M,Bares R.The role of single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography in benign and malignant bone disease.Semin Nucl Med. 2006;36(4):286-289.
[17] Hirschmann MT,Davda K,Rasch H,et al.Clinical value of combined single photon emission computerized tomography and conventional computer tomography (SPECT/CT) in sports medicine.Sports Med Arthrosc. 2011;19:174-181.
[18] Navalkissoor S,Nowosinska E,Gnanasegaran G,et al. Single-photon emission computed tomography- computed tomography in imaging infection.Nucl Med Commun.2013;34:283-290.
[19] 高化,李锦军,王炳强,等.磁共振成像与核素骨显像对骨质疏松性椎体骨折诊断的比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011, 8(21):657-659.
[20] Irani FG,Morales JP,Sabharwal T,et al.Successful treatment of a chronic post-traumatic 5-year-old osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture by percutaneous vertebroplasty.Br J Radiol.2005;78: 261-264.
[21] Palestro CJ,Love C,Schneider R.The evolution of nuclear medicine and the musculoskeletal system.Radiol Clin N Am.2009;47:505-532.
[22] Shen F,Yan ZQ,Guo CA,et al.Prediction of traumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head by single photon emission computerized tomography and computerized tomography: an experimental study in dogs.Chin J Traumatol.2011;14(4):227-232.
[23] More AE,Blake GM,Taylor KA,et al.Changes observed in radionuclide bone scans and after teriparatide treatment for osteoporosis.Eur J Nuel Med Mol Imaging. 2012;9(2):326-336.
[24] Matin P.Bone scintigraphy in the diagnosis and management of traumatic injury.Semin Nucl Med. 1983; 13:104-122.
[25] Bredella MA,Essary BA,Torriani M,et al.Use of FDG-PET in differentiating benign from maligant compression fractures.Skeletal Radiol.2008;37(5): 405-413.
[26] Langdon J,Way A,Heaton S,et al.Vertebral compression fractures new clinical signs to aid diagnosis.Arm R Coll Surg Enngl.2010;92(2):163-166.
[27] Zukotynski K,Curtis C,Grant FD,et al.The value of SPECT in the detection of stress injury to the pars interarticularis in patients with low back pain.J Orthop Surg Res. 2010;5:13.
[28] Bayer LR,Widding A,Diemer H.Fifteen minutes bone scintigraphy in patients with clinically suspected scaphoid fracture and normal x-rays.Injury.2000;31: 243-248.
[29] Ohishi T,Takahashi M,Yamanashi A,et al.Sequential changes of bone metabolism in normal and delayed union of the spinel.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2008;466: 402-410.
[30] 江晓兵,莫凌,姚珍松,等.SPECT、SPECT-CT 与 MRI 对新鲜骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的诊断价值[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(10):891-897. |
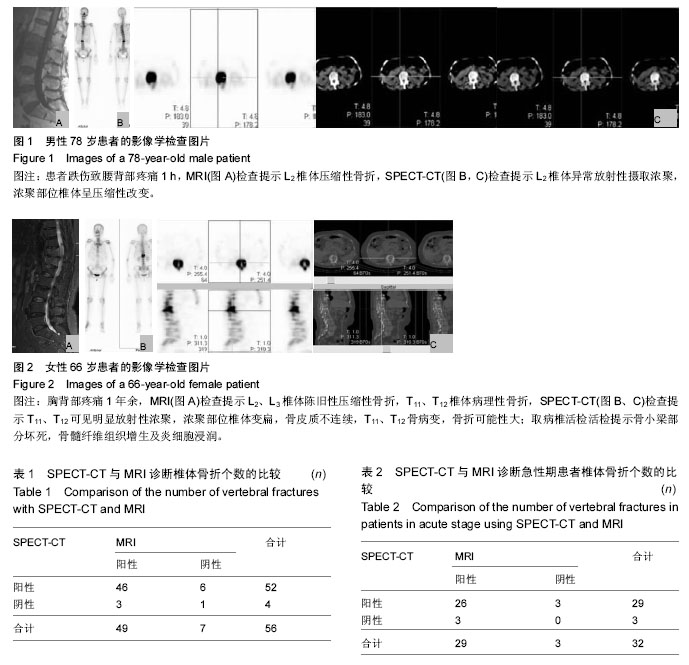
.jpg)
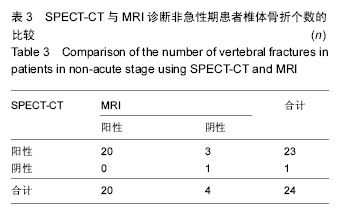
.jpg)