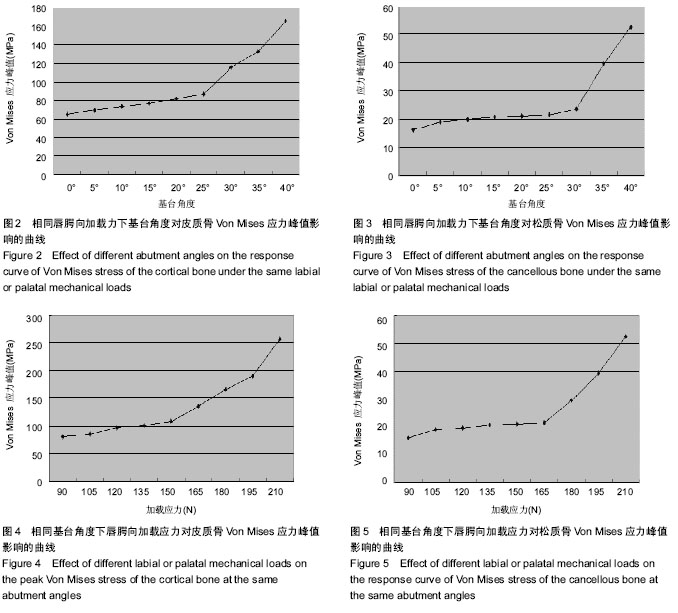
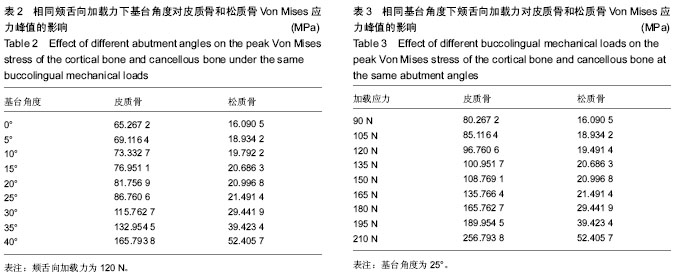
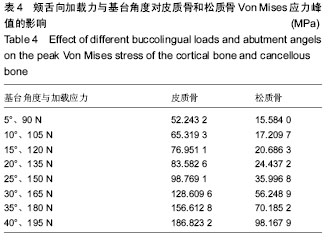
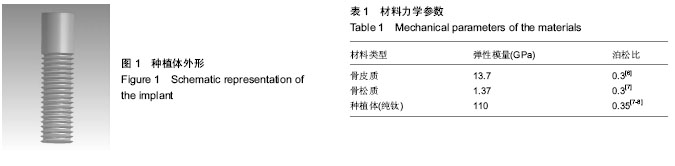
| [1] Boerrigter EM,Geertman ME,Van Oort RP,et al.Patient satisfaction and chewing ability with implant-retained mandibular overdentures: a comparison with new complete dentures with or without preprosthetic surgery.J Oral Maxillofac Surg.1995; 53(10):1167-1173.
[2] Cehreli M,Duyck J,De Cooman M,et al.Implant design and interface force transfer. A photoelastic and strain-gauge analysis.Clin Oral Implants Res.2004;15(2):249-257.
[3] Zienkiewicz OC.The finite element method in engineering science.4th ed.New York:McGraw-Hill International Book Co.1989:100-120.
[4] Lazzara RJ, Porter SS.Platform switching: a new concept in implant dentistry for controlling postrestorative crestal bone levels.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2006;26(1):9-17.
[5] 兰泽栋,林珠,龙红月,等.支抗种植体不同螺纹顶角对骨界面应力分布的影响[J].广东牙病防治,2003,11(4):259-261.
[6] Meijer HJ,Kuiper JH,Starmans FJ,et al.Stress distribution around dental implants: influence of superstructure, length of implants, and height of mandible.J Prosthet Dent. 1992;68(1): 96-102.
[7] Benzing UR,Gall H,Weber H.Biomechanical aspects of two different implant-prosthetic concepts for edentulous maxillae.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.1995;10(2):188-198.
[8] Schroeder A,Suffer F,Buser D,et al.Oral Implantology,Basics,ITI Hollow Cy linder system. Stultgart:theieme, 1996:37-58.
[9] Steigenga JT,al-Shammari KF,Nociti FH,et al.Dental implant design and its relationship to long-term implant success. Implant Dent.2003;12(4):306-317.
[10] Ujigawa K,Kato Y,Kizu Y,et al.Three-dimensional finite elemental analysis of zygomatic implants in craniofacial structures.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;36(7):620-625.
[11] Block MS,Delgadao A,Fontenot MG,et al.The effect of diam—eter and lengh of hydroxyapatite—coated dental implants on ultimate pullout force in dog alveolar bone.J Oral Maxillofac Surg.1990;48(8):174-178.
[12] 赖红吕,张志勇,张保卫,等.三种载荷条件下种植体骨界面应力分布特征[J].上海口腔医学,2002,11(3):253-255.
[13] Akca K,Iplikciglu H.Finite element stress analysis of the effect of short implant usage in place of cantilever extensions in mandibular posterior edentulism.J Oral Rehabil.2002;29(4): 350-356.
[14] Cehreli M,Duyck J,De Cooman M,et al.Implant design and interface force transfer. A photoelastic and strain-gauge analysis.Clin Oral Implants Res.2004;15(2):249-257.
[15] Esposito M,Hirsch JM,Lekholm U,et al.Differential diagnosis and treatment strategies for biologic complications and failing oral implants:a review of the literature.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.1999;14(4):473-490.
[16] Perenyi J,Bene L,Radnai M,et al.[Model investigation of push-out test used for quantitative evaluation of dental implant osseointegration].Fogorv Sz.2002;95(3):105-111.
[17] Rieger MR,Adams WK,Kinzel GL.A finite element survey of eleven endosseous implants.J Prosthet Dent.1990;63(4): 457-465.
[18] Dibart S,Warbington M,Su MF,et al.In vitro evaluation of the implant—abutment bacterial seal:The locking taper system.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2005;20(5):732-737.
[19] 杨秋燕,陈江,杜志斌,等.上颌前牙平台转换种植体周围应力分布的有限元分析[J].福建医科大学学报,2010,44(1):1-4. |