| [1] Sehat KR ER, Newman JH. How much blood is really lost in total knee arthroplasty? Correct blood loss management should take hidden loss into account. Knee. 2000;7(3):151-155.
[2] 中华医学会风湿病学分会. 骨关节炎诊断及治疗指南[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2010,14(6):416-419.
[3] 中华医学会风湿病学分会. 类风湿关节炎诊断及治疗指南[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2010,14(4):265-270.
[4] Pattison E, Protheroe K, Pringle RM, et al. Reduction in haemoglobin after knee joint surgery. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973;32(6):582-584.
[5] Erskine JG, Fraser C, Simpson R, et al. Blood loss with knee joint replacement. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1981; 26(5): 295-297.
[6] McManus KT, Lotke PA. Non-invasive assessment of post-operative bleeding in TKA patients with Tc-99m RNCs. J Nuclear Med. 1987;28:565.
[7] Park JH, Rasouli MR, Mortazavi SM, et al. Predictors of perioperative blood loss in total joint arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(19):1777-1783.
[8] Prasad N, Padmanabhan V, Mullaji A. Blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: an analysis of risk factors. Int Orthop. 2007;31(1):39-44.
[9] Bierbaum BE, Callaghan JJ, Galante JO, et al. An analysis of blood management in patients having a total hip or knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81(1):2-10.
[10] Yau WP, Tang WM, Ng TP, et al. Factors leading to blood transfusion among Chinese patients undergoing total knee replacements: a retrospective study. J Orthop Surg. 2004;12(2):153-157.
[11] 覃健,余存泰,徐中和,等. 全髋关节及全膝关节置换术后隐陛失血的临床影响[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2006,26(5): 323-326.
[12] 赵磊尚,赵其纯,胡飞,等.隐性失血对全膝关节置换术后功能恢复的影响[J].安徽医科大学学报,2014,49(5): 682-683.
[13] 王英振,徐郭.全膝关节置换术围手术期隐性失血的危险因素研究[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2013,7(3): 341-345.
[14] 邱旭升,陈东阳,徐志宏,等.全膝关节置换术后隐性失血危险因素的分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2012,8(6):510-512.
[15] Gao FQ, Li ZJ, Zhang K, et al. Impact factors for hidden blood loss after primary total knee arthroplasty. Zhonghua wai ke za zhi. 2011;49(5):419-423.
[16] 赵旻暐,李子剑,张克. 氨甲环酸在人工全膝关节置换术中的应用[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2014,8(2):236-239.
[17] 赵辉,张钱吴,李吴祝. 氨甲环酸减少全膝关节置换术失血量的Meta分析[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2009,29(6):524-529.
[18] Zhang Y, Fu X, Liu WX, et al. Safety and efficacy of intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2014;37(9):e775-782.
[19] Yang Y, Lv YM, Ding PJ, et al. The reduction in blood loss with intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid in unilateral total knee arthroplasty without operative drains: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014.
[20] Morais S, Ortega-Andreu M, Rodriguez-Merchan EC, et al. Blood transfusion after primary total knee arthroplasty can be significantly minimised through a multimodal blood-loss prevention approach. Int Orthop. 2014;38(2):347-354.
[21] Martin JG, Cassatt KB, Kincaid-Cinnamon KA, et al. Topical administration of tranexamic acid in primary total hip and total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(5):889-894.
[22] Jang B, Kao M, Bohm MT, et al. Intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid to reduce blood loss after total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg. 2014;22(2):146-149.
[23] Alshryda S, Sukeik M, Sarda P, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the topical administration of tranexamic acid in total hip and knee replacement. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(8):1005-1015.
[24] Aguilera X, Martinez-Zapata MJ, Hinarejos P, et al. Topical and intravenous tranexamic acid reduce blood loss compared to routine hemostasis in total knee arthroplasty: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015;135(7):1017-1025.
[25] Chen X, Xie S, Wang K. [Effectiveness of tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty]. Zhongguo xiu fu chong jian wai ke za zhi. 2014;28(11):1338-1341.
[26] Gao F, Sun W, Guo W, et al. Topical Application of Tranexamic Acid Plus Diluted Epinephrine Reduces Postoperative Hidden Blood Loss in Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(12):2196-2200.
[27] Huang GP, Jia XF, Xiang Z, et al. Tranexamic Acid Reduces Hidden Blood Loss in Patients Undergoing Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Comparative Study and Meta-Analysis. Med Sci Monit. 2016;22:797-802.
[28] Huang Z, Zhang W, Li W, et al. [a Prospective Randomized Self-Controlled Study on Effect Of Tranexamic Acid In Reducing Blood Loss In Total Knee Arthroplasty]. Zhongguo xiu fu chong jian wai ke za zhi. 2015;29(3):280-283.
[29] Panteli M, Papakostidis C, Dahabreh Z, et al. Topical tranexamic acid in total knee replacement: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee. 2013; 20(5):300-309.
[30] Poeran J, Rasul R, Suzuki S, et al. Tranexamic acid use and postoperative outcomes in patients undergoing total hip or knee arthroplasty in the United States: retrospective analysis of effectiveness and safety. BMJ. 2014;349:g4829.
[31] Shen PF, Hou WL, Chen JB, et al. Effectiveness and safety of tranexamic acid for total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:576-581.
[32] Tan J, Chen H, Liu Q, et al. A meta-analysis of the effectiveness and safety of using tranexamic acid in primary unilateral total knee arthroplasty. J Surg Res. 2013;184(2):880-887.
[33] Wei Z, Liu M. The effectiveness and safety of tranexamic acid in total hip or knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of 2720 cases. Trans Med. 2015;25(3): 151-162.
[34] Gao FQ, Sun W, Li ZR, et al. Correlation between the coverage percentage of prosthesis and postoperative hidden blood loss in primary total knee arthroplasty. Chin Med J 2014;127(12):2265-2269.
[35] Liu J, Li YM, Cao JG, et al. Effects of knee position on blood loss following total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, controlled study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015; 10:69. |
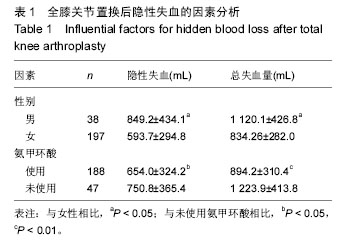
.jpg)
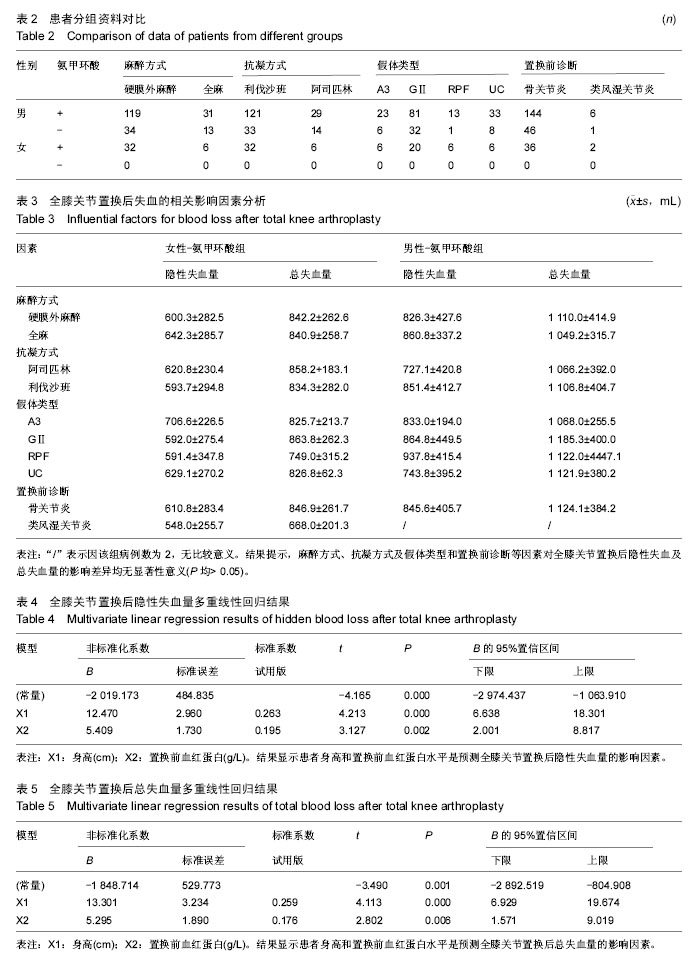
.jpg)