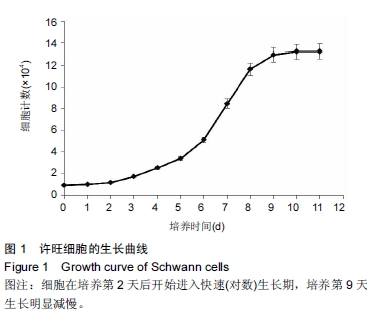
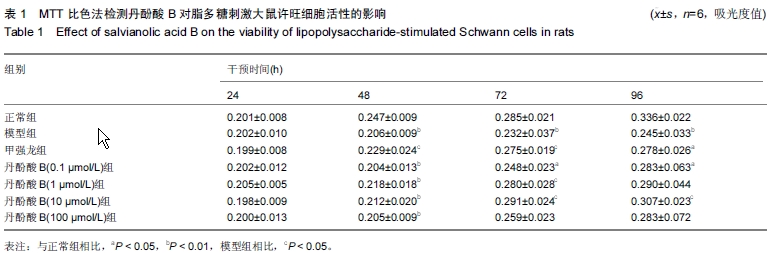
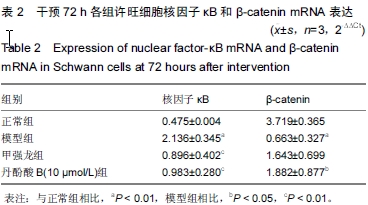
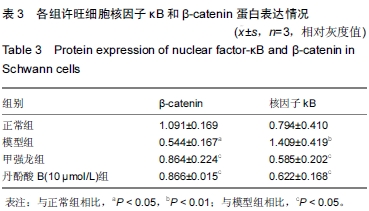
| [1] Stephan K, Huber S, Haberle S, et al. Spinal cord injury-incidence, prognosis, and outcome: an analysis of the Trauma Register DGU. Spine J. 2015;15(9):1994-2001.
[2] Jazayeri SB, Beygi S, Shokraneh F, et al. Incidence of traumatic spinal cord injury worldwide: a systematic review. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(5):905-918.
[3] Ydens E, Lornet G, Smits V, et al. The neuroinflammatory role of Schwann cells in disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2013;55:95-103.
[4] Terenghi G. Peripheral nerve regeneration and neurotrophic factors. J Anat. 1999;194(Pt 1):1-14.
[5] Fawcett JW, Asher RA. The glial scar and central nervous system repair. Brain Res Bull. 1999;49(6):377-391.
[6] Richner M, Ulrichsen M, Elmegaard SL, et al. Peripheral nerve injury modulates neurotrophin signaling in the peripheral and central nervous system. Mol Neurobiol. 2014; 50(3):945-970.
[7] Grigoryan T, Birchmeier W. Molecular signaling mechanisms of axon-glia communication in the peripheral nervous system. Bioessays. 2015;37(5):502-513.
[8] 时素华,李志刚,秦丽娜,等.脊髓损伤相关信号通路及中医药治疗研究[J].北京中医药,2014,33(4):308-310.
[9] 吴俊哲,王伟群,曾元桂,等.中医药治疗脊髓损伤及骨质松疏的研究进展[J].中药材,2014,37(9):1699-1702.
[10] 赵先,王婧雯,陆杨,等.丹酚酸B药理作用的研究进展[J].西北药学杂志,2015,30(1):107-110.
[11] 马萌萌,郭虹,张晗,等.丹酚酸B对脑损伤神经细胞的保护作用[J].天津中医药大学学报,2015,34(1):55-58.
[12] 杨春壮,刘长发,杨春佳.丹参注射液治疗急性脊髓损伤疗效观察[J].中医药信息,2003,20(6):36.
[13] 侯建雄,马海燕,李莉.前后路联合手术配合丹参注射液治疗颈椎骨折伴脊髓损伤临床观察[J].河北医药,2013,35(12):1872-1874.
[14] Shu T, Pang M, Rong L, et al. Protective effects and mechanisms of salvianolic acid B against H(2)O(2)-induced injury in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural stem cells. Neurochem Res. 2015;40(6):1133-1143.
[15] 荀翀.丹酚酸B在脊髓损伤中的作用及其相关机制的实验研究[D].大连:大连医科大学,2014.
[16] Wang Y, Jiang YF, Huang QF, et al. Neuroprotective effects of salvianolic acid B against oxygen-glucose deprivation/ reperfusion damage in primary rat cortical neurons. Chin Med J (Engl). 2010;123(24):3612-3619.
[17] Xun C, Hu Y, Lu M, et al. Study of effect of salvianolic acid B on motor function recovery in rats with spinal cord injury. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:931850.
[18] Tao YY, Wang QL, Shen L, et al. Salvianolic acid B inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation through transforming growth factor beta-1 signal transduction pathway in vivo and in vitro. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2013;238(11):1284-1296.
[19] 谭志强.甲强龙冲击疗法对急性颈脊髓损伤的临床研究[J].中国医学创新,2014,11(34):73-76.
[20] Costa DD, Beghi E, Carignano P, et al. Tolerability and efficacy of erythropoietin (EPO) treatment in traumatic spinal cord injury: a preliminary randomized comparative trial vs. methylprednisolone (MP). Neurol Sci. 2015;36(9):1567-1574.
[21] 朱庄臣,焦伟,蔡国栋,等.大剂量甲强龙治疗急性脊髓损伤后早期并发症的研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(16):1454-1457.
[22] 周孝斌,李志忠,孙国栋.许旺细胞在脊髓损伤中的研究进展[J].海南医学,2014,25(7):1004-1007.
[23] Cameron AA, Vansant G, Wu W, et al. Identification of reciprocally regulated gene modules in regenerating dorsal root ganglion neurons and activated peripheral or central nervous system glia. J Cell Biochem. 2003;88(5):970-985.
[24] Sun L, Pan J, Peng Y, et al. Anabolic steroids reduce spinal cord injury-related bone loss in rats associated with increased Wnt signaling. J Spinal Cord Med. 2013;36(6):616-622.
[25] Briona LK, Poulain FE, Mosimann C, et al. Wnt/ss-catenin signaling is required for radial glial neurogenesis following spinal cord injury. Dev Biol. 2015;403(1):15-21.
[26] 梁新军,吴燕峰,唐勇,等.大鼠脊髓损伤后Wnt信号分子的表达变化[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2009,19(12):931-934.
[27] 李雪鹏.脊髓损伤后肌成束蛋白(FSCN1)的表达与功能分析[D].长春:吉林大学,2014.
[28] 韦竑宇,梁立.他莫昔芬对大鼠脊髓损伤后炎性反应及细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国医药导报,2014,11(34):23-26.
[29] 陈凯,张俐.丹参及其制剂对脊髓损伤的保护作用及机制研究概况[J].中华中医药杂志,2012,27(11):2887-2890.
[30] 周秀梅,陈龙,邵一叶,等.microRNA-146a在LPS诱导的大鼠许旺细胞损伤模型中的表达[J].中国临床医学,2015,22(3):288-290.
[31] Witcher KG, Eiferman DS, Godbout JP. Priming the Inflammatory Pump of the CNS after Traumatic Brain Injury. Trends Neurosci. 2015;38(10):609-620.
[32] Lee DH, Steinacker P, Seubert S, et al. Role of glial 14-3-3 gamma protein in autoimmune demyelination. J Neuroinflammation. 2015;12(1):187.
[33] Alkabie S, Boileau AJ. The role of therapeutic hypothermia after traumatic spinal cord injury-a systematic review. World Neurosurg. 2015.
[34] Kabu S, Gao Y, Kwon BK, et al. Drug delivery, cell-based therapies, and tissue engineering approaches for spinal cord injury. J Control Release. 2015.
[35] Sanna MD, Stark H, Lucarini L, et al. Histamine H4 receptor activation alleviates neuropathic pain through differential regulation of ERK, JNK and P38 MAPK phosphorylation. Pain. 2015.
[36] Madathil SK, Saatman KE. IGF-1/IGF-R Signaling in Traumatic Brain Injury: Impact on Cell Survival, Neurogenesis, and Behavioral Outcome. In: Kobeissy FH, editor. Brain Neurotrauma: Molecular, Neuropsychological, and Rehabilitation Aspects. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press. 2015.
[37] Zhang B, Bailey WM, Braun KJ, et al. Age decreases macrophage IL-10 expression: Implications for functional recovery and tissue repair in spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2015;273:83-91.
[38] Xu J, E XQ, Liu HY, et al. Angelica Sinensis attenuates inflammatory reaction in experimental rat models having spinal cord injury. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(6):6779-6785.
[39] Alawieh A, Sabra M, Sabra Z, et al. Molecular Architecture of Spinal Cord Injury Protein Interaction Network. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0135024.
[40] Bastien D, Bellver Landete V, et al. IL-1α Gene Deletion Protects Oligodendrocytes after Spinal Cord Injury through Upregulation of the Survival Factor Tox3. J Neurosci. 2015; 35(30):10715-10730.
[41] Wang J, Pearse DD. Therapeutic hypothermia in spinal cord injury: the status of its use and open questions. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(8):16848-16879.
[42] Quinzaños-Fresnedo J, Sahagún-Olmos RC. Micro RNA and its role in the pathophysiology of spinal cord injury-a further step towards neuroregenerative medicine. Cir Cir. 2015; 83(5):442-447.
[43] Ansari MA. Temporal profile of M1 and M2 responses in the hippocampus following early 24h of neurotrauma. J Neurol Sci. 2015;357(1-2):41-49.
[44] Impellizzeri D, Ahmad A, Di Paola R, et al. Role of Toll like receptor 4 signaling pathway in the secondary damage induced by experimental spinal cord injury. Immunobiology. 2015;220(9):1039-1049.
[45] Guo L, Quan ZX, Zhao ZH, et al. Effects of musk ketone on nerve recovery after spinal cord injury. Genet Mol Res. 2015; 14(2):2958-2963.
[46] Goldshmit Y, Kanner S, Zacs M, et al. Rapamycin increases neuronal survival, reduces inflammation and astrocyte proliferation after spinal cord injury. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2015; 68:82-91. |