中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (3): 346-351.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.03.008
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
经骨形态发生蛋白7成骨预处理聚乳酸三维支架的体外培养
贝抗胜1,刘延晓2,熊英辉1,吴礼杨1,卢林俊1
- 贝抗胜,男,1953年生,浙江省宁波市人,汉族,1974年赣南医学院毕业,硕士,主任医师,主要从事骨科研究。
A three-dimensional polylactic acid scaffold pretreated with bone morphogenetic protein 7
Bei Kang-sheng1, Liu Yan-xiao2, Xiong Ying-hui1, Wu Li-yang1, Lu Lin-jun1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Yue Bei People’s Hospital, Shaoguan 512026, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Quzhou People’s Hospital, Quzhou 324000, Zhejiang Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
骨形态发生蛋白7:骨形态发生蛋白是目前已知最有效的促骨生长因子,有学者认为骨形态发生蛋白7是促进和诱导成骨分化的重要的细胞外信号分子,在通路中发挥着启动和调节的作用。骨形态发生蛋白7存在浓度-效应钟型曲线,适当浓度范围才能最有效发挥作用,骨形态发生蛋白7的优势局限于较低的浓度范围5-100 µg/L。
聚乳酸:是一种新型的生物降解材料,使用可再生的植物资源(如玉米)所提出的淀粉原料制成,具有良好的组织相容性和优异的机械性能。聚乳酸已被广泛应用于生物医药领域,作为手术缝合线、骨固定植入物、药物控释载体和组织工程支架应用于临床。
背景:为改善聚乳酸的细胞亲和性,前期实验在其表面加入骨形态发生蛋白7功能基团,制备了经骨形态发生蛋白成骨预处理的聚乳酸三维支架。
目的:验证经骨形态发生蛋白成骨预处理聚乳酸三维支架与骨膜来源细胞的相容性。
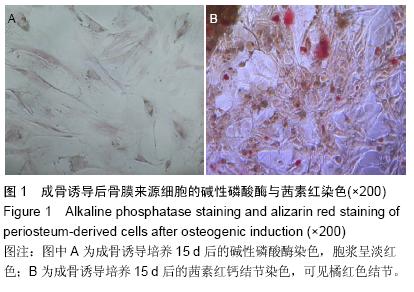
方法:取传至3代后成骨诱导分化的人骨膜来源细胞,实验组以1×109 L-1的细胞浓度接种于含聚乳酸支架的培养板内,聚乳酸支架预先经含骨形态发生蛋白7的成骨诱导培养液浸泡24 h;对照组直接以1×109 L-1的细胞浓度接种于培养板内。培养后1,3,5,7,9,11 d,采用CCK-8法检测细胞增殖能力;培养后3,6,9,12 d,电镜下观察细胞-支架复合体。
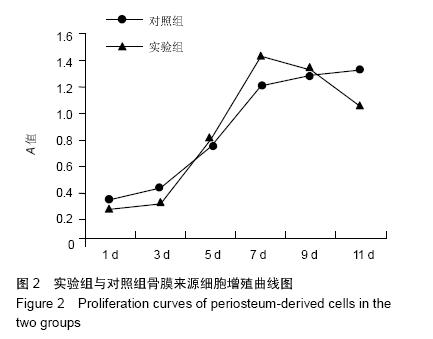
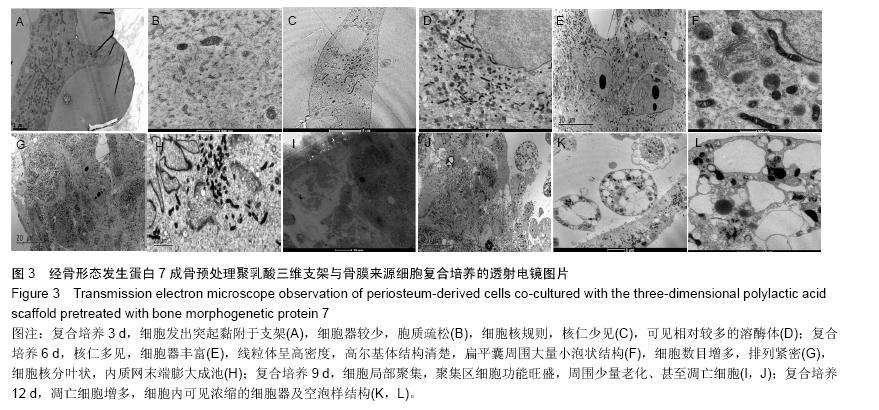
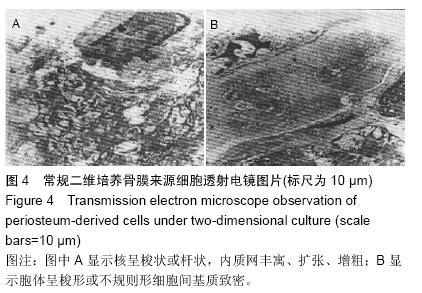
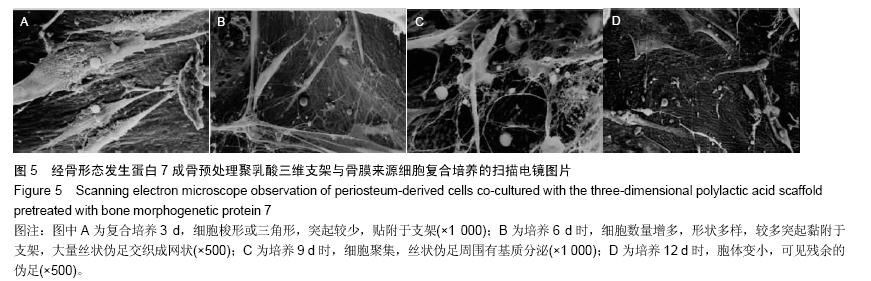
结果与结论:①细胞增殖结果:两组细胞生长曲线均呈“S”型,实验组对数生长期细胞增殖较快,平稳期细胞数目明显下降,对照组平稳期细胞数目继续上升。②透射电镜观察结果:复合培养3-6 d时,支架表面细胞黏附数量逐渐增多,细胞生物状态良好,细胞器旺盛,至第9天,开始出现细胞老化及凋亡。③扫描电镜观察结果:复合培养3-9 d时,支架表面细胞黏附数量逐渐增多,增殖旺盛,至12 d时见凋亡细胞。④结果表明,经骨形态发生蛋白成骨预处理聚乳酸三维支架具有良好的细胞相容性,其与细胞复合培养1周为较佳的体外复合培养时间。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-2511-2255(贝抗胜)
.jpg)