| [1] 汪智文,姜为民,张宗余,等.椎间桥形固定颈部融合器与传统融合器联合钛板治疗脊髓型颈椎病的临床疗效比较[J].中华外科杂志,2014,52(6):425-430.
[2] 章波,唐龙,杨波,等.多节段脊髓型颈椎病的手术治疗:三种手术方法的初期临床疗效比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2015,23(1):5-11.
[3] Luo J, Cao K, Huang S, et al. Comparison of anterior approach versus posterior approach for the treatment of multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(8):1621-1630.
[4] 谢冲,金格勒,李忠伟,等.颈前路与后路内固定系统置入治疗多节段脊髓型颈椎病的meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(17):2762-2769.
[5] 陈定中.单纯前入路与后入路治疗多节段脊髓型颈椎病的疗效对比研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2015,14(13): 1111-1113.
[6] Healy AT, Lubelski D, West JL, et al. Biomechanics of open-door laminoplasty with and without preservation of posterior structures. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;22:1-6.
[7] in SW, Kim SH, Kim BJ, et al. Modified Open-door Laminoplasty Using Hydroxyapatite Spacers and Miniplates. Korean J Spine. 2014;11(3):188-194.
[8] heng Z, Chen W, Yan S, et al. Expansive Open-Door Cervical Laminoplasty: In Situ Reconstruction of Extensor Muscle Insertion on the C2 Spinous Process Combined With Titanium Miniplates Internal Fixation. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(28):e1171.
[9] Machino M, Yukawa Y, Hida T, et al. Modified double-door laminoplasty in managing multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy: surgical outcome in 520 patients and technique description. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(3):135-140.
[10] Ozawa T, Toyone T, Shiboi R, et al. Modified Open-Door Laminoplasty Using a Ceramic Spacer and Suture Fixation for Cervical Myelopathy. Yonsei Med J. 2015;56(6):1651-1655.
[11] 李玉伟,严晓云,王海蛟,等.保留C2、3棘突肌肉附着点的改良颈椎管扩大成形[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24:(1): 30-34.
[12] Mao JP, Tian W, Liu B, et al. Short-term clinical outcome of modified expansive open-door cervical laminoplasty preserving posterior extensor musculature inserted into C2 and C7 spinous process. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2010;90(5):337-341.
[13] Takeuchi K, Yokoyama T, Aburakawa S, et al. Axial symptoms after cervical laminoplasty with C3 laminectomy compared with conventional C3-C7 laminoplasty: a modified laminoplasty preserving the semispinalis cervicis inserted into axis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(22):2544-2549.
[14] Mori E, Ueta T, Maeda T, et al. Effect of preservation of the C6 spinous process and its paraspinal muscular attachment on the prevention of postoperative axial neck pain in C3-6 laminoplasty.J Neurosurg Spine. 2015;22(3):221-229.
[15] Riew KD, Raich AL, Dettori JR, et al. Neck Pain Following Cervical Laminoplasty: Does Preservation of the C2 Muscle Attachments and/or C7 Matter? Evid Based Spine Care J. 2013;4(1):42-53.
[16] 牛硕,孙宇.系统性回顾改良颈椎椎管扩大椎板成形的疗效及其对轴性症状的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2012, 22(1):72-76.
[17] 朱远熔,肖光华,张巧燕,等.一种简易抗阻肌力训练操辅助治疗颈椎病的临床研究[J].中国康复医学,2015,30(5): 506-508.
[18] Yonenobu K, Fuji T, Ono K, et al. Choice of surgical treatment for multisegmental cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1985;10(8): 710-716.
[19] Bakhtadze MA, Vernon H, Zakharova OB, et al. The neck disability index-russian language version (NDI-RU): a study of validity and reliability. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(14):1115-1121.
[20] Kawaguchi Y, Matsui H, Ishihara H, et al. Axial symptoms after en bloc cervical laminoplasty. J Spinal Disord.1999;12(5):392-395.
[21] Hosono N, Yonenobu K, Ono K. Neck and shoulder pain after laminoplasty. A noticeable complication. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1996;21(17):1969-1973.
[22] Nurboja B, Kachramanoglou C, Choi D. Cervical laminectomy vs laminoplasty: is there a difference in outcome and postoperative pain? Neurosurgery. 2012; 70(4):965-970.
[23] Wang SJ, Jiang SD, Jiang LS, et al. Axial pain after posterior cervical spine surgery: a systematic review. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(2):185-194.
[24] Fujibayashi S, Neo M, Yoshida M, et al. Neck muscle strength before and after cervical laminoplasty: relation to axial symptoms. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010;23(3): 197-202.
[25] Lin S, Zhou F, Sun Y, et al. Changes of sagittal balance of cervical spine after open-door expansive laminoplasty. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014;94(35): 2726-2730.
[26] Lin S, Zhou F, Sun Y, et al. The severity of operative invasion to the posterior muscular-ligament complex influences cervical sagittal balance after open-door laminoplasty. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(1):127-135.
[27] 王辉,丁文元,马雷,等.颈椎术后轴性症状[J].颈腰疼杂志, 2014,35(2):146-149.
[28] 刘晓伟,赵建宁,许斌.颈后路减压手术后轴性疼痛及其预防措施的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014,24(6): 567-570
[29] Hosono N, Sakaura H, Mukai Y, et al. The source of axial pain after cervical laminoplasty-C7 is more crucial than deep extensor muscles. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(26):2985-2988.
[30] [30]王健,罗浩,梁卫东,等.改良单开门椎管扩大成形修复慢性压迫性颈脊髓病:颈椎稳定性随访[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(48):7751-7756.
[31] Sakaura H, Hosono N, Mukai Y, et al. Preservation of muscles attached to the C2 and C7 spinous processes rather than subaxial deep extensors reduces adverse effects after cervical laminoplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(16):E782-E786.
[32] Sakaura H, Hosono N, Mukai Y, et al. Medium-term outcomes of C3-6 laminoplasty for cervical myelopathy: a prospective study with a minimum 5-year follow-up. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(6):928-933.
[33] Sakaura H, Hosono N, Mukai Y, et al. C3-6 laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy maintains satisfactory long-term surgical outcomes. Global Spine J. 2014;4(3):169-174.
[34] Takeuchi K, Yokoyama T, Aburakawa S. et al. Axial symptoms after cervical laminoplasty with C3 laminectomy compared with conventional C3-C7 laminoplasty: a modified laminoplasty preserving the semispinalis cervicis inserted into axis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(22):2544-2549.
[35] Mesfin A, Park MS, Piyaskulkaew C, et al. Neck Pain following Laminoplasty. Global Spine J. 2015;5(1): 17-22.
[36] Falla D, O'Leary S, Fagan A, et al. Recruitment of the deep cervical flexor muscles during a postural-correction exercise performed in sitting. Man Ther. 2007;12(2): 139-143.
[37] Gross A, Kay TM, Paquin JP, et al.Exercises for mechanical neck disorders. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;28;1:CD004250.
[38] Zhang P, Shen Y, Zhang YZ, et al. Preserving the C7 spinous process in laminectomy combined with lateral mass screw to prevent axial symptom. J Orthop Sci. 2011;16(5):492-497.
[39] Kotani Y, Abumi K, Ito M, et al. Minimum 2-year outcome of cervical 1aminoplasty with deep extensor muscle preserving approach:impact on cervical spine function and quality of life. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(5): 663-671.
[40] 王彦伟,王明金,卢学伟,等.抗阻训练对老龄大鼠骨骼肌新生细胞核数量的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2012,27(6): 504-509.
[41] Lee JP, Tseng WY, Shau YW, et al. Measurement of segmental cervical multifidus contraction by ultrasonography in asymptomatic adults. Man Ther. 2007;12(3):286-294.
[42] O'Leary S, Cagnie B, Reeve A, et al. Is there altered activity of the extensor muscles in chronic mechanical neck pain? A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2011;92(6):929-934.
[43] 曹俊明,申勇,杨大龙,等.颈椎椎板成形后颈部轴性症状的影响因素及防治[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(21): 1629-1631. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
多节段脊髓型颈椎病:是指脊髓型颈椎病脊髓受压3个节段或3个节段以上,患者具备明显的上运动元损伤的临床表现,常需要手术解决,而手术方式分为3种,前路减压融合、后路椎管扩大成形、前后路联合手术,前路手术可以直接去除压迫因素,但长节段固定会影响颈椎的活动度,加速邻近节段的退变,后路椎管扩大成形脊髓后移达到间接减压目的,对颈椎的活动都影响相对较小,因而成为治疗多节段脊髓型颈椎病的经典术式。
肌肉等长收缩:是指肌肉收缩活动过程中保持长度不变,不引发运动,不导致靶组织或器官的位移,收缩过程中肌肉的张力增加,等张收缩则与之对应。
文题释义:
多节段脊髓型颈椎病:是指脊髓型颈椎病脊髓受压3个节段或3个节段以上,患者具备明显的上运动元损伤的临床表现,常需要手术解决,而手术方式分为3种,前路减压融合、后路椎管扩大成形、前后路联合手术,前路手术可以直接去除压迫因素,但长节段固定会影响颈椎的活动度,加速邻近节段的退变,后路椎管扩大成形脊髓后移达到间接减压目的,对颈椎的活动都影响相对较小,因而成为治疗多节段脊髓型颈椎病的经典术式。
肌肉等长收缩:是指肌肉收缩活动过程中保持长度不变,不引发运动,不导致靶组织或器官的位移,收缩过程中肌肉的张力增加,等张收缩则与之对应。.jpg) 文题释义:
多节段脊髓型颈椎病:是指脊髓型颈椎病脊髓受压3个节段或3个节段以上,患者具备明显的上运动元损伤的临床表现,常需要手术解决,而手术方式分为3种,前路减压融合、后路椎管扩大成形、前后路联合手术,前路手术可以直接去除压迫因素,但长节段固定会影响颈椎的活动度,加速邻近节段的退变,后路椎管扩大成形脊髓后移达到间接减压目的,对颈椎的活动都影响相对较小,因而成为治疗多节段脊髓型颈椎病的经典术式。
肌肉等长收缩:是指肌肉收缩活动过程中保持长度不变,不引发运动,不导致靶组织或器官的位移,收缩过程中肌肉的张力增加,等张收缩则与之对应。
文题释义:
多节段脊髓型颈椎病:是指脊髓型颈椎病脊髓受压3个节段或3个节段以上,患者具备明显的上运动元损伤的临床表现,常需要手术解决,而手术方式分为3种,前路减压融合、后路椎管扩大成形、前后路联合手术,前路手术可以直接去除压迫因素,但长节段固定会影响颈椎的活动度,加速邻近节段的退变,后路椎管扩大成形脊髓后移达到间接减压目的,对颈椎的活动都影响相对较小,因而成为治疗多节段脊髓型颈椎病的经典术式。
肌肉等长收缩:是指肌肉收缩活动过程中保持长度不变,不引发运动,不导致靶组织或器官的位移,收缩过程中肌肉的张力增加,等张收缩则与之对应。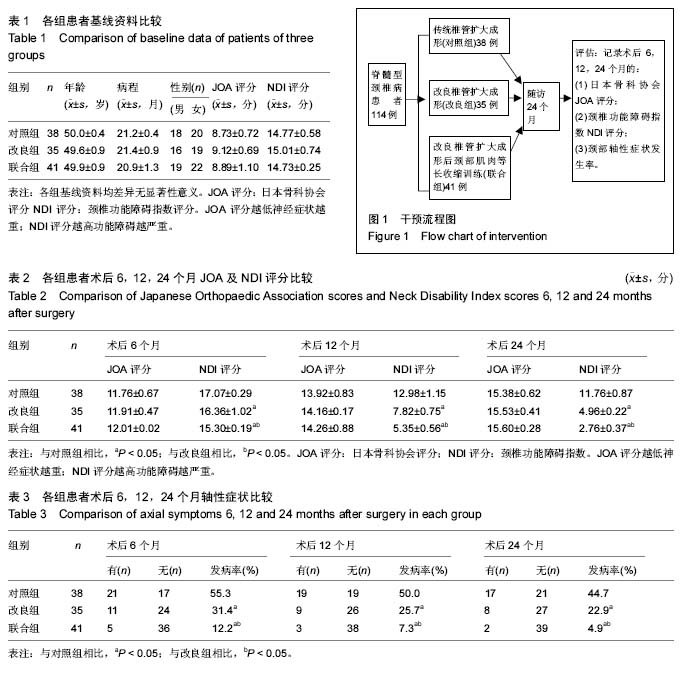
.jpg) 文题释义:
多节段脊髓型颈椎病:是指脊髓型颈椎病脊髓受压3个节段或3个节段以上,患者具备明显的上运动元损伤的临床表现,常需要手术解决,而手术方式分为3种,前路减压融合、后路椎管扩大成形、前后路联合手术,前路手术可以直接去除压迫因素,但长节段固定会影响颈椎的活动度,加速邻近节段的退变,后路椎管扩大成形脊髓后移达到间接减压目的,对颈椎的活动都影响相对较小,因而成为治疗多节段脊髓型颈椎病的经典术式。
肌肉等长收缩:是指肌肉收缩活动过程中保持长度不变,不引发运动,不导致靶组织或器官的位移,收缩过程中肌肉的张力增加,等张收缩则与之对应。
文题释义:
多节段脊髓型颈椎病:是指脊髓型颈椎病脊髓受压3个节段或3个节段以上,患者具备明显的上运动元损伤的临床表现,常需要手术解决,而手术方式分为3种,前路减压融合、后路椎管扩大成形、前后路联合手术,前路手术可以直接去除压迫因素,但长节段固定会影响颈椎的活动度,加速邻近节段的退变,后路椎管扩大成形脊髓后移达到间接减压目的,对颈椎的活动都影响相对较小,因而成为治疗多节段脊髓型颈椎病的经典术式。
肌肉等长收缩:是指肌肉收缩活动过程中保持长度不变,不引发运动,不导致靶组织或器官的位移,收缩过程中肌肉的张力增加,等张收缩则与之对应。