| [1] 张龙城,胡万青,林文彪,等.rhBMP-2/CHA修复甲状软骨缺损的实验研究[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2014,43(3):316-320.
[2] 谭崇才,王文慧,陈剑飞,等.喉软骨支架缺损应用骨形态发生蛋白再生的实验研究[J].临床耳鼻咽喉科杂志,2002,16(9):477-480.
[3] 胡鹏,谭崇才,王文慧,等.犬甲状软骨缺损应用骨形态发生蛋白材料修复的实验研究[J].昆明医学院学报,2003,24(3):126-126.
[4] Hsu CM,Hsu CH,Yang MY,et al.Glottal insufficiency with thyroid cartilage implantation: Our experience in eight patients. Clin Otolaryngol.2012;37(5):399-405.
[5] 杨彩荣,梁传余,黄玮,等.同种脱细胞软骨基质与软骨细胞复合物修复兔甲状软骨缺损的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2005,19(6):478-480.
[6] 韩培,蒋垚,陈旸,等.重组骨形态发生蛋白-2结合软骨下钻孔治疗犬关节软骨全层缺损的实验研究[J].上海医学,2004,27(5): 327-330.
[7] 马洪斌,李运祥,王铭伦,等.腺病毒携带骨形态发生蛋白14基因转染脂肪干细胞修复损伤关节软骨?[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(1):54-60.
[8] 王鑫,李彦林,金耀峰,等.Ad-BMP-2、Ad-TGF-β3转染 BMSCs 复合 DBM构建软骨修复猪关节软骨缺损的研究[J].实用医学杂志,2014,30(18):2880-2882.
[9] 贺继平,苏晓云.转化生长因子β1与骨形态发生蛋白2联合修复膝关节软骨损伤[J].解剖学报,2011,42(4):537-541.
[10] 王卫东,殷力,王刚,等.骨形态发生蛋白-2基因的克隆及重组真核表达质粒的构建[J].中华显微外科杂志,2010,33(3): 229-231.
[11] 胡万青.骨形态发生蛋白复合物结合CAD/CAM技术原位修复喉甲状软骨缺损的实验研究[D].桂林医学院,2013.
[12] Stancoven BW, Lee J, Dixon DR, et al.Effect of bone morphogenetic protein-2, demineralized bone matrix and systemic parathyroid hormone (1-34) on local bone formation in a rat calvaria critical-size defect model. J Periodontal Res.2013;48(2):243-251.
[13] 胡晓梅,王俊锋,杨松涛,等.菟丝子总多糖对家兔全层关节软骨缺损Ⅱ型胶原表达的影响[J].实用医院临床杂志,2011,8(1): 23-25.
[14] 廖军义.Sox9增强骨形态发生蛋白2诱导的间充质干细胞成软骨分化抑制成骨分化[D].重庆医科大学,2014.
[15] 李红喜,张睿,李华哲,等.软骨细胞联合BMP/bFGF移植对关节软骨损伤的修复作用[J].现代生物医学进展,2013,13(22): 4237-4241.
[16] Fujita N, Matsushita T, Ishida K, et al.An analysis of bone regeneration at a segmental bone defect by controlled release of bone morphogenetic protein 2 from a biodegradable sponge composed of gelatin and β-tricalcium phosphate. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2012;6(4):291-298.
[17] 潘海涛,林欣,宋磊,等.骨形态发生蛋白/碱性成纤维细胞生长因子复合材料修复关节软骨缺损的实验研究[J].首都医科大学学报,2006,27(3):397-399.
[18] Rousseau M,Anderson DE,Lillich JD,et al.In vivo assessment of a multicomponent and nanostructural polymeric matrix as a delivery system for antimicrobials and bone morphogenetic protein-2 in a unicortical tibial defect in goats.Am J Vet Res. 2014;75(3):240-250.
[19] 李涛涛.重组EGFP慢病毒载体示踪转染的脐带间充质干细胞联合β-磷酸三钙移植治疗免股骨头缺损性坏死的研究[D].青岛大学,2011.
[20] 刘锋,姚剑平.β-TCP-透明质酸复合支架结合自体MSCs和rhBMP2修复兔关节软骨缺损的实验研究[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2008,2(5):547-553.
[21] Murakami N, Saito N, Horiuchi H, et al.Repair of segmental defects in rabbit humeri with titanium fiber mesh cylinders containing recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2) and a synthetic polymer. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;62(2):169-174.
[22] 朱国华,王建伟,田小武,等.骨软骨移植联合rhBMP -2/bFGF修复软骨缺损[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(21):1815-1819.
[23] 王富友.组织工程骨软骨仿生设计与初步构建[D].第三军医大学,2008.
[24] 束志勇,查振刚,汪炬,等.PLGA-Ⅱ型胶原复合rhBMP-2/bFGF修复兔膝关节软骨的缺损[J].暨南大学学报:自然科学与医学版,2009,30(2):180-184.
[25] Nakamura Y, Inloes JB, Katagiri T, et al.Chondrocyte-Specific MicroRNA-140 Regulates Endochondral Bone Development and Targets Dnpep To Modulate Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling.Molecular and Cellular Biology.2011; 31(14):3019-3028.
[26] 王晋平.计算机技术辅助构建复杂形状软骨的实验研究[D].第四军医大学,2007.
[27] 胡鹏.犬甲状软骨缺损应用骨形态发生蛋白材料修复的实验研究[D].昆明医学院,2001.
[28] 胡万青.骨形态发生蛋白复合物结合CAD/CAM技术原位修复喉甲状软骨缺损的实验研究[D].桂林医学院,2013.
[29] Mokbel N, Naaman N, Nohra J,et al.Healing patterns of critical size bony defects in rats after grafting with bone substitutes soaked in recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: Histological and histometric evaluation.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;51(6):545-549.
[30] 胡鹏,谭崇才,王文慧,等.犬甲状软骨缺损应用骨形态发生蛋白材料修复的实验研究[J].昆明医学院学报,2003,24(3): 126-126.
[31] 谭崇才,王文慧,陈剑飞,等.喉软骨支架缺损应用骨形态发生蛋白再生的实验研究[J].临床耳鼻咽喉科杂志,2002,16(9):477- 480.
[32] 胡鹏.犬甲状软骨缺损应用骨形态发生蛋白材料修复的实验研究[D].昆明医学院,2001. |
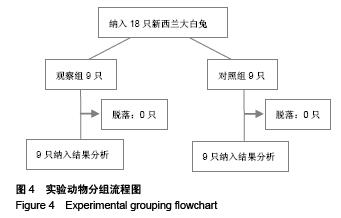
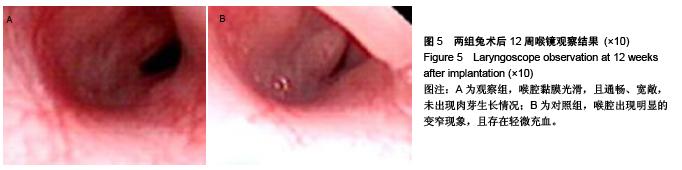
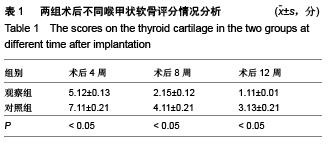
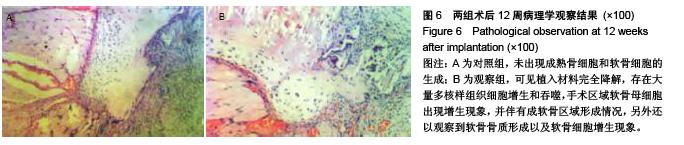
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
