| [1] Etebar S, Cahill DW. Risk factors for adjacent-segment failure following lumbar fixation with rigid instrumentation for degenerative instability. J Neurosurg.1999;90(2 Suppl): 163-169.
[2] Manchikanti L, Kaye AD, Manchikanti K, et al. Efficacy of epidural injections in the treatment of lumbar central spinal stenosis: a systematic review. Anesth Pain Med. 2015;5(1): e23139.
[3] Kalff R, Ewald C, Waschke A, et al. Degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis in older people: current treatment options. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013;110(37):613-623; quiz 624.
[4] 陈君生,包健,朱大成,等.脊柱融合术后邻近节段的加速退变(附107例报告)[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2002,10(z2):1437-1438.
[5] Liang J, Dong Y, Zhao H. Risk factors for predicting symptomatic adjacent segment degeneration requiring surgery in patients after posterior lumbar fusion. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014;9:97.
[6] Saavedra-Pozo FM, Deusdara RA, Benzel EC. Adjacent segment disease perspective and review of the literature. Ochsner J. 2014;14(1):78-83.
[7] Zhu Z, Liu C, Wang K, et al. Topping-off technique prevents aggravation of degeneration of adjacent segment fusion revealed by retrospective and finite element biomechanical analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10(1):10.
[8] Yang M, Li C, Chen Z, et al. Short term outcome of posterior dynamic stabilization system in degenerative lumbar diseases. Indian J Orthop. 2014;48(6):574-581.
[9] Erbulut DU, Zafarparandeh I, Ozer AF, et al. Biomechanics of posterior dynamic stabilization systems. Adv Orthop. 2013; 2013:451956.
[10] 徐西强,李峰,吴华.棘突间动态稳定系统(Wallis)在腰椎退变性疾病中的临床应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(1):18-19.
[11] 姜建元.关于腰椎非融合技术的一点浅见[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2011,21(8):623-624.
[12] 张文志,段丽群,尚希福,等.Wallis棘突间动态稳定系统治疗腰椎间盘突出症的初步临床应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(3): 203-205.
[13] 周现杰,邹国耀,唐志宏.Wallis动态稳定系统置入治疗单纯性腰椎间盘突出症的临床疗效分析[J].航空航天医学杂志,2014,(11): 1510-1513.
[14] 车武,姜允琦,马易群,等.单节段椎弓根螺钉固定联合上方棘突间Coflex置入的生物力学评价[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(1): 62-66.
[15] Polikeit A, Nolte LP, Ferguson SJ. The effect of cement augmentation on the load transfer in an osteoporotic functional spinal unit: finite-element analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(10):991-996.
[16] Kim DH, Kim KH, Kim YC. Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Spinal Techniques[M]. 沈惠良,海涌,洪毅,等,译.北京:北京大学医学出版社,2012:22-23.
[17] Landi A, Marotta N, Morselli C, et al. Pannus regression after posterior decompression and occipito-cervical fixation in occipito-atlanto-axial instability due to rheumatoid arthritis: case report and literature review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013;115(2):111-116.
[18] Landi A. Interspinous posterior devices: What is the real surgical indication? World J Clin Cases. 2014;2(9):402-408.
[19] Lee YS, Kim YB, Park SW. Survival rates and risk factors for cephalad and L5-s1 adjacent segment degeneration after L5 floating lumbar fusion : a minimum 2-year follow-up. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015;57(2):108-113.
[20] Soh J, Lee JC, Shin BJ. Analysis of risk factors for adjacent segment degeneration occurring more than 5 years after fusion with pedicle screw fixation for degenerative lumbar spine. Asian Spine J. 2013;7(4):273-281.
[21] Cho KS, Kang SG, Yoo DS, et al. Risk factors and surgical treatment for symptomatic adjacent segment degeneration after lumbar spine fusion. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009; 46(5):425-430.
[22] Park P, Garton HJ, Gala VC, et al. Adjacent segment disease after lumbar or lumbosacral fusion: review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(17):1938-1944.
[23] Mayer HM, Korge A. Non-fusion technology in degenerative lumbar spinal disorders: facts, questions, challenges. Eur Spine J. 2002;11 Suppl 2:S85-91.
[24] Schmoelz W, Erhart S, Unger S, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of a posterior non-fusion instrumentation of the lumbar spine. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(5):939-945.
[25] Omidi-Kashani F, Hasankhani EG, Ashjazadeh A. Lumbar spinal stenosis: who should be fused? An updated review. Asian Spine J. 2014;8(4):521-530.
[26] 毛仲轩,江建明,闫慧博,等.CoflexTM和椎弓根钉棒系统联合应用对腰椎三维运动的影响[J].南方医科大学学报,2010,30(4): 863-866.
[27] Wan Z, Wang S, Kozánek M, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of the X-Stop device for surgical treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012;25(7):374-378.
[28] Adelt D, Taylor J, Zucherman J, et al. Clinical Symposium II: Interspinous-based Dynamic Stabilization. SAS J. 2008;2(3): 150-154.
[29] Richards JC, Majumdar S, Lindsey DP, et al. The treatment mechanism of an interspinous process implant for lumbar neurogenic intermittent claudication. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(7):744-749.
[30] Lindsey DP, Swanson KE, Fuchs P, et al. The effects of an interspinous implant on the kinematics of the instrumented and adjacent levels in the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(19):2192-2197.
[31] Swanson KE, Lindsey DP, Hsu KY, et al. The effects of an interspinous implant on intervertebral disc pressures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(1):26-32.
[32] Zucherman JF, Hsu KY, Hartjen CA, et al. A multicenter, prospective, randomized trial evaluating the X STOP interspinous process decompression system for the treatment of neurogenic intermittent claudication: two-year follow-up results. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(12):1351-1358.
[33] Epstein NE. A review of interspinous fusion devices: High complication, reoperation rates, and costs with poor outcomes. Surg Neurol Int. 2012;3:7.
[34] Sclafani JA, Liang K, Ohnmeiss DD, et al. Clinical outcomes of a polyaxial interspinous fusion system. Int J Spine Surg. 2014;8.
[35] 刘瑞,徐林,张元智,等.Wallis腰椎非融合系统的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(13):2287-2291.
[36] Schulte TL, Hurschler C, Haversath M, et al. The effect of dynamic, semi-rigid implants on the range of motion of lumbar motion segments after decompression. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(8):1057-1065.
[37] Boeree N. Dynamic stabilization of the lumbar motion segment with the wallis system. Proceeding of Spinal Arthroplasty Society-New York, 2005.
[38] 潘奇林,徐小雄,杨毅,等.棘间动态系统Coflex对比传统融合固定手术治疗腰椎退行性疾病的系统综述与Meta分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(1):35-40.
[39] Richter A, Schütz C, Hauck M, et al. Does an interspinous device (Coflex) improve the outcome of decompressive surgery in lumbar spinal stenosis? One-year follow up of a prospective case control study of 60 patients. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(2):283-289.
[40] Schmier JK, Halevi M, Maislin G, et al. Comparative cost effectiveness of Coflex® interlaminar stabilization versus instrumented posterolateral lumbar fusion for the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis and spondylolisthesis. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2014;6:125-131.
[41] 祖丹,海涌,鲁世保,等.腰椎棘突间动态稳定装置Coflex最佳置入位置的生物力学研究[J].中华外科杂志,2014,52(3):179-183.
[42] 陈小龙,海涌,关立,等.Topping-off手术治疗腰椎退行性疾病的影像学分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(1):6-12.
[43] 祖丹,海涌,云才,等.腰椎棘突间动态稳定装置Coflex不同置入深度对相邻节段运动范围影响的生物力学研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014,24(10):933-937.
[44] Adelt D, Samani J, Kim WK, et al. Coflex interspinous stabilization:clinical and radiographic results from an international multicenter retrospective study. Paradigm Spine J. 2007;1:1-4.
[45] 倪文飞,徐华梓,池永龙,等.Coflex腰椎棘突间动态稳定系统手术并发症分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(10):928-933.
[46] 臧磊,海涌,苏庆军,等.棘突间动态稳定装置Coflex植入并发症的探讨[J].中华医学杂志,2012,50(9):782-787.
[47] Kumar N, Shah SM, Ng YH, et al. Role of coflex as an adjunct to decompression for symptomatic lumbar spinal stenosis. Asian Spine J. 2014;8(2):161-169.
[48] Xu C, Ni WF, Tian NF, et al. Complications in degenerative lumbar disease treated with a dynamic interspinous spacer (Coflex). Int Orthop. 2013;37(11):2199-2204.
[49] Park SC, Yoon SH, Hong YP, et al. Minimum 2-year follow-up result of degenerative spinal stenosis treated with interspinous u (coflex). J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009;46(4): 292-299.
[50] 王占长,赵旭红,梁宁,等.Coflex植入术治疗退行性腰椎管狭窄症41例的临床观察[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2014,9(4): 43-47.
[51] 海涌.严格掌握适应证慎重开展腰椎棘突间动态稳定技术[J].中华外科杂志,2012,50(9):769-771.
[52] Wilke HJ, Drumm J, Häussler K, et al. Biomechanical effect of different lumbar interspinous implants on flexibility and intradiscal pressure. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(8):1049-1056.
[53] 曾攀.有限元分析及应用[M].北京:清华大学出版社有限公司, 2004.
[54] Viceconti M, Cristofolini L, Baleani M, et al. Pre-clinical validation of a new partially cemented femoral prosthesis by synergetic use of numerical and experimental methods. J Biomech. 2001;34(6):723-731.
[55] Stolk J, Verdonschot N, Cristofolini L, et al. Finite element and experimental models of cemented hip joint reconstructions can produce similar bone and cement strains in pre-clinical tests. J Biomech. 2002;35(4):499-510.
[56] [56] Müller R, Kampschulte M, Khassawna TE, et al. Change of mechanical vertebrae properties due to progressive osteoporosis: combined biomechanical and finite-element analysis within a rat model. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2014;52(4): 405-414.
[57] 卢昌怀,刘志军,张宏波,等.骨水泥量及分布对椎体成形术后相邻椎体生物力学影响的三维有限元分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2015, (1):29-33.
[58] Pasha S, Aubin CE, Parent S, et al. Biomechanical loading of the sacrum in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2014;29(3):296-303.
[59] 袁高翔,张伟滨.有限元分析在骨骼肌肉系统模型材料特性研究中的应用[J].国际骨科学杂志,2011,32(6):352-355.
[60] El-Rich M, Arnoux PJ, Wagnac E, et al. Finite element investigation of the loading rate effect on the spinal load-sharing changes under impact conditions. J Biomech. 2009;42(9):1252-1262.
|
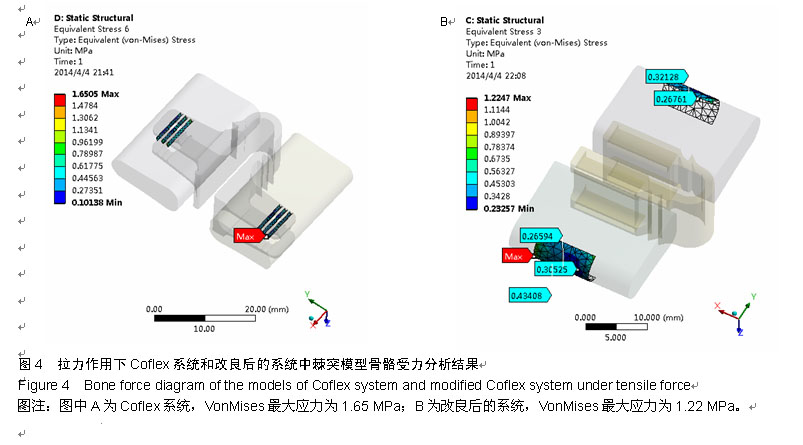
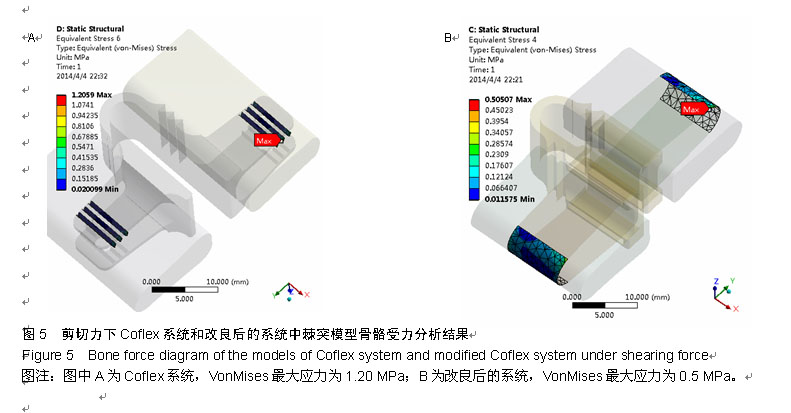
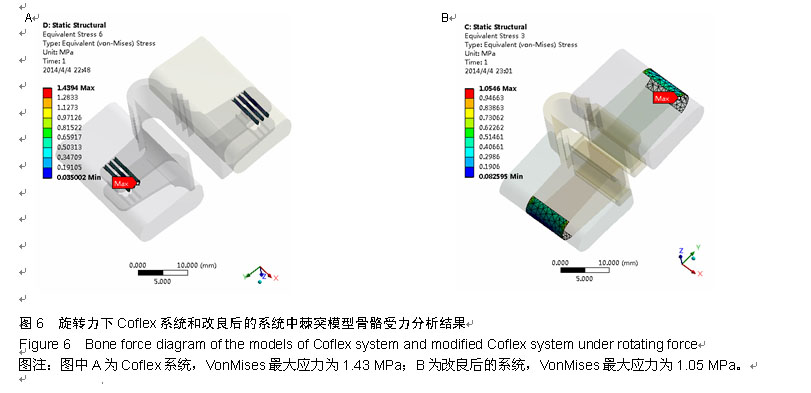
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)