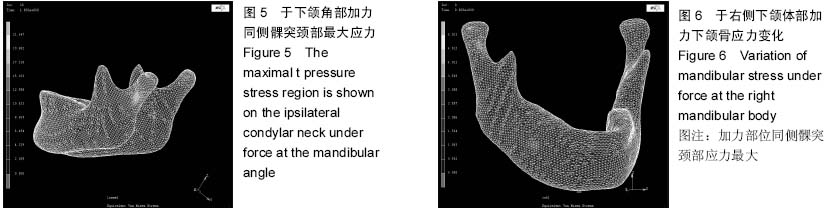
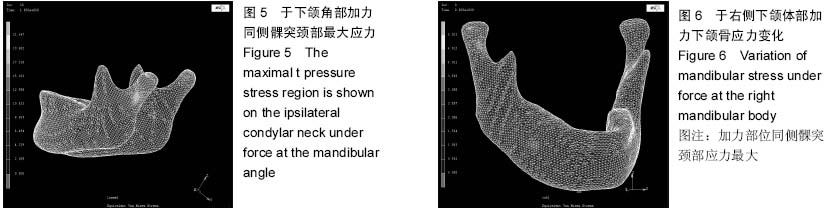
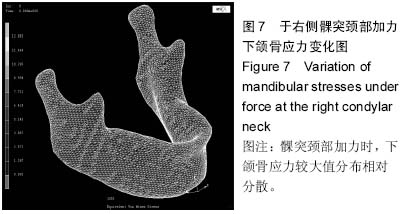
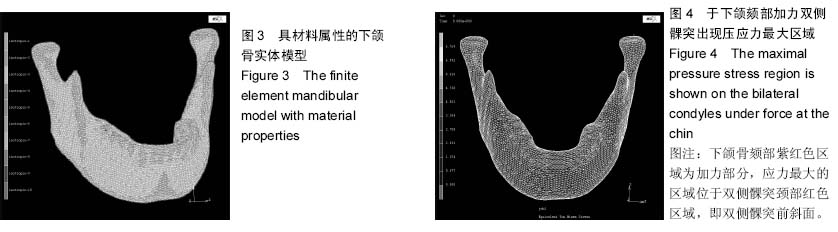
| [1] 殷学民,张君伟,任晓旭,等.下颌支矢状骨劈开术数字模型的建立及不同固定方式的稳定性分析[J].上海口腔医学,2013,22(3): 241-246.
[2] Murakami K,Sugiura T,Yamamoto K,et al,Biomechanical analysis of the strength of the mandible after marginal resection.J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2011;69(6):1798-1806.
[3] 曹力飞,申铁兵.三维有限元分析下颌骨生物力学的研究进展[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2014,12(6):554-557.
[4] 邱蔚六.口腔颌面外科理论与实践[J].北京:人民卫生出版社, 1997: 479-479.
[5] Hart RT, Hennebel VV, Thongpreda N, et al. Modeling the biomechanlcs of the numdible. A three dimensional finite element study.J Biomecb.1992;25(3):261-286.
[6] Ashman RB, Van Buskirk WC. The elstic properties of a human mandible. Adv Dent Res. 1987;1(2):64-64.
[7] 张震康,傅民魁.颞下颌关节病[J].北京:人民卫生出版社, 1987:157-157.
[8] Meijer HT, Starmaas FJ, Bosman F. et al. A comparison of three finite element models of an edentulous mandible pirvided withimplants. J Oral Rehabil.1993;20(2):147-157.
[9] 邱蔚六.口腔颌面外科学,3版.北京:人民卫生出版社,1997:183.
[10] Cattaneo PM, Dalstra M, Frich LH. A three-dimensional finite element model from computed tomography data: a semi-automated. Proc Inst Mech Eng.2001;215(2):203-213.
[11] Gross MD, Arbel G, Hershkovitz I. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the facial skeleton on simulated occlusal loadin. J Oral Rehabi.2001;2(87):684-946.
[12] Choi AH, Ben-Nissan B, Conway RC. Three-dimensionalmodelling and finite element analysis of the human mandibleduring clenching. Aust Dent J. 2005; 50(1):42-48.
[13] You SL Huang YL,Sun M,et al.Kouqiang Yixue Yanjiu.2008; 24(4); 381-383.
[14] Zhang J,LuoQ,Wang JP,et al.Zhongguo Meirong Yixue.2010; 19(3):344-347.
[15] Okumura N,Stegaroiu R,Nishiyama H,et al.Finite element analysis 0f implant-embedded maxilla model fromCTdata: CoMParison with the conventional model. J Prosthodont Res. 2011;55(1):24-31.
[16] Quereshy FA,Savell TA,Palomo JM.Applications of cone beam computered tomography in the practice of oral and maxillofacial surgery,J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;66(4): 791-796.
[17] 殷学民,李燕,张美超,等.含完整牙列下颌骨生物力学模型的建立[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2011,9(3):195-197.
[18] Carvalho Silva G,Pereira Cornacchia TM,Barbosa de Las Casas E,et al.A method fou obtaining a three-dimensional geometric model of dental implants for analysis via the finite element method.Implant Dent.2013;22(3):309-314.
[19] 白乐康,安虹,杜斌.无牙颌患者垂直距离对髁突前斜面应力分布的影响[J].口腔医学,2007,27(2):67-69.
[20] 胡凯,张晔缨,柳青明.模拟功能咬合时人颞下颌关节内的应力分布特征和位移特征[J].解放军医学杂志,2003,28(1):63-65.
[21] 孙健,张富强,王冬梅,等.三种加载方式下正常人下颌骨三维有限元应力分布分析[J].上海口腔医学,2004,13(1):41-43.
[22] 张海钟,步荣发,柳春明,等.颅面骨撞击伤的生物力学研究[J].中华创伤杂志,2004, 20(1):26-29.
|