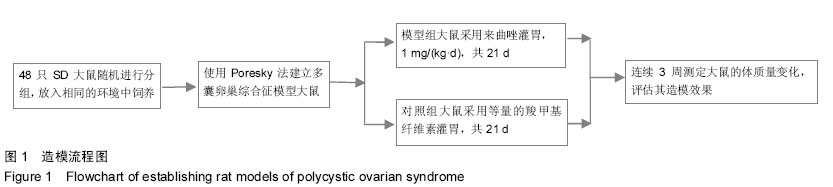
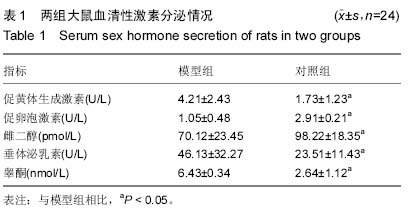
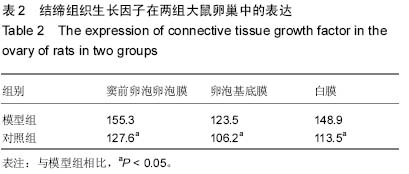
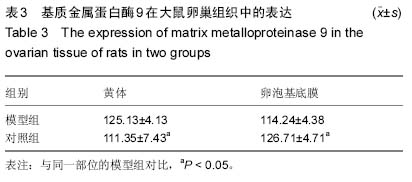
| [1] Lowe P, Kovacs G, Howlett D, et al. Incidence of polycystic ovaries and polycystic ovary syndrome amongst women in Melbourne, Australia. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2005; 45(1):17-19.
[2] 李洪忠,杜艳秋,侯丽辉,等.多囊卵巢综合征对健康的长期影响研究综述[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2012,07(7):630-632.
[3] 吕雯,麻亚茜,娄阁,等.上皮性卵巢肿瘤细胞外基质的表达及意义[J].现代妇产科进展,2002,11(1):21-23.
[4] 赵志明,杨素娟,杨暖,等.MMP-2,-9及其抑制物TIMP-1在多囊卵巢综合征患者黄素化颗粒细胞上的表达[J].生殖医学杂志,2014, 23(6):464-469.
[5] 张静波,李聪,李英红,等.AEG-1和MMP-9在上皮性卵巢癌组织中的表达及其临床相关性和病理特征[J].实用肿瘤学杂志,2013, 27(3):234-238.
[6] 吕跃峰.卵巢组织中结蹄组织、肝细胞生长因子及间隙连接蛋白在多囊卵巢综合征患者中的表达及其干预治疗[J].中国医药导报, 2013,10(19):23-25.
[7] 杨正望,周芳,谈珍瑜,等.不同造模方法对大鼠多囊卵巢综合征模型的影响[J].中国实验动物学报,2010,18(1):13-16.
[8] 马琳琳,吴效科.多囊卵巢综合征产科并发症及其防治[C].全国中西医结合妊娠期疾患专题学术会议论文集,2011:23-26.
[9] 张多加,吴效科.多囊卵巢综合征与表观遗传学[J].中国妇幼保健,2013,28(33):5574-5576.
[10] 王海燕,郑鹏生,曹浩哲,等.两种剂量LE和CC对PCOS不孕患者促排卵效果比较[J].中国妇幼健康研究,2013,24(3):384-385, 397.
[11] 唐小玲,毛绍蓉.更年期雌激素、孕酮、睾酮与肥胖的关系[J].标记免疫分析与临床,2010,17(2):132-133, 121.
[12] 赵岫,张琴,高晓杰,等.小剂量雌激素联合促性腺激素释放素类似物治疗儿童特发性中枢性性早熟[J].新乡医学院学报,2011, 28(4): 454-457.
[13] 曹姗姗,田秀珠.CTGF HGF及Cx 43在多囊卵巢综合征大鼠卵巢中的表达及二甲双胍的干预作用[J].中国药物与临床,2012, 12(12): 1554-1556.
[14] 孟艳岑,张明敏,崔丹丹,等.补肾、活血对超促排卵小鼠着床期间子宫内膜MMP-2、MMP-9、TIMP-3表达的影响[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2013,42(6):627-632.
[15] 王俊杰,雷小敏,易慕华,等.PCOS患者着床窗口期子宫内膜组织中MMP-2、MMP-9、TIMP-1的表达变化及意义[J].山东医药, 2009,49(50):13-15.
[16] 赵志明,孙亚楠,郝桂敏,等.多囊卵巢综合征患者卵泡液 MMP-2、9及其抑制物水平的研究[J].河北医药,2012,34(10): 1460-1462.
[17] Baka S, Zourla K, Kouskouni E, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 and their tissue inhibitors in the follicular fluid of patients with polycystic ovaries undergoing in vitro fertilization. In Vivo. 2010;24:293-299.
[18] Lewandowski KC, Komorowski J, O’Callaghan CJ, et al. Increased circulating levels of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in women with the polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:1173-1177.
[19] 姚莉娟,徐晓娟,王婧婧,等.体现中医病因病机的多囊卵巢综合征动物模型评价及筛选[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2014, 16(10):2137-3148.
[20] 张海荣,张彦春,王蔼明,等.多囊卵巢综合征模型大鼠血清生长素水平及卵巢组织生长素的表达及意义[J].解放军医学杂志,2012, 37(2):113-116.
[21] 杜芳,王继东,姚珍薇.再生基因Reg IV在多囊卵巢综合征(PCOS)模型大鼠卵巢中的表达[J].生殖与避孕,2012,32(11):721-727.
[22] 王铮,张婷婷,朱焰,等.益气养阴化瘀方对多囊卵巢综合征模型大鼠高雄激素血症及胰岛素抵抗的影响[J].生殖与避孕,2010, 30(3):145-150.
[23] 杨正望,尤昭玲,冯光荣,等.多囊卵巢综合征动物模型的构建及中药干预机制述评[J].湖南中医学院学报,2006,26(1):56-58.
[24] 吴雏燕,江钟立,邱树卫,等.一种新的稳定多囊卵巢综合征大鼠模型的建立[J].中国康复医学杂志,2008,23(4):334-338.
[25] Manneras L, Cajander S, Holmang A, et al. A new rat model exhibiting both ovarian and metabolic characteristics of polycystic ovary syndrome. Endocrinology. 2007; 148(8): 3781-3791.
[26] 邝少松,黄小琼,饶子亮,等.大鼠多囊卵巢综合征动物模型血脂代谢及抗氧化作用[J].中国比较医学杂志,2007,17(9):519-522.
[27] 孙林,魏巍,关咏梅,等.u-PA、u-PAR和PAI-1在睾酮联合hCG致多囊卵巢大鼠中的表达与意义[J].生殖与避孕,2006,26(10): 579-583.
[28] 夏燕,王惠仔,郑建淮.多囊卵巢综合征大鼠模型诱导的实验研究[J].中国优生与遗传杂志,2010,18(7):124-125.
[29] Liu X, Andoh K, Mizunuma H,et al. Effects of recombinant human FSH (rhFSH), urinary purified FSH (uFSH), and hMG on small preantral follicles and tertiary follicles from normal adult and androgen-sterilized female mice. Fertil Steril. 2000; 73(2):372-380.
[30] Yavasoglu L, Kucuk M, Coskun A,et al. Polycystic ovary syndrome and prolactinoma association. Intern Med. 2009; 48(8):611-613.
[31] Takahashi N, Takeda K, Imai M. Inhibitory effects of p-dodecylaminophenol on the invasiveness of human fibrosarcoma cell line HT1080. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013; 21(19):6015-6021.
[32] Santos FC, Rochel-Maia SS, Fochi RA, et al. MMP-2 and MMP-9 localization and activity in the female prostate during estrous cycle. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2011;173(3):419-427.
[33] Xu X, Jackson PL, Tanner S, et al. A self-propagating matrix metalloprotease-9 (MMP-9) dependent cycle of chronic neutrophilic inflammation. PLoS One. 2011;6(1):e15781.
[34] Cauwe B, Martens E, Van den Steen PE, et al. Adenylyl cyclase-associated protein-1/CAP1 as a biological target substrate of gelatinase B/MMP-9. Exp Cell Res. 2008;314(15): 2739-2749.
[35] Xiong H, Zhang ZG, Tian XQ, et al. Inhibition of JAK1, 2/STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and reduces tumor cell invasion in colorectal cancer cells. Neoplasia. 2008;10(3):287-297.
[36] Ding Q, Jin T, Wang Z, et al. Catalase potentiates retinoic acid-induced THP-1 monocyte differentiation into macrophage through inhibition of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. J Leukoc Biol. 2007; 81(6):1568-1576. |