中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (2): 248-253.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.02.017
• 组织构建与生物活性因子 tissue construction and bioactive factors • 上一篇 下一篇
MicroRNA-491-5p调控基质金属蛋白酶9参与退变性腰椎侧凸的发病机制
王 磊1,李天旺1,刘建强2,刘晓宗3,王照国4,田 艳1,张永兴1,王 伟1
- 1解放军第252医院脊柱外科,河北省保定市 071000;2保定市骨科医院骨科,河北省保定市 071000;3保定市第一中心医院,河北省保定市 071000;4保定市阜平县医院骨科,河北省保定市 073200
MicroRNA-491-5p is involved in the pathogenesis of degenerative lumbar scoliosis by targeting matrix metalloproteinase 9
Wang Lei1, Li Tian-wang1, Liu Jian-qiang2, Liu Xiao-zong3, Wang Zhao-guo4, Tian Yan1, Zhang Yong-xing1, Wang Wei1
- 1Department of Spinal Surgery, the 252nd Hospital of PLA, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Baoding Orthopedics Hospital, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China; 3Baoding First Central Hospital, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China; 4Department of Orthopedics, Hospital of Fuping County, Baoding 073200, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
腰椎侧凸:指脊柱的一个或数个节段在冠状面上偏离身体中线向侧方弯曲,形成一个带有弧度的脊柱畸形,通常还伴有脊柱的旋转和矢状面上后突或前突的增加或减少,同时还有肋骨左右高低不等平、骨盆的旋转倾斜畸形和椎旁的韧带和肌肉的异常,它是一种症状或X射线体征,可由多种疾病引起。
基质金属蛋白酶:是一个大家族,因其需要Ca2+、Zn2+等金属离子作为辅助因子而得名。其家族成员具有相似的结构,一般由5个功能不同的结构域组成:①疏水信号肽序列。②前肽区,主要作用是保持酶原的稳定。当该区域被外源性酶切断后,基质金属蛋白酶酶原被激活。③催化活性区,有锌离子结合位点,对酶催化作用的发挥至关重要。④富含脯氨酸的铰链区。⑤羧基末端区,与酶的底物特异性有关。其中酶催化活性区和前肽区具有高度保守性。
背景:miRNAs广泛参与蛋白表达的调控,在机体的多种生理和病理过程中发挥重要的作用,但是目前对其在椎间盘退变中的表达谱及发挥的作用知之甚少。
目的:比较退变性腰椎侧凸患者与正常对照组椎间盘组织中miRNAs表达谱的差异,确定退变性腰椎侧凸特异性相关的miRNAs,并对其进行功能验证。
方法:对获取的退变性腰椎侧凸57例患者手术髓核组织和腰椎骨折42例患者正常髓核组织依次进行总RNA提取,其中,各取10例进行miRNA芯片筛查,挑选表达有差异的microRNA。随后,采用RT-qPCR技术对其进行验证。对表达显著差异的miRNA进行探究。进一步对其进行功能验证,确定其与Ⅱ型胶原表达的关系。运用Western与荧光素酶报告系统进一步确定靶基因。
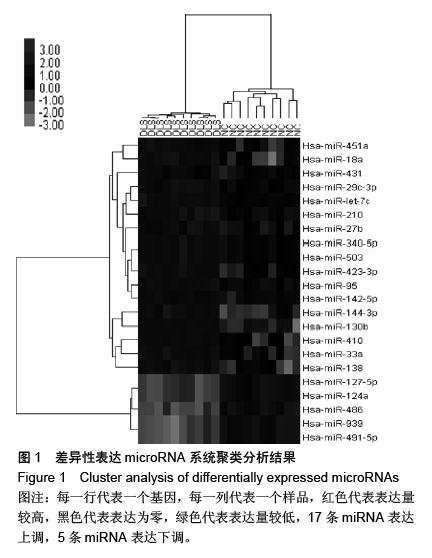
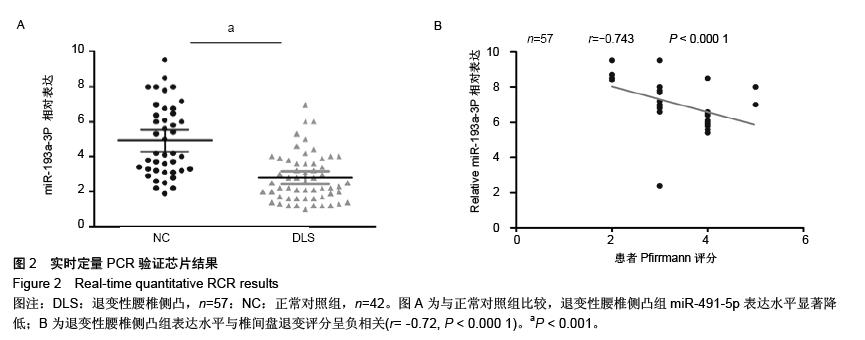
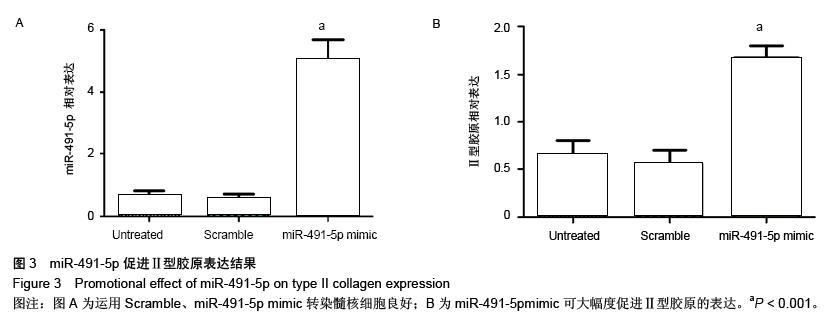
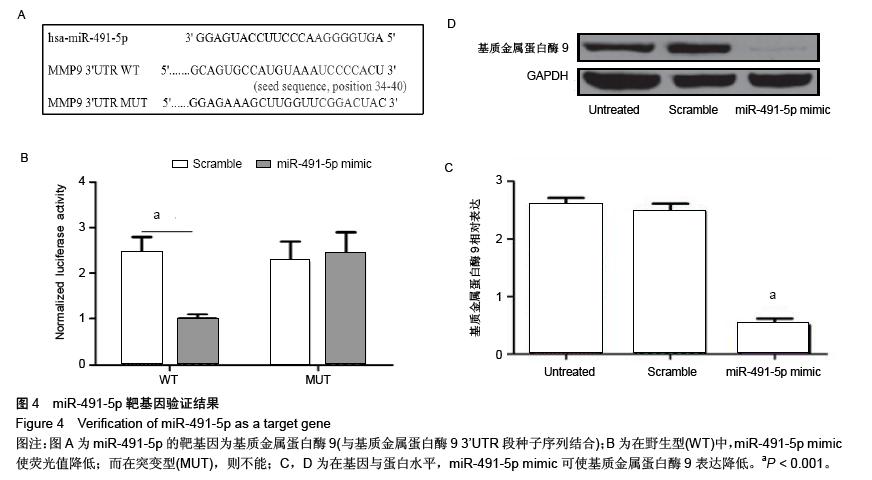
结果与结论:与正常对照相比,22条miRNA表达存在显著差异(17条表达 上调和5条表达下调)。随后进行RT-qPCR验证,与正常对照相比,miR-491-5p在退变性腰椎侧凸患者椎间盘组织中,表达显著下调。此外,miR-491-5p表达水平与椎间盘退变评分密切相关。高表达miR-491-5p促进Ⅱ型胶原表达。生物信息学软件证实,基质金属蛋白酶9为miR-491-5p理论上的靶基因。荧光素酶报告系统证实miR-491-5p影响基质金属蛋白酶9的表达。结果表明,下调的miR-491-5p通过调控基质金属蛋白酶9,导致椎间盘组织中Ⅱ型胶原的丢失,进而引起椎间盘退变及退变性腰椎侧凸;miR-491-5p可成为治疗退变性腰椎侧凸的一个新的治疗靶点。