| [1] 张海兵.纳米羟基磷灰石骨水泥翻修和强化椎弓根螺钉的生物力学研究[D].南华大学,2005.
[2] 刘达,伍红桦,郑伟,等.骨质疏松尸体腰椎中膨胀式椎弓根螺钉与骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉固定稳定性的比较研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014,24(7):638-642,643.
[3] Garo A,Arnoux PJ,Wagnac E, et al.Calibration of the mechanical properties in a finite element model of a lumbar vertebra under dynamic compression up to failure.Med Biol Eng Comput.2011;49(12):1371-1379.
[4] 刘达,康夏,郑伟,等.骨质疏松绵羊腰椎膨胀式椎弓根螺钉与骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉固定稳定性的动态比较研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014,24(8):747-751.
[5] 于滨生,郑召民,庄新明,等.不同椎弓根螺钉固定及骨水泥强化方法在骨质疏松骶骨上锚定强度的比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2009,19(12):927-930.
[6] 范海涛,申才良,董福龙,等.不同强化技术在骨质疏松椎体钉道的力学研究[J].安徽医科大学学报,2012,47(3):342-344.
[7] 张海兵,金大地,瞿东滨,等.骨水泥在骨质疏松椎体中强化和翻修椎弓根螺钉的生物力学研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2007, 25(5):587-589.
[8] 樊仕才,金大地,张忠民,等.骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉固定治疗老年退行性腰椎不稳的临床疗效分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2010, 20(9):741-744.
[9] Arai Y,Hirai T,Yoshii T,et al.A prospective comparative study of 2 minimally invasive decompression procedures for lumbar spinal canal stenosis: Unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression(ULBD) versus muscle-preserving interlaminar decompression(MILD). Spine. 2014;39(4):332-340.
[10] Tsutsui S,Kagotani R,Yamada H,et al.Can decompression surgery relieve low back pain in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis combined with degenerative lumbar scoliosis?Eur Spine J.2013;22(9):2010-2014.
[11] 樊友亮,吴一雄,胡辉东,等.经椎弓根动态稳定系统(Dynesys)与后路椎间融合治疗腰椎管狭窄症的临床比较研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(11):1016-1019.
[12] Barz T,Melloh M,Staub LP,et al.Increased intraoperative epidural pressure in lumbar spinal stenosis patients with a positive nerve root sedimentation sign.Eur Spine J.2014; 23(5):985-990.
[13] Wang Y,Bünger CE,Zhang Y,et al.Lowest instrumented vertebra selection in Lenke 3C and 6C scoliosis: What if we choose lumbar apical vertebra as distal fusion end?.Eur Spine J.2012;21(6):1053-1061.
[14] 代飞,刘瑶瑶,孙东,等.新型可注射骨水泥椎弓根螺钉与骨水泥钉道强化在治疗腰椎滑脱伴骨质疏松中的比较研究[J].脊柱外科杂志,2014,0(5):257-261.
[15] 高明暄,李旭升,任民,等.可注射磷酸钙骨水泥对不同骨质椎弓根螺钉的强化作用[J].实用骨科杂志,2013,19(12):1094-1097.
[16] Li H,Na W,Jiang Y,et al.Percutaneous nephrolithotomy versus ureteroscopic lithotomy for large (>15 mm) impacted upper ureteral stones in different locations: Is the upper border of the fourth lumbar vertebra a good indication for choice of management method?J Endourol. 2013;27(9):1120-1125.
[17] 李鹏,毛克亚,王岩,等.骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉在腰椎滑脱伴骨质疏松椎体中的临床应用[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2011,17(11): 961-963.
[18] 杨述华,傅德皓,刘昌胜,等.磷酸钙骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉对骨质疏松性椎体骨折的临床意义[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2003,11(23): 1616-1618.
[19] 于亮,蒋伟宇,赵刘军,等.骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉固定结合椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性胸腰段爆裂骨折[J].浙江中医药大学学报,2014,388):984-987.
[20] 吴李勇,陈少坚,凌广烽,等.空心带侧孔椎弓根螺钉灌注骨水泥强化技术治疗老年性胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J].颈腰痛杂志, 2014, 35(6): 423-426.
[21] 陈继良,王晓露,王旭,等.经椎弓根植骨联合骨水泥强化螺钉在骨质疏松椎体骨折的临床应用[J].吉林医学,2013,34(31):6442- 6444.
[22] 于滨生,郑召民,庄新明.不同椎弓根螺钉固定及骨水泥强化方法在骨质疏松骶骨上锚定强度的比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2009, 19(12):927-930.
[23] 朱科军,李松强.短节段椎弓根螺钉固定复位结合骨水泥伤椎强化治疗老年人胸腰椎爆裂骨折[J].浙江创伤外科, 2013,18(3): 354-355.
[24] 杨岱青.骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉内固定伤椎椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体骨折效果观察[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2013, 22(4):393-394.
[25] Lin T,Cai XZ,Shi MM,et al.In vitro and in vivo evaluation of vancomycin-loaded PMMA cement in combination with ultrasound and microbubbles-mediated ultrasound.Biomed Res Int.2015;2015:309739.
[26] Pflugmacher R,Bornemann R,Koch EM,et al.Comparison of clinical and radiological data in the treatment of patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures using radiofrequency kyphoplasty or balloon kyphoplasty.Z Orthop Unfall. 2012;150(1):56-61.
[27] 樊仕才,朱青安,王柏川,等.聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯强化对骨质疏松椎弓根螺钉固定的生物力学作用[J].中华骨科杂志,2001,21(2):93-96.
[28] 辛世樵.骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉治疗骨质疏松性椎体骨折的临床观察[J].航空航天医学杂志,2013,24(9):1081-1082.
[29] Güner MD, Tuncbilek S, Akan B,et al. Two cases with HSS/DRESS syndrome developing after prosthetic joint surgery: does vancomycin-laden bone cement play a role in this syndrome?BMJ Case Rep.2015;2015.pii: bcr2014207028. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2014-207028.
[30] 方永超,冯新民,陶玉平,等.骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉内固定伤椎椎体成形术治疗伴神经症状的骨质疏松性椎体骨折[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012,22(4):376-378.
[31] 张海兵,金大地,瞿东滨.骨水泥在骨质疏松椎体中强化和翻修椎弓根螺钉的生物力学研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2007,25(5): 587-589.
[32] 张东.骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉固定手术在老年退行性腰椎不稳治疗中的应用研究[J].成都医学院学报,2012,7(4):590-591.
|
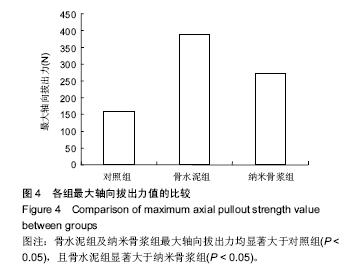
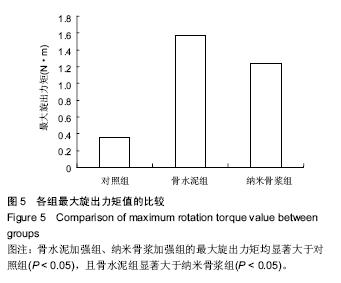
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)