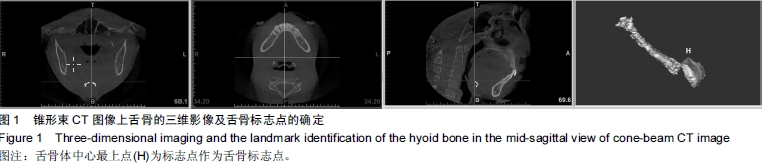
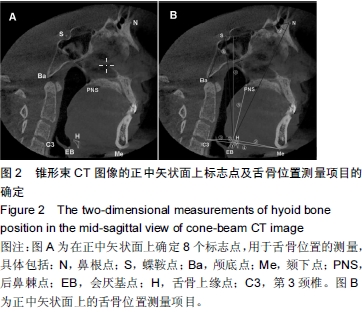
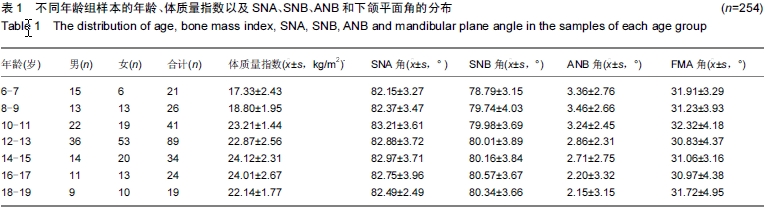
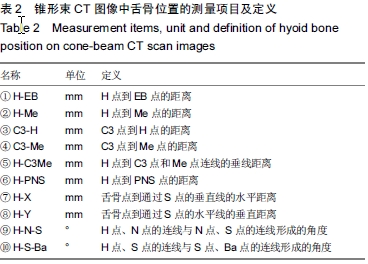
| [1] Zheng L, Jahn J, Vasavada AN. Sagittal plane kinematics of the adult hyoid bone. J Biomech.2012; 45(3): 531-536.
[2] Sheng CM, Lin LH, Su Y, et al. Developmental changes in pharyngeal airway depth and hyoid bone position from childhood to young adulthood. Angle Orthod 2009;79:484-490.
[3] Lin YC, Lin HC, Tsai HH. Changes in the pharyngeal airway and position of the hyoid bone after treatment with a modified bionator in growing patients with retrognathia. J Clin Exp Med. 2011;3:93-98.
[4] Aboudara C, Hatcher D, Nielsen I, et al. A three-dimensional evaluation of the upper airway in adolescents. Orthod Craniofac Res.2003;6:173-175.
[5] Hodges RJ, Atchison KA, White SC. Impact of cone-beam computed tomography on orthodontic diagnosis and treatment planning. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2013; 143:665-674.
[6] Yamashina A, Tanimoto K, Sutthiprapaporn P, et al. The reliability of computed tomography (CT) values and dimensional measurements of the oropharyngeal region using cone beam CT: comparison with multidetector CT. Dentomaxillofac Rad.2008;37:245-251.
[7] Lenza M, Lenza MM, Dalstra M, et al. An analysis of different approaches to the assessment of upper airway morphology: a CBCT study. Orthod Craniofac Res.2010;13:96-105.
[8] Ghoneima A, Kula K. Accuracy and reliability of cone-beam computed tomography for airway volume analysis. Eur J Orthod.2013;35(2):256-261.
[9] Souza KR, Oltramari-Navarro PV, Navarro Rde L, et al. Reliability of a method to conduct upper airway analysis in cone-beam computed tomography. Braz Oral Res.2013; 27(1):48-54.
[10] Baumgaertel S, Palomo JM, Palomo L, et al. Reliability and accuracy of cone-beam computed tomography dental measurements.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.2009; 136(1): 19-25; discussion 25-28.
[11] Tso HH, Lee JS, Huang JC, et al. Evaluation of the human airway using cone-beam computerized tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2009;108: 768-776.
[12] Guijarro-Martínez R, Swennen GR. Three-dimensional cone beam computed tomography definition of the anatomical subregions of the upper airway: a validation study.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;42(9):1140-1149.
[13] 张明烨,李永明,陈金武,等.骨性Ⅰ类不同垂直骨面型成人上气道的三维测量分析[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2013, 29(2): 209-213.
[14] 傅民魁.口腔正畸学[M]. 6版,北京:人民卫生出版社, 2012:85-87.
[15] 中国肥胖问题工作组.中国学龄儿童青少年超重、肥胖筛查体重指数值分类标准[J].中华流行病学杂志, 2004, 25(2):97-102.
[16] Kim MA, Kim BR, Youn JK, et al. Head posture and pharyngeal airway volume changes after bimaxillary surgery for mandibular prognathism, J Craniomaxillofac Surg.2014; 42(5):531-535.
[17] Wang RY, Han M, Liu H, et al. Establishment of reference mandibular plane for anterior alveolar morphology evaluation using cone beam computed tomography. J Zhejiang Univ-Sc B 2012;13(11):942-947.
[18] 王松,蒋英英,郝建忠. 锥形束CT评价直立体位下上气道正常值:山东地区6-19岁人群测量分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(7):1143-1148
[19] Jiang YY, Xu X, Su HL, et al. Gender-related difference in the upper airway dimensions and hyoid bone position in Chinese Han children and adolescents aged 6-18 years using cone beam computed tomography. Acta Odontol Scand.2015; 73(5):391-400.
[20] Kim MA, Kim BR, Choi JY, et al. Three-dimensional changes of the hyoid bone and airway volumes related to its relationship with horizontal anatomic planes after bimaxillary surgery in skeletal Class Ⅲ patients. Angle Orthod.2013;83(4):623-629.
[21] 王雷,韩培辉,李永明,等.骨性Ⅲ类错牙合患者双颌手术后鼻咽及口咽部气道及其周围软硬组织的变化[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2012,28(3):333-337.
[22] Li YM, Liu JL, Zhao JL, et al. Morphological changes in the pharyngeal airway of female skeletal class Ⅲ patients following bimaxillary surgery: a cone beam computed tomography evaluation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2014; 43(7):862-867.
[23] Shin JH, Kim MA, Park IY, et al. A 2-year follow-up of changes after bimaxillary surgery in patients with mandibular prognathism: 3-dimensional analysis of pharyngeal airway volume and hyoid bone position. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015; 73(2):340.e1-9.
[24] Panou E, Motro M, Ate? M, et al. Dimensional changes of maxillary sinuses and pharyngeal airway in Class Ⅲ patients undergoing bimaxillary orthognathic surgery. Angle Orthod 2013;85(2):824-831.
[25] Hong JS, Park YH, Kim YJ, et al. Three-dimensional changes in pharyngeal airway in skeletal class Ⅲ patients undergoing orthognathic surgery.J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011;69: e401-e408.
[26] Lee Y, Chun YS, Kang N, et al. Volumetric Changes in the Upper Airway After Bimaxillary Surgery for Skeletal Class Ⅲ Malocclusions: A Case Series Study Using 3-Dimensional Cone-Beam Computed Tomography. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012;70(12):2867-2875.
[27] Lee JY, Kim YI, Hwang DS, et al. Effect of maxillary setback movement on upper airway in patients with class Ⅲ skeletal deformities: cone beam computed tomographic evaluation. J Craniofac Surg.2013;24(2):387-391.
[28] 陈科名,杨崇实,邓锋.不同矢状骨面型错颌畸形患者气道大小形态的CBCT研究[J].口腔医学研究, 2012,28(1):54-57.
[29] Chiang CC, Jeffres MN, Miller A, et al. Three- dimensional airway evaluation in 387 subjects from one university orthodontic clinic using cone beam computed tomography. Angle Orthod 2012; 82:985-992.
[30] 曾祥龙, 唐志慧. 矢状骨面型与上气道形态和舌骨位置关系的研究[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志, 2004, 18( 3): 231-234.
[31] 高太智,魏琳,郭泾. 济南地区儿童上气道及舌骨位置正常参考值的研究[J]. 广东牙病防治, 2010,18(11):517-520.
[32] 郭涛,丁寅.正常骨面型儿童、成人上气道形态的X线头影测量分析[J].北京口腔医学, 2006, 14(4):247-250.
[33] 郭涛,丁寅.正常骨面型儿童、成人舌骨位置的X线头影测量分析[J]. 口腔医学, 2007,27(1):29-31.
[34] 唐志慧,曾祥龙.恒牙早期正常骨面型青少年上气道形态和舌骨位置的X线头影测量研究[J].北京大学学报:医学版2002,34(2): 140-143.
[35] Alves M Jr, Baratieri C, Nojima LI, et al. Three-dimensional assessment of pharyngeal airway in nasal-and mouth- breathing children.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;75(9): 1195-1199. |