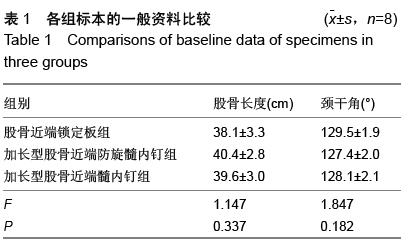
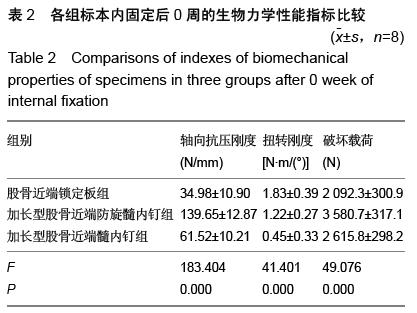
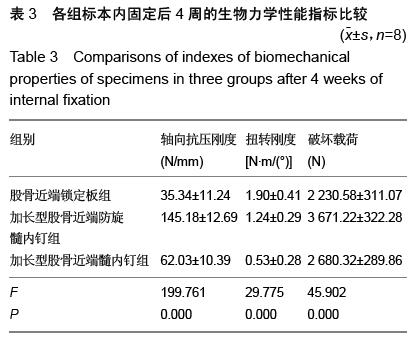
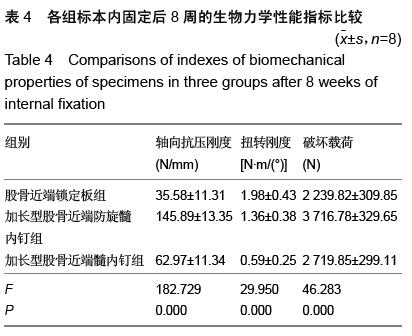
| [1] 王久清,黄昌林,杨雪迎,等.不同治疗方式在老年股骨粗隆间骨折中的对照分析[J].现代生物医学进展,2015,15(2): 287-290. [2] 朱新红,黄飞,陶德刚,等.股骨干骨折合并同侧股骨近端骨折的诊断和治疗[J].实用骨折杂志,2014,20(11): 1035-1037.[3] Park KT,Lee KB.Sequential subtrochanteric femoral fracture after atypical diaphyseal fracture in a long-term bisphosphonate user: a case report.Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2015;82(2):157-160.[4] 翟利锋,陈亿民,毕大卫,等.股骨粗隆下骨折的分型与手术治疗策略[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2014,29(8):766-768.[5] 曹启斌.股骨转子下骨折手术治疗及分型进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(10):906-908.[6] 樊国军,依里克,纳贝•加依吐尕尼,等.PFN与PFLP治疗股骨转子下骨折临床疗效研究[J].新疆医学,2014,44(9): 56-59.[7] Ma KL,Wang X,Luan FJ,et al.Proximal femoral nails antirotation, Gamma nails, and dynamic hip screws for fixation of intertrochanteric fractures of femur: A meta-analysis.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014; 100(8): 859-866.[8] 吴俊,商晓军,刘锦波,等.加长型PFNA治疗股骨粗隆周围骨折合并同侧股骨干骨折[J].医学研究杂志,2011,40(10): 122-124.[9] Bong MR,Patel V,Iesaka K,et al.Comparison of a sliding hip screw with a trochanteric lateral support plate to an intramedullary hip screw for fixation of unstable intertrochanteric hip fractures: a cadaver study. J Trauma. 2004;56(4):791-794.[10] 马健超,陈皓,赵贺,等.股骨干骨折合并同侧股骨颈骨折35例[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,34(15):4378-4379.[11] Juhasz K,Gajdacsi J,Molics B,et al.Predictors of 10-Year Mortality After Primary Femoral Neck Fracture In Elderly Patients.Value Health. 2015; 18(7): A638. [12] 杜长岭,马信龙,马剑雄,等.利用有限元分析股骨颈骨折内固定术后前倾角变化对股骨近端力学的影响[J].医用生物力学,2012,27(6):603-607,635.[13] Hak DJ,Mauffrey C,Hake M,et al.fractures: shaftandneckfemoralIpsilateral current diagnostic and treatment strategies.Orthopedics. 2015;38(4): 247-251. [14] 赵海生,徐耀增,王贵贤,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗股骨转子下骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(48): 8368-8373.[15] Song KS,Ramnani K,Cho CH,et al.Ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fracture in children: a report of two cases and a literature review.J Orthop Traumatol. 2013; 14(2):147-154.[16] Miedel R,Tornkvist H,Ponzer S,et al.Musculoskeletal function and quality of life in elderly patients after a subtrochanteric femoralfracture treated with a cephalomedullary nail.J Orthop Trauma. 2011;25(4): 208-213.[17] 马剑雄,王杰,杨阳,等.股骨转子下骨折治疗的研究进展[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2014,20(3):327-330.[18] 徐刚.不同角度螺旋固定股骨颈骨折并发转子下骨折风险的生物力学分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2007, 22(12):984-986.[19] Ozturkmen Y,Uzumcugil O,Sukur E,et al.The use of a cementless modular stem in the treatment of subtrochanteric femoral fractures in conjunction with ipsilateral coxarthrosis.Orthopedics. 2011;34(1):13.[20] 任雅春.不同固定方案治疗股骨转子下骨折疗效对比[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2015,23(6):51-53.[21] Birmingham P,McHale KA.Case reports: treatment of subtrochanteric and ipsilateral femoral neck fractures in an adult with osteopetrosis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(8):2002-2008.[22] 章年年,叶招明,朱仰义,等.双螺钉系统与3枚空心加压螺钉治疗股骨颈骨折的比较研究[J].中国骨伤,2013,26(7): 565-571.[23] 李山珠,赵宏谋,袁锋,等.加长螺旋刀片股骨抗旋髓内钉治疗股骨干合并同侧股骨颈骨折16例[J].中华创伤杂志, 2012,28(9):801-804.[24] Ricci WM,Gallagher B,Haidukewych GJ.Intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fractures:current concepts.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2009;17(5):296-305.[25] 王飞,蒋继亮,陈约东,等.股骨近端解剖型锁定钢板内固定治疗股骨粗隆下粉碎性骨折的临床观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2014,29(2):178-179.[26] Ozkan K,Turkmen i,Sahin A,et al.A biomechanical comparison of proximal femoral nails and locking proximal anatomic femoralplates in femoral fracture fixation: A study on synthetic bones.Indian J Orthop. 2015;49(3):347-351.[27] Guo Q,Shen Y,Zong Z,et al.Percutaneous compression plate versus proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in treating elderly patients with intertrochanteric fractures: a prospective randomized study.J Orthop Sci. 2013;18(6):977-986. [28] Wang WY,Liu L,Wang GL,et al. Ipsilateral basicervical femoral neck and shaft fractures treated with long proximal femoral nail antirotation or various plate combinations: comparative study. J Orthop Sci. 2010; 15(3):323-330.[29] Zhou F,Zhang ZS,Yang H,et al.Less invasive stabilization system (LISS) versus proximal femoral nail anti-rotation (PFNA) in treating proximal femoral fractures: a prospective randomized study.J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26(3):155-162.[30] Helin M,Pelissier A,Boyer P,et al.lengthening proximal femoral nail anti™ nail limit impactionDoes the fracture?A 115 case-control series. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(1):45-49.[31] 曾立军,谢京平,郭光宇,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗股骨转子下骨折的疗效分析[J].中外医学研究, 2015,13(3): 136-137.[32] 张庆林,冯彩燕,李江,等.加长型PFNA内固定治疗骨质疏松性股骨转子下骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2014,20(7): 644-647.[33] 李辉,胡跃,蒋玉权,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗股骨转子下骨折[J].临床军医杂志,2014,42(3):254-256,290.[34] 郝晓东,蒋攀峰,郑云龙,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗股骨转子下骨折临床观察[J].河南外科学杂志,2014,20(4): 18-20.[35] Gadegone W,Lokhande V,Salphale Y,et al. Long proximal femoral nail in ipsilateral fractures proximal femur and shaft of femur. Indian J Orthop. 2013;47(3): 272-277.[36] 罗加龙,王艇,张俊,等.股骨近端PFN及加长型PFN治疗股骨近端骨折的临床分析[J].求医问药,2013,11(2): 246-247.[37] 李仁斌,林炎斌,庄研,等.股骨颈合并同侧粗隆下骨折3种内固定方式的生物力学分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2015,30(2):133-135.[38] 王岩松,李宏彦,李玉前.普通型与加长型股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗股骨转子间骨折的比较[J].南通大学学报(医学版),2015,35(4):295-297.[39] Black SR,Kwon MS,Cherkashin AM,et al.Lengthening in Congenital Femoral Deficiency: A Comparison of Circular External Fixation and a Motorized Intramedullary Nail. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015; 97(17):1432-1440.[40] Pairon P,Ossendorf C,Kuhn S,et al.Intramedullary nailing after external fixation of the femur and tibia: a review of advantages and limits. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2015;41(1):25-38.[41] Turgut A,Kalenderer O,Gunayd?n B,et al.Fixation of intertrochanteric femur fractures using Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA) in the lateral decubitus position without a traction table. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2014;48(5):513-520. |
.jpg)