中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (43): 6962-6965.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.43.014
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
胸腰椎体压缩性骨折行椎体后凸成形注射骨水泥的治疗时机
丁克海1,纪 标2,周其佳1,孙月柏1,左松球1,王庆刚1
- 1盐城市阜宁县人民医院骨科,江苏省盐城市 224400;2南通医学院第四附属医院(盐城市第一人民医院)骨科,江苏省南通市 224000
Treatment timing for kyphoplasty with bone cement injection in patients with thoracolumbar vertebral compression fractures
Ding Ke-hai1, Ji Biao2, Zhou Qi-jia1, Sun Yue-bai1, Zuo Song-qiu1, Wang Qing-gang1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Jiangsu Funing People’s Hospital, Yancheng 224400, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, the Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Nantong Medical College, Nantong 224000, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
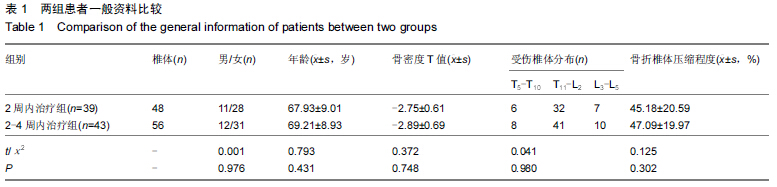
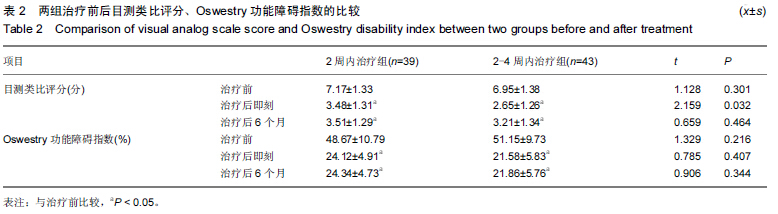
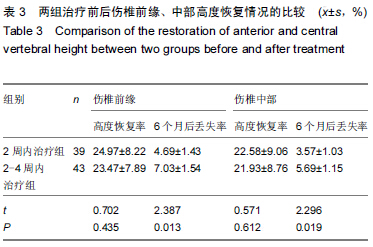
背景:相关研究表明,椎体后凸成形注射骨水泥治疗后椎体高度的恢复与受伤时间密切相关,不同时间的手术对患者术后并发症的发生情况也有着重要影响。 目的:比较胸腰椎体压缩性骨折2周内及2-4周期间行经皮椎体后凸成形注射骨水泥治疗的临床疗效,探讨经皮椎体后凸成形术的最佳手术时机。 方法:纳入82例胸腰椎骨折患者,年龄55-85岁,其中39例于伤后2周内进行经皮椎体后凸成形注射骨水泥治疗,另43例于伤后2-4周期间进行经皮椎体后凸成形注射骨水泥治疗。比较两组治疗后的目测类比评分、伤椎前缘和中部高度恢复情况及伤椎骨水注射量和渗漏情况;治疗后6个月,采用Oswestry功能障碍指数评估两组患者日常活动功能。 结果与结论:两组治疗后即刻及6个月的目测类比评分和Oswestry功能障碍指数均低于治疗术前(P < 0.05),2周内治疗组治疗后即刻的目测类比评分高于2-4周内治疗组(P < 0.05)。两组治疗后6个月的伤椎前缘和中部高度恢复率比较差异无显著性意义,但2周内治疗组伤椎前缘和中部高度丢失率低于2-4周内治疗组(P < 0.05)。两组骨水泥注入量与骨水泥渗漏率比较差异无显著性意义。表明2周内行经皮椎体后凸成形注射骨水泥治疗后疼痛明显,但对近期椎体高度丢失率影响较小,因此可作为治疗胸腰椎压缩性骨折的优选治疗时机。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程