中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (16): 2354-2359.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.16.010
• 材料生物相容性 material biocompatibility • 上一篇 下一篇
新型纳米材料无定形磷酸钙药物支架置入小型猪冠状动脉后的生物相容性
谭 峥,李 莉,马 燚
- 河北医科大学唐山临床医学院、河北医科大学附属唐山工人医院、河北省唐山市工人医院,河北省唐山市 063000
A novel amorphous calcium phosphate drug-eluting stent: its biocompatibility after implantation into mini-swine coronary artery
Tan Zheng, Li Li, Ma Yi
- Tangshan Clinical Medical School of Hebei Medical University, Affiliated Tangshan Worker’ s Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
药物深层支架:药物深层支架携带雷帕霉素和紫杉醇等药物的支架。涂层的作用包括防止支架内急性或亚急性血栓形成,防止或降低再狭窄发生率。支架置入后发生再狭窄的主要原因是内皮过度增生,药物深层则可防止这种血管内皮增生,通过有效抑制局部平滑肌增殖,减少支架内再狭窄的出现。
无定形磷酸钙:属于无机可降解聚合物家族成员,具有良好的可溶性和再矿化性,被广泛应用于医学领域。从无定形磷酸钙中释放出来的离子可以有效中和聚合物材料降解时释放出来的酸性代谢产物,有效改善聚合物材料的生物相容性,并可调节聚合物的机械性能,降解性和生物学活性。
背景:以往冠状动脉植入支架大多为聚左旋乳酸,但存在早期支撑力不足的问题,且会产生一定的酸性产物,导致血管局部出现炎性反应。
目的:探讨新型纳米材料无定形磷酸钙药物支架置入小型猪冠状动脉后的生物相容性。
方法:20只小型猪随机等分为观察组和对照组,对动物右侧股动脉予以逐层分离,分别置入新型生物全降解支架和聚左旋乳酸支架。
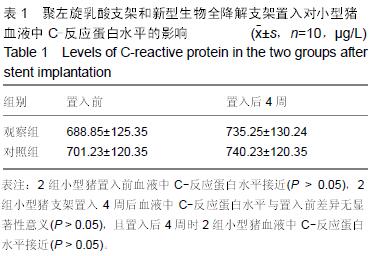
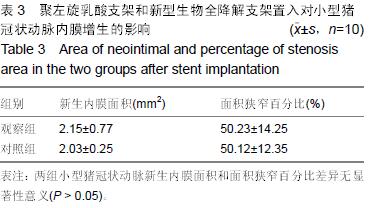
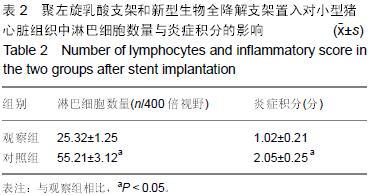
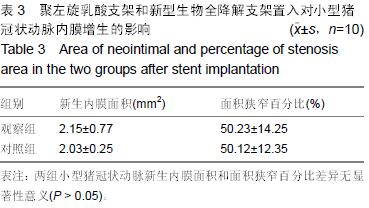
结果和结论:①支架置入后即刻进行冠状动脉造影:可见2组支架置入血管管腔均处于良好的通畅状态;②置入后4周冠状动脉造影复查:管腔通畅,未出现支架血栓形成与管腔狭窄,2组情况接近;③置入前和置入后4周2组动物血液相关指标检测:C-反应蛋白水平接近。置入后4周,观察组小型猪心脏组织中的淋巴细胞数量与炎症积分均显著低于对照组,而新生内膜面积和面积狭窄百分比与对照组接近;④结果提示新型纳米材料无定形磷酸钙药物支架置入小型猪冠状动脉后具有良好的生物相容性。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-9212-4737(谭峥)

.jpg)
.jpg)