| [1] Höntzsch D, Blauth M, Attal R,et al.Angle-stable fixation of intramedullary nails using the Angular Stable Locking System® (ASLS). Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2011;23(5):387-396.
[2] Ehlinger M, Adam P, Arlettaz Y,et al. Minimally-invasive fixation of distal extra-articular femur fractures with locking plates: limitations and failures. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2011;97(6):668-674.16:28 2016-9-6
[3] Nayak RM, Koichade MR, Umre AN,et al.Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis using a locking compression plate for distal femoral fractures. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong).2011;19(2):185-190.
[4] Malviya A, Reed MR, Partington PF. Acute primary total knee arthroplasty for peri-articular knee fractures in patients over 65 years of age.Injury.2011;42(11):1368-1371.
[5] Lopes JB, Figueiredo CP, Caparbo VF,et al. Osteoporotic fractures in the Brazilian community- dwelling elderly: prevalence and risk factors. J Clin Densitom. 2011;14(3):359-366.
[6] [6] Weil YA, Rivkin G, Safran O,et al. The outcome of surgically treated femur fractures associated with long-term bisphosphonate use. J Trauma. 2011;71(1): 186-190.
[7] Hierholzer C, von Rüden C, Pötzel T, et al. Outcome analysis of retrograde nailing and less invasive stabilization system in distal femoral fractures: A retrospective analysis. Indian J Orthop. 2011;45(3): 243-250.
[8] Shih KS, Hsu CC, Hsu TP. A biomechanical investigation of the effects of static fixation and dynamization after interlocking femoral nailing: A finite element study. J Trauma. 2012;72(2):E46-E53.
[9] Salas C, Mercer D, DeCoster TA, et al. Experimental and probabilistic analysis of distal femoral periprosthetic fracture: a comparison of locking plate and intramedullary nail fixation. Part A: experimental investigation. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2011;14(2):157-164.
[10] Han QT, Wang YJ, Tang HW. Biomechanical comparison of three methods of internal fixation for distal femoral fractures. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2010; 23(8):601-604.
[11] Efstathopoulos N, Nikolaou VS, Xypnitos FN, et al.Investigation on the distal screw of a trochanteric intramedullary implant (Fi-nail) using a simplified finite element model. Injury. 2010;41(3):259-265.
[12] Chang CY, Rupp JD, Reed MP, et al.Predicting the effects of muscle activation on knee, thigh, and hip injuries in frontal crashes using a finite-element model with muscle forces from subject testing and musculoskeletal modeling. Stapp Car Crash J. 2009; 53:291-328.
[13] Bougherara H, Zdero R, Miric M, et al.The biomechanics of the T2 femoral nailing system: a comparison of synthetic femurs withfinite element analysis. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2009;223(3):303-314.
[14] Chen SH, Yu TC, Chang CH, et al. Biomechanical analysis of retrograde intramedullary nail fixation in distal femoral fractures. Knee. 2008;15(5):384-389.
[15] Mann KA, Lee J, Arrington SA, et al.Predicting distal femur bone strength in a murine model of tumor osteolysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(6): 1271-1278.
[16] Shih KS, Tseng CS, Lee CC, et al.Influence of muscular contractions on the stress analysis of distal femoral interlocking nailing. Clin Biomech(Bristol, Avon). 2008;23(1):38-44.
[17] Mahaisavariya B, Sitthiseripratip K, Suwanprateeb J. Finite element study of the proximal femur with retained trochanteric gamma nail and after removal of nail. Injury. 2006;37(8):778-785.
[18] Cegoñino J, García Aznar JM, Doblaré M, et al. A comparative analysis of different treatments for distal femur fractures using the finite element method. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2004;7(5): 245-256.
[19] Dubov A, Kim SY, Shah S, et al.The biomechanics of plate repair of periprosthetic femur fractures near the tip of a total hip implant: the effect of cable-screw position. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2011;225(9):857-865.
[20] Shah S, Kim SY, Dubov A, et al.The biomechanics of plate fixation of periprosthetic femoral fractures near the tip of a total hip implant: cables, screws, or both? Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2011;225(9):845-856.
[21] Wilson LJ, Richards CJ, Irvine D, et al. Irvine D,Risk of periprosthetic femur fracture after anterior cortical bone windowing: a mechanical analysis of short versus long cemented stems in pigs. Acta Orthop. 2011;82(6): 674-678.
[22] Chen SH, Tai CL, Yu TC, et al. Modified fixations for distal femur fractures following total knee arthroplasty: a biomechanical and clinical relevance study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016. [Epub ahead of print]
[23] Filardi V.The healing stages of an intramedullary implanted tibia: A stress strain comparative analysis of the calcification process.J Orthop. 2015;12(Suppl 1):S51-61.
[24] Yoshimoto K, Nakashima Y, Nakamura A, et al. Neck fracture of femoral stems with a sharp slot at the neck: biomechanical analysis.J Orthop Sci. 2015;20(5):881-887.
[25] Li L, Yu M, Ma R, et al.Initial Stability of Subtrochanteric Oblique Osteotomy in Uncemented Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Preliminary Finite Element Study. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:1969-1975.
[26] Märdian S, Schaser KD, Duda GN, et al. Working length of locking plates determines interfragmentary movement in distal femur fracturesunder physiological loading. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2015;30(4): 391-396.
[27] Zhang J, Ebraheim N, Li M, et al.External fixation using locking plate in distal tibial fracture: a finite element analysis.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25(6): 1099-1104.
[28] Leonidou A, Moazen M, Lepetsos P, et al. The biomechanical effect of bone quality and fracture topography on locking plate fixation in periprosthetic femoral fractures. Injury. 2015;46(2):213-217.
[29] Mahaisavariya B, Chantarapanich N, Riansuwan K, et al. Prevention of excessive medialisation of trochanteric fracture by a buttress screw: a novel methodand finite element analysis. J Med Assoc Thai. 2014;97 Suppl 9:S127-132.
[30] Martelli S, Pivonka P, Ebeling PR. Femoral shaft strains during daily activities: Implications for atypical femoral fractures. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2014; 29(8):869-876.
[31] Tan CO, Battaglino RA, Doherty AL, et al.Adiponectin is associated with bone strength and fracture history in paralyzed men with spinal cord injury.Osteoporos Int. 2014;25(11):2599-2607.
[32] Sun ZH, Liu YJ, Li H. Femoral stress and strain changes post-hip, -knee and -ipsilateral hip/knee arthroplasties: a finiteelement analysis. Orthop Surg. 2014;6(2):137-144.
[33] Tran TN, Warwas S, Haversath M, et al.Experimental and computational studies on the femoral fracture risk for advanced core decompression.Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2014;29(4):412-417.
[34] Kimura G, Onishi E, Kawanabe K, et al.Characteristic loosening of the distally straight cylindrical femoral stem. J Orthop Sci. 2014;19(3):437-442.
[35] Shih KS, Hsu CC, Hsu TP, et al. Biomechanical analyses of static and dynamic fixation techniques of retrograde interlocking femoralnailing using nonlinear finite element methods.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2014;113(2):456-464.
[36] Edwards WB, Schnitzer TJ, Troy KL.Bone mineral and stiffness loss at the distal femur and proximal tibia in acute spinal cord injury.Osteoporos Int. 2014;25(3): 1005-1015.
[37] Erhardt JB, Khoo PP, Stoffel KK, et al.Periprosthetic fractures around polished collarless cemented stems: the effect of stem design on fracture pattern.Hip Int. 2013;23(5):459-464.
[38] Chen SH, Chiang MC, Hung CH, et al.Finite element comparison of retrograde intramedullary nailing and locking plate fixation with/without an intramedullary allograft for distal femur fracture following total knee arthroplasty.Knee. 2014;21(1):224-231. |
.jpg)
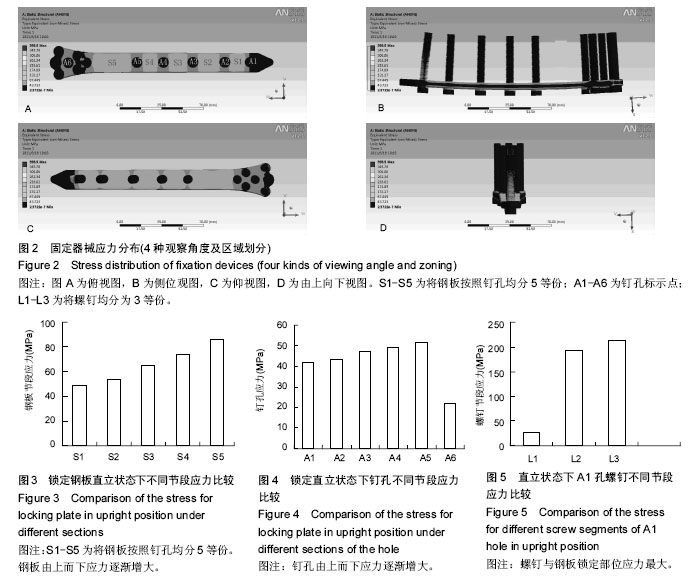
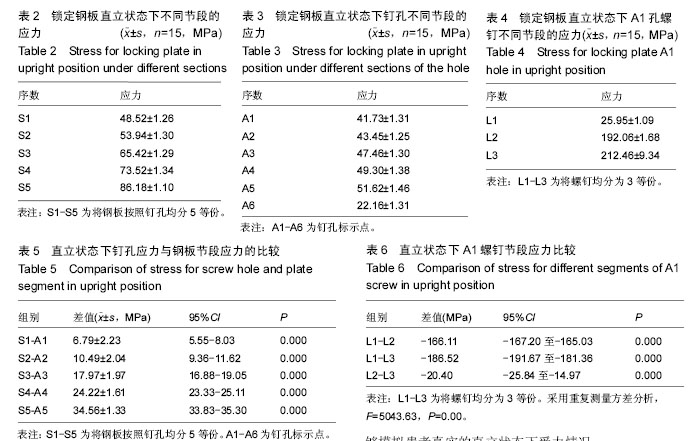
.jpg)
.jpg)