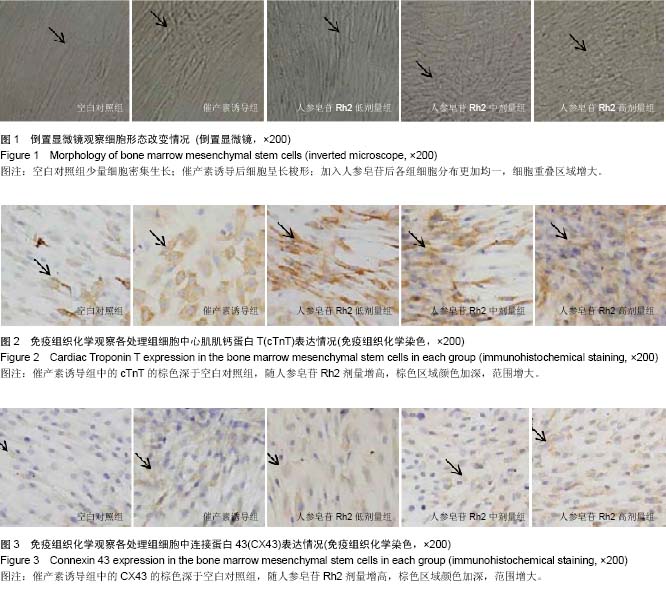
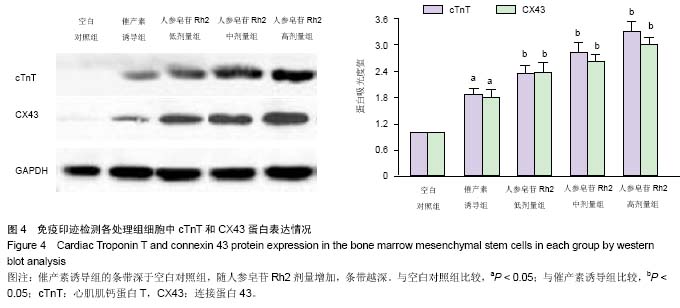
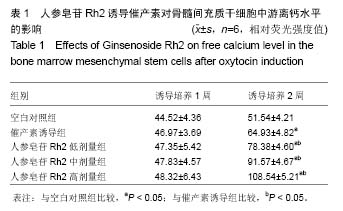
| [1] Choi SH, Jung SY, Kwon SM, et al. Perspectives on stem cell therapy for cardiac regeneration. Advances and challenges. Circ J. 2012;76(6):1307-1312.
[2] Leistner DM, Fischer-Rasokat U, Honold J, et al. Transplantation of progenitor cells and regeneration enhancement in acute myocardial infarction (TOPCARE-AMI): final 5-year results suggest long-term safety and efficacy. Clin Res Cardiol. 2011;100(10):925-934.
[3] Clifford DM, Fisher SA, Brunskill SJ, et al. Stem cell treatment for acute myocardial infarction. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;2:CD006536.
[4] Delewi R, Andriessen A, Tijssen JG, et al. Impact of intracoronary cell therapy on left ventricular function in the setting of acute myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled clinical trials. Heart. 2013;99(4): 225-232.
[5] Wu J, Li J, Zhang N, et al. Stem cell-based therapies in ischemic heart diseases: a focus on aspects of microcirculation and inflammation. Basic Res Cardiol. 2011; 106(3):317-324.
[6] Zimmet H, Porapakkham P, Sata Y, et al. Short- and long-term outcomes of intracoronary and endogenously mobilized bone marrow stem cells in the treatment of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; a meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Eur J Heart Fail. 2012;14(1):91-105.
[7] Zhang Z, Li S, Cui M, et al. Rosuvastatin enhances the therapeutic efficacy of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells for myocardial infarction via PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK pathways. Basic Res Cardiol. 2013;108(2):333.
[8] Dong Q, Yang Y, Song L, et al. Atorvastatin prevents mesenchymal stem cells from hypoxia and serum-free injury through activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Int J Cardiol. 2011;153(3):311-316.
[9] Song L, Yang YJ, Dong QT, et al. Atorvastatin enhance efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells treatment for swine myocardial infarction via activation of nitric oxide synthase. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e65702.
[10] Qian HY, Yang YJ, Huang J, et al. Effects of Tongxinluo-facilitated cellular cardiomyoplasty with autologous bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells on postinfarct swine hearts. Chin Med J (Engl). 2007;120(16): 1416-1425.
[11] 陈声武,王岩,王毅,等.人参皂苷Rg1和Rh2抗肿瘤作用的研究[J].吉林大学学报:医学版,2003,29(1):25-28.
[12] Liu J,He J,Huang L,et al.Neuroprotective effects of ginsenoside Rb1 on hippocampal neuronal injury and neurite outgrowth. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(9):943-950.
[13] Ke LN, Guo W, Xu JW,et al.Ginsenoside Rb1 attenuates activated microglia-induced neuronal damage. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(3):252-259.
[14] Moran AE, Foronzanfar MH, Roth G, et al. The Global Burden of Ischemic Heart Disease in 1990 and 2010: the Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study. Circulation. 2014;129(14): 1493-1501.
[15] Hahn JY, Yu CW, Park HS, et al. Long-term effects of ischemic postconditioning on clinical outcomes: 1-year follow-up of the POST randomized trial. Am Heart J. 2015; 169(5):639-646.
[16] Cherubini A, Palomba A, Morosin M, et al. Achieving optimal cholesterol levels in patients with chronic ischemic heart disease: from guidelines to the real world. G Ital Cardiol (Rome). 2015;16(4):240-249.
[17] Trifunovi? Z, Obradovi? S, Balint B, et al. Functional recovery of patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy treated with coronary artery bypass surgery and concomitant intramyocardial bone marrow mononuclear cell implantation-a long-term follow-up study. Vojnosanit Pregl. 2015;72(3): 2252-2232.
[18] Al-Amran FF, Shahkolahi M, Oxytocin ameliorates the immediate myocardial injury in heart transplant through down regulation of the neutrophil dependent myocardial apoptosis. Heart Views. 2014;15(2):37-45.
[19] Gutkowska J, Jankowski M, Antunes-Rodrigues J, The role of oxytocin in cardiovascular regulation. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2014;47(3):206-214.
[20] Gonzalez-Reyes A, Menaouar A, Yip D, et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying oxytocin-induced cardiomyocyte protection from simulated ischemia-reperfusion. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015.
[21] Menaouar A, Florian M, Wang D, et al. Anti-hypertrophic effects of oxytocin in rat ventricular myocytes. Int J Cardiol. 2014;175(1):38-49.
[22] Wei S1, Wo BL, Qi HP, et al. Early amniotomy and early oxytocin for prevention of, or therapy for, delay in first stage spontaneous labour compared with routine care. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;8:CD006794.
[23] Nankali A, Keshavarzi F, Fakheri T, et al. Effect of intraumbilical vein oxytocin injection on third stage of labor. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2013;52(1):57-60.
[24] Bouchard F, Paquin J, Skeletal and cardiac myogenesis accompany adipogenesis in P19 embryonal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2009;18(7):1023-1032.
[25] Noiseux N, Borie M, Desnoyers A, et al. Preconditioning of stem cells by oxytocin to improve their therapeutic potential. Endocrinology. 201;153(11):5361-5372.
[26] Simsek Y, Celik O, Karaer A, et al. Elevated cardiac oxidative stress in newborn rats from mothers treated with atosiban. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2012;285(3):655-661.
[27] 王琪,张文祥,王思平,等.肌肉注射人脐带间充质干细胞健康大鼠心肌组织ki-67、phh3及cTnT的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(41):6671-6677.
[28] Saad Y, Shugman IM, Kumar M, et al, Safety and efficacy of same-day discharge following elective percutaneous coronary intervention, including evaluation of next day troponin T levels. 2015;24(4):368-376.
[29] 王伟光,张权宇,曹钰琨,等.к阿片受体可通过抑制β肾上腺素受体进而调节心肌细胞CX43发挥抗缺血/再灌注性心律失常[J].中国药理学通报,2010,26(4):471-476.
[30] Ladenvall P, Andersson B, Dellborg M, et al. Genetic variation at the human connexin 43 locus but not at the connexin 40 locus is associated with left bundle branch block. Open Heart. 2015;2(1):e000187.
[31] Kirca M, Kleinbongard P, Soetkamp D, et al. Interaction between Connexin 43 and nitric oxide synthase in mice heart mitochondria. J Cell Mol Med. 2015;19(4):815-825.
[32] Gao J, Zhao Y, Wang Y, et al. Anti-arrhythmic effect of acupuncture pretreatment in the rats subjected to simulative global ischemia and reperfusion-involvement of intracellular Ca(2+) and connexin 43. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015; 15:5. |