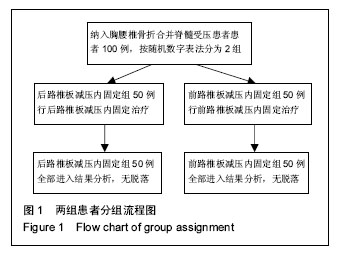
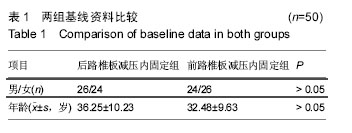
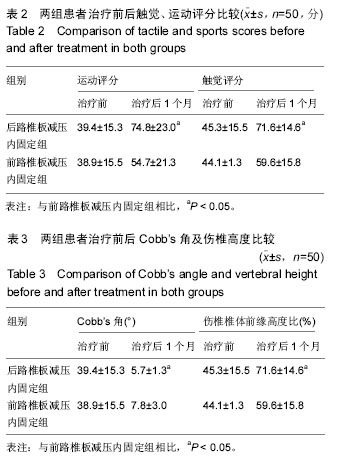
| [1] 唐善保,叶明.胸腰段脊柱骨折合并脊髓损伤的早期治疗[J].医学信息,2010,23(5):69-70.[2] 董泽,刘志斌.胸腰段脊柱骨折三柱重建的试验研究[J].中国伤残医学,2012,20(5):41-42.[3] 王大民,肖克明,邵楠.后路内固定融合术治疗脊柱胸腰段骨折疗效观察[J].医学临床研究,2011,28(6):1168-1170.[4] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印钦,等主编.实用骨科学[M].3版.北京:人民军医出版社,2008:723-740.[5] 王亦璁.骨与关节损伤[M].3版. 北京:人民卫生出版社, 2009:1233-1275.[6] 马立泰,刘浩,龚全,等.胸腰段骨折前路手术切口平面对术后脊柱侧方成角的影响[J].中华创伤杂志,2011,27(10): 868-871.[7] 文坤树,蒋波,蔡勇平,等.椎弓根钉棒系统治疗胸、腰椎骨折56例体会[J].重庆医学,2012,41(15):1496-1498.[8] 马立泰,刘浩,洪瑛,等.胸腰椎骨折前路手术中冠状面Cobb角变化规律及其影响因素的多元线性回归分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,18(10):830-835.[9] 施能槐.前路手术治疗胸腰段爆裂性骨折18例疗效分析[J].广西医科大学学报,2011,28(1):128-130.[10] 邵本应.胸腰段脊柱骨折合并脊髓损伤的早期治疗[J].实用骨科杂志,2010,11(2):155-156.[11] 冯占远.椎弓根螺钉联合连接棒内固定治疗胸腰段脊柱骨折临床分析[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2011,14(24): 66-67.[12] 李云峰,陆坚,刘百伟,等.重建椎体完整性和稳定性在胸腰椎骨折中的应用[J].实用骨科杂志,2012,18(1):4-7.[13] 尚晖,常巍,王达义,等.前路椎间盘松解矫形治疗无神经症状胸腰段陈旧性骨折伴后凸畸形的疗效观察[J].中国全科医学,2011,14(12):1357-1359.[14] 陈应超,李健,胸腰椎爆裂骨折的治疗和展望[J].中国矫形外科,2010,18(2):132-136.[15] Hua YJ, Wang RY, Guo ZH, et al. [Clinical studies of pedicle screw-rod fixation of thoracolumbar burst fractures through posterior unilateral approach after vertebrae corpectomy fusion]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2016;29(1):27-32. [16] Aono H, Tobimatsu H, Ariga K, et al. Surgical outcomes of temporary short-segment instrumentation without augmentation for thoracolumbar burst fractures. Injury. 2016. pii: S0020-1383(16)30030-4. [17] Li K, Li Z, Ren X, et al. Effect of the percutaneous pedicle screw fixation at the fractured vertebra on the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures. Int Orthop. 2016. [Epub ahead of print][18] Wu C, Tan L, Lin X, et al. [Clinical application of individualized reference model of sagittal curves and navigation templates of pedicle screw by three-dimensional printing technique for thoracolumbar fracture with dislocation]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015;29(11):1381-1388.[19] Haq MI, Khan SA, Aurangzeb A, et al. Radiological outcome of transpedicular screws fixation in the management of thoracolumbar spine injury. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2015;27(1):171-173.[20] Liu L, Gan Y, Zhou Q, et al. Improved Monosegment Pedicle Instrumentation for Treatment of Thoracolumbar Incomplete BurstFractures. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:357206. [21] Jeon CH, Lee HD, Lee YS, et al. Is It Beneficial to Remove the Pedicle Screw Instrument After Successful Posterior Fusion of Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(11):E627-633.[22] Phan K, Rao PJ, Mobbs RJ. Percutaneous versus open pedicle screw fixation for treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: Systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2015;135:85-92.[23] Zhang Z, Chen G, Sun J, et al. Posterior indirect reduction and pedicle screw fixation without laminectomy for Denis type Bthoracolumbar burst fractures with incomplete neurologic deficit. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:85.[24] He SH, Ma DJ, Sun ZT, et al. [Internal fixation combined with bone grafting through the injured pedicle for the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures via a paraspinal intermuscular approach under MAST Quadrant retractor]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2015;28(1):17-20.[25] Wang F, He XJ. [Long-term effects on health-related quality of life after short-segment pedicle fixation of thoracolumbar fractures without neurologic injury]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2015;28(1):12-16. [26] Li GM, Tang DZ.[Short-segment posterior pedicle screw combined with vertebral arch bone grafting forthoracolumbar burst fractures]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2015;28(1):8-11.[27] Grossbach AJ, Viljoen SV, Hitchon PW, et al. Vertebroplasty plus short segment pedicle screw fixation in a burst fracture model in cadaveric spines. J Clin Neurosci. 2015;22(5):883-888.[28] Ökten A?, Gezercan Y, Özsoy KM, et al. Results of treatment of unstable thoracolumbar burst fractures using pedicle instrumentation with and without fracture-level screws. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2015; 157(5):831-836. [29] Park HY, Lee SH, Park SJ, et al.Minimally invasive option using percutaneous pedicle screw for instability of metastasis involvingthoracolumbar and lumbar spine : a case series in a single center.J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015;57(2):100-107. [30] Eschler A, Ender SA, Schiml K, et al. Bony healing of unstable thoracolumbar burst fractures in the elderly using percutaneously applied titanium mesh cages and a transpedicular fixation system with expandable screws. PLoS One. 2015;10(2):e0117122. [31] Chen T, Long L, Cao G, et al. Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by posterior laminotomy decompression and bonegrafting via injured vertebrae. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014; 28(10):1236-1240. [32] Meng X, Zeng K, Turghunjan-Abdurxit, et al. Effectiveness of pedicle screw fixation combined with non-fusion technology for treatment ofthoracolumbar fracture through Wiltse paraspinal approach. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014; 28(9):1106-1109.[33] Dobran M, Iacoangeli M, Di Somma LG, et al. Neurological outcome in a series of 58 patients operated for traumatic thoracolumbar spinal cordinjuries. Surg Neurol Int. 2014;5(Suppl 7): S329-332. [34] Wu AM, Zheng YJ, Lin Y, et al. Transforaminal decompression and interbody fusion in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractureand dislocation with spinal cord injury. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e105625.[35] Bakhsheshian J, Dahdaleh NS, Fakurnejad S, et al. Evidence-based management of traumatic thoracolumbar burst fractures: a systematic review of nonoperative management. Neurosurg Focus. 2014; 37(1):E1.[36] Farooque K, Kandwal P, Gupta A. Subacute post-traumatic ascending myelopathy (SPAM): two cases of SPAM following surgical treatment of thoracolumbar fractures. Neurol India. 2014;62(2): 192-194. [37] Bailey CS, Urquhart JC, Dvorak MF, et al. Orthosis versus no orthosis for the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures without neurologic injury: a multicenter prospective randomized equivalence trial. Spine J. 2014;14(11):2557-2564. [38] Qian L, Pan J, Liu ZD, et al.The correlation between vertebral wedge-shaped changes in X-ray imaging at supine and standing positions and the efficacy of operative treatment of thoracolumbar spinal fracture in the elderly. Spinal Cord. 2013;51(12):904-908. |
.jpg)
.jpg)