中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (2): 297-303.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.02.025
• 组织构建循证医学 evidence-based medicine in tissue construction • 上一篇
太极运动对脑卒中患者运动、情绪及生活质量影响的系统评价和Meta分析
覃 林1,韦 霞1,刘 琳2,朱 欢1
- 1广西民族师范学院体育与健康教育系,广西壮族自治区崇左市 532200;2上海体育学院运动科学学院,上海市 200438
Effectiveness of Tai Chi on movement, emotion and quality of life in patients with stroke: a Meta-analysis
Qin Lin1, Wei Xia1, Liu Li2, Zhu Huan1
- 1Department of Sports and Health Education, Guangxi Normal University for Nationalities, Chongzuo 532200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2School of Sports Science, Shanghai University of Sport, Shanghai 200438, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
太极运动的生理作用:①促进大脑中枢神经系统中各功能中枢之间的联络和协调,延长中枢神经兴奋过程和抑制过程的持续时间,增强周围神经传导功能,提高灵敏性。②增强自主神经系统功能,能提高副交感神经兴奋性,增强神经内分泌活动,提高免疫力。③能有效调节情感活动,提高心理素质。降低精神方面的应激阈值,发展理性思维、提高自控能力。④缓慢发展心肺功能,增强消化系统功能,提高内分泌活动。能有效降低血糖,提高血液中超氧化物岐化酶和过氧化氢酶的含量,它们是清除氧自由基的酶物质,这些酶物质的增多,就可以阻抗氧自由基对细胞的强氧化破坏作用,减少细胞的死亡和癌变。能使外周血液中免疫细胞数量增加。促进组织细胞的新陈代谢。⑤发展耐力,提高关节的柔韧性,能有效地减缓关节的生理退化过程,改善关节功能。
脑卒中:脑卒中又称“中风”、“脑血管意外”,是一种急性脑血管疾病,是由于脑部血管突然破裂或因血管阻塞导致血液不能流入大脑而引起脑组织损伤的一组疾病,包括缺血性和出血性卒中。
背景:太极运动可以放松患者受累肌肉,增强肌肉柔韧性和力量,促进脑卒中患者正常运动模式,抑制异常姿势和痉挛模式,提高患者运动控制能力,改善平衡功能。
目的:系统评价太极运动对脑卒中患者运动、情绪及生活质量的影响。
方法:计算机检索PubMed、EMbase、Web of Science、EBSCO、Google Scholar、中国知网、重庆维普和万方等数据库中关于太极运动对脑卒中患者平衡功能、步行能力、情绪状态和生活质量等指标康复效果的随机对照试验(RCT),检索时间均从建库至2015年7月1日,2名研究者依照纳入和排除标准独立筛选文献、提取资料和方法学质量评价后,采用RevMan 5.3软件进行Meta分析。
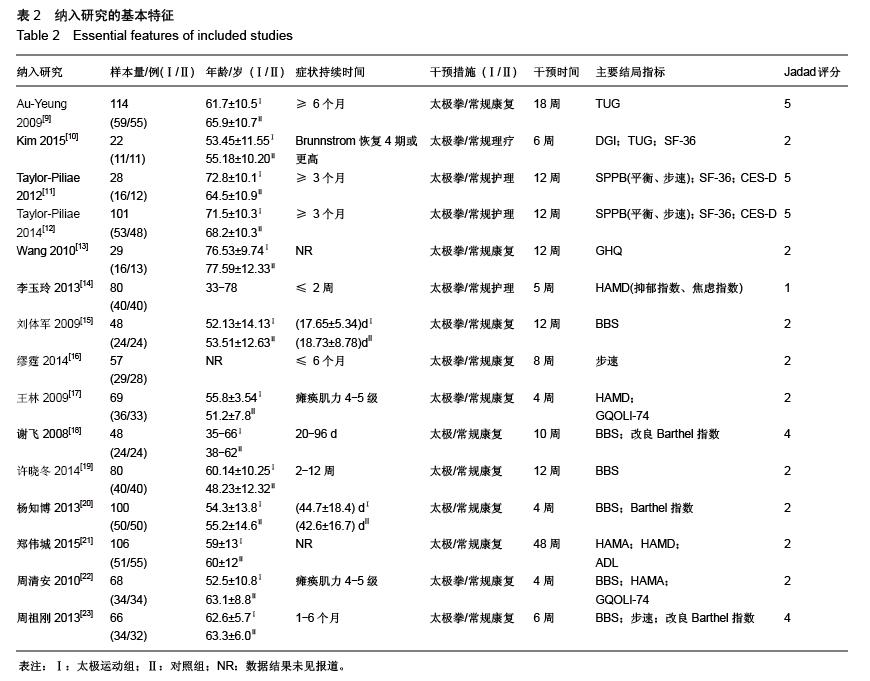
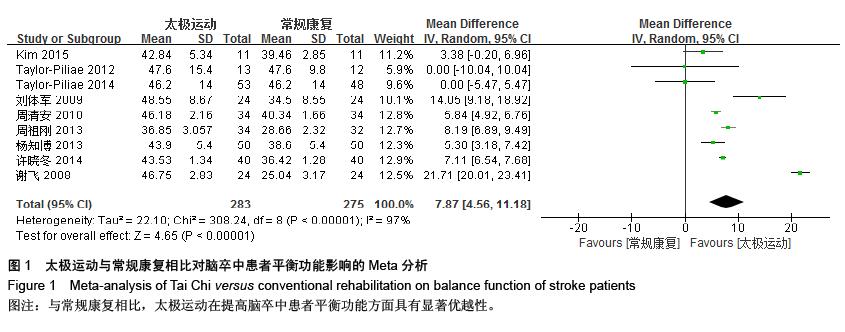
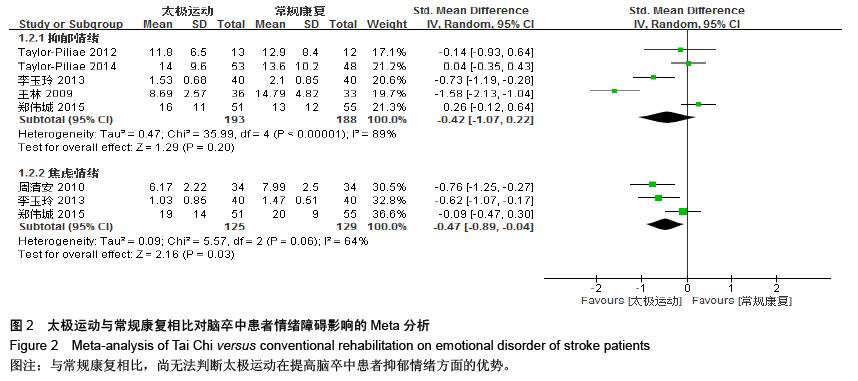
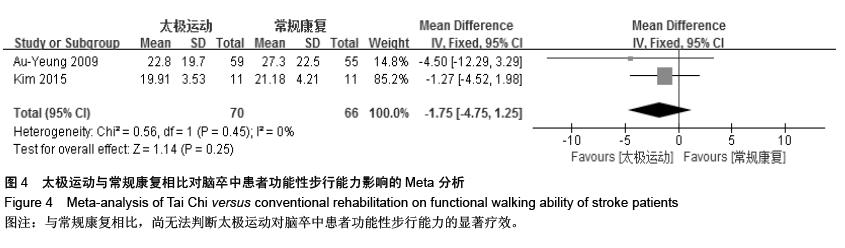
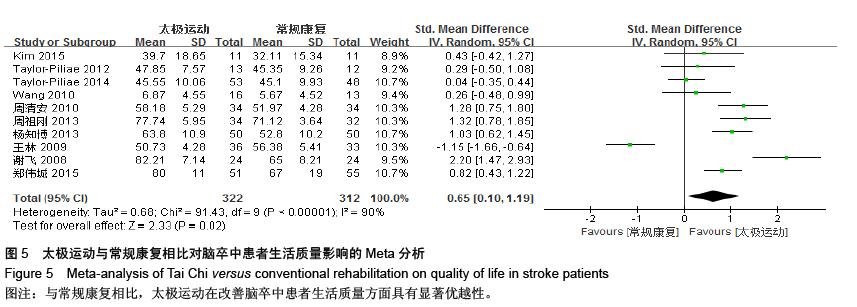
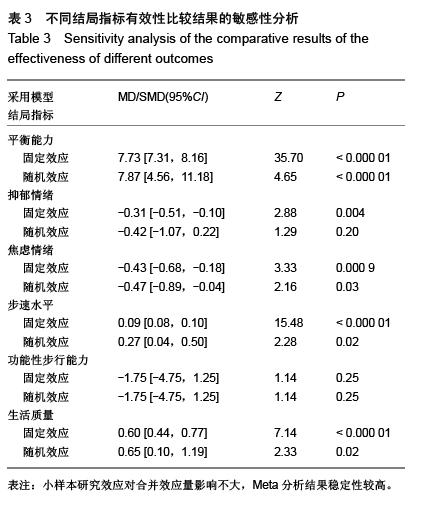
结果与结论:最终纳入15个RCT,共1 016例患者。Meta分析结果显示:太极运动在改善脑卒中患者平衡功能[MD=7.87,95%CI (4.56,11.18),P < 0.000 01]、步速[MD=0.27,95%CI(0.04,3.94),P=0.02]、焦虑情绪[SMD=-0.47, 95%CI(-0.89,-0.04),P=0.03]和生活质量方面[SMD=0.65,95%CI(0.10,1.19), P明显优于常规康复组,且差异均有显著性意义,而在功能性步行能力和抑郁情绪方面明显倾向于太极运动组,但差异无显著性意义。结果说明,太极运动在能够显著改善脑卒中患者平衡功能、步速水平、焦虑状态和生活质量,但在抑郁情绪和功能性步行能力等方面的优势性还需更多大样本、高质量的临床随机对照试验加以验证。
=0.02]
ORCID: 0000-0002-5856-0559(韦霞)
.jpg)