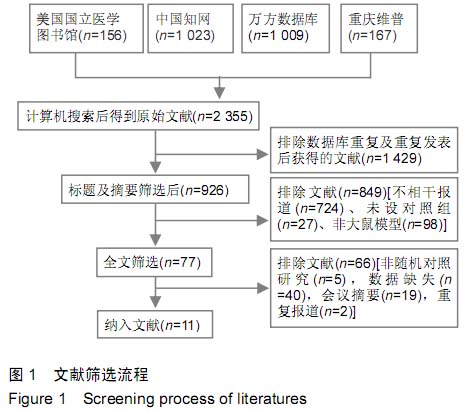
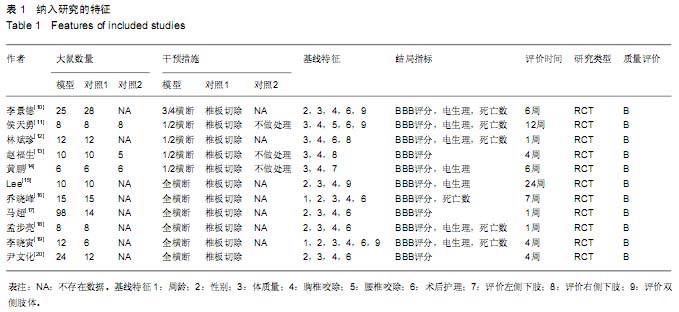
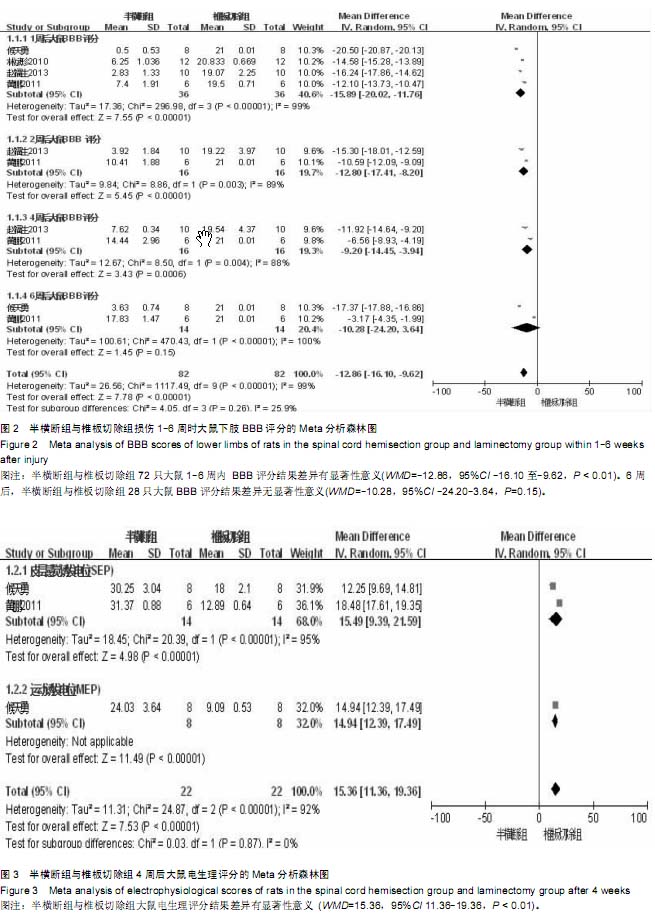
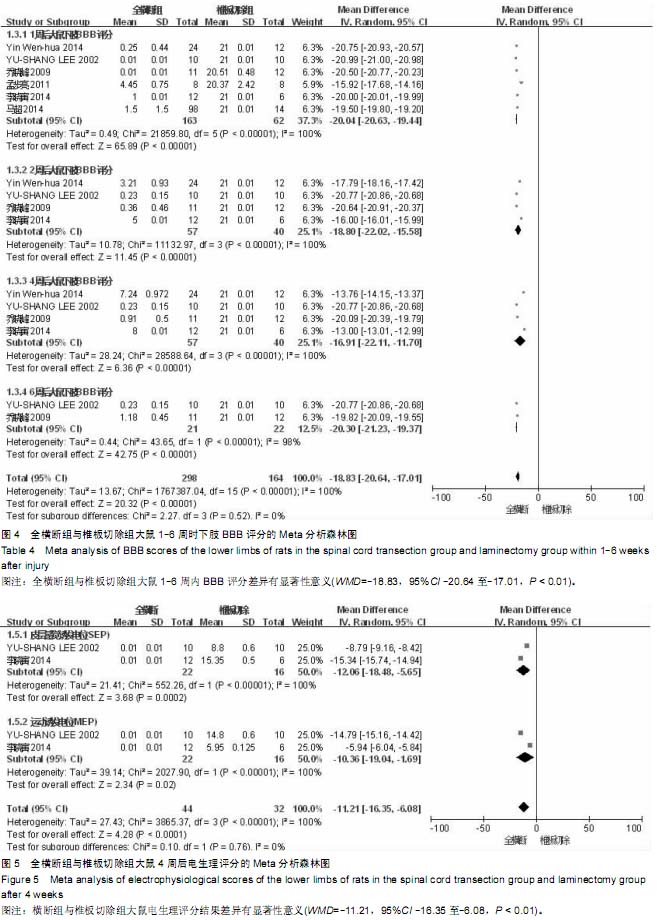
| [1] Zhang N, Fang M, Chen H, et al. Evaluation of spinal cord injury animal models. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(22):2008- 2012.
[2] Rodicio MC, Barreiro-Iglesias A. Lampreys as an animal model in regeneration studies after spinal cord injury. Rev Neurol. 2012;55(3):157-166.
[3] Oakden W, Kwiecien JM, O'Reilly MA, et al. A non-surgical model of cervical spinal cord injury induced with focused ultrasound and microbubbles. J Neurosci Methods. 2014; 235:92-100.
[4] Min SH, Lee SH, Shim H, et al. Development of complete thoracic spinal cord transection model in rats for delayed transplantation of stem cells. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36(3):E155-163.
[5] Dietz V, Curt A. Translating preclinical approaches into human application. Handb Clin Neurol. 2012;109:399-409.
[6] Saruhashi Y, Young W. Effect of mianserin on locomotory function after thoracic spinal cord hemisection in rats. Exp Neurol. 1994;129(2):207-216.
[7] Darian-Smith C, Tan A, Edwards S. Comparing thalamocortical and corticothalamic microstructure and spatial reciprocity in the macaque ventral posterolateral nucleus (VPLc) and medial pulvinar. J Comp Neurol. 1999;410(2): 211-234.
[8] Rouleau P, Guertin PA. A valuable animal model of spinal cord injury to study motor dysfunctions, comorbid conditions, and aging associated diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(24): 4437-4447.
[9] 祖波,尹宗生.机械性脊髓损伤模型的建立及其评价[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(12):151-153.
[10] 李景德,卢培刚.脊髓3/4横断伤动物模型的建立及其电生理评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(2):257-260.
[11] 侯天勇,伍亚民,李强,等.大鼠脊髓半切块状缺损模型的建立及科学性评估[J].创伤外科杂志,2006,8(4):362-365.
[12] 林斌珍,刘文革.大鼠T7脊髓半横切损伤模型的建立及饲养护理[J].福建医药杂志,2010,32(1):82-86.
[13] 赵富生,武庚,武杨,等.大鼠脊髓楔型半切空洞模型的建立及评估[J].实验动物科学,2013,30(4):13-17.
[14] 黄鹏,余瑛,王永堂,等.大鼠脊髓半横切损伤动物模型的建立与神经功能评价[J].实用医学杂志,2011,27(6):954-956.
[15] Lee YS, Hsiao I, Lin VW. Peripheral nerve grafts and aFGF restore partial hindlimb function in adult paraplegic rats. J Neurotrauma. 2002;19(10):1203-1216.
[16] 乔晓峰,杨建华,朱光宇,等.脊髓损伤模型的制备及其评价[J].中国全科医学,2009,12(14):1279-1281.
[17] 马超,徐震,王卓强,等.脊髓全横断模型大鼠损伤区白细胞介素17的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(18):2824-2829.
[18] 孟步亮,巴迎春,宋士娜,等.脊髓全横断大鼠模型的构建[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(7):1215-1218.
[19] 李晓寅,陈旭义,涂悦,等.精确显微技术条件下构建脊髓损伤模型的脊髓离断状态[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(27): 4282-4286.
[20] 尹文化,雷英,马国栋,等.脊髓全横断模型大鼠的行为学与病理学对照[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(36):5847-5854.
[21] Han Q, Cao C, Ding Y, et al. Plasticity of motor network and function in the absence of corticospinal projection.Exp Neurol. 2015; 267:194-208.
[22] Alastrue-Agudo A, Erceg S, Cases-Villar M, et al. Experimental cell transplantation for traumatic spinal cord injury regeneration: intramedullar or intrathecal administration. Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1210:23-35.
[23] Penha EM, Aguiar PH, Barrouin-Melo SM, et al. Clinical neurofunctional rehabilitation of a cat with spinal cord injury after hemilaminectomy and autologous stem cell transplantation. Int J Stem Cells. 2012;5(2):146-150.
[24] Ramer LM, Ramer MS, Bradbury EJ. Restoring function after spinal cord injury: towards clinical translation of experimental strategies. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13(12):1241-1256.
[25] Young W. Spinal cord regeneration. Cell Transplant. 2014; 23(4-5):573-611.
[26] Tabakow P, Raisman G, Fortuna W, et al. Functional regeneration of supraspinal connections in a patient with transected spinal cord following transplantation of bulbar olfactory ensheathing cells with peripheral nerve bridging. Cell Transplant. 2014;23(12):1631-1655.
[27] Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC, et al. MASCIS evaluation of open field locomotor scores: effects of experience and teamwork on reliability. Multicenter Animal Spinal Cord Injury Study. J Neurotrauma. 1996;13(7): 343-359.
[28] Jazayeri SB, Firouzi M, Abdollah Zadegan S, et al. The effect of timing of decompression on neurologic recovery and histopathologic findings after spinal cord compression in a rat model. Acta Med Iran. 2013;51(7):431-437.
[29] Cloud BA, Ball BG, Chen BK, et al. Hemisection spinal cord injury in rat: the value of intraoperative somatosensory evoked potential monitoring. J Neurosci Methods. 2012; 211(2): 179-184.
[30] 闫慧博,金大地,鲁凯伍,等.稳定性大鼠脊髓全横断模型的建立[J].实验动物科学与管理,2000,17(4):55-56. |