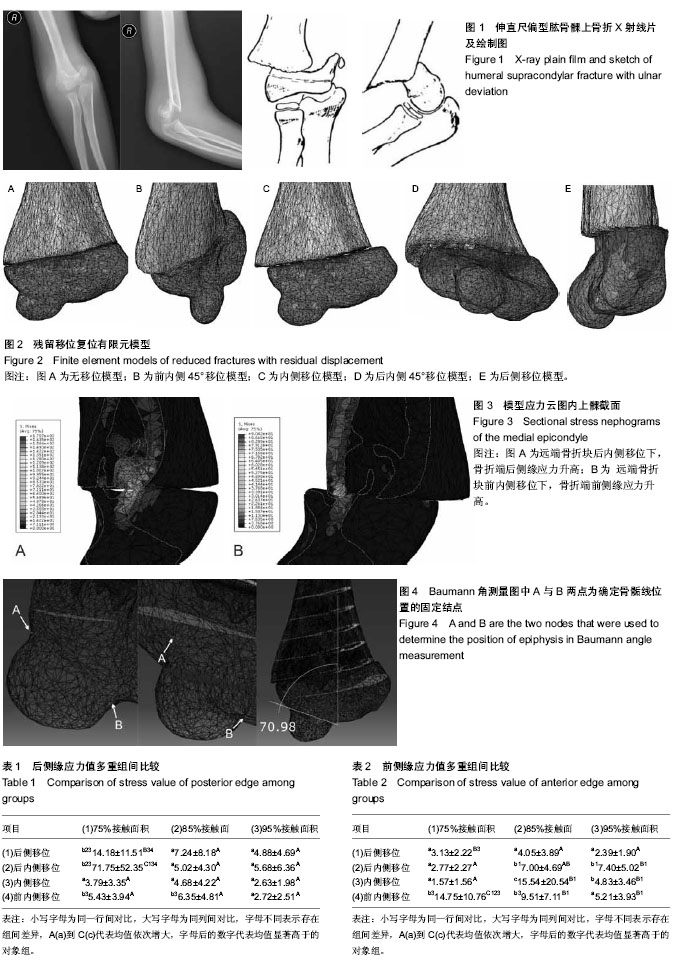
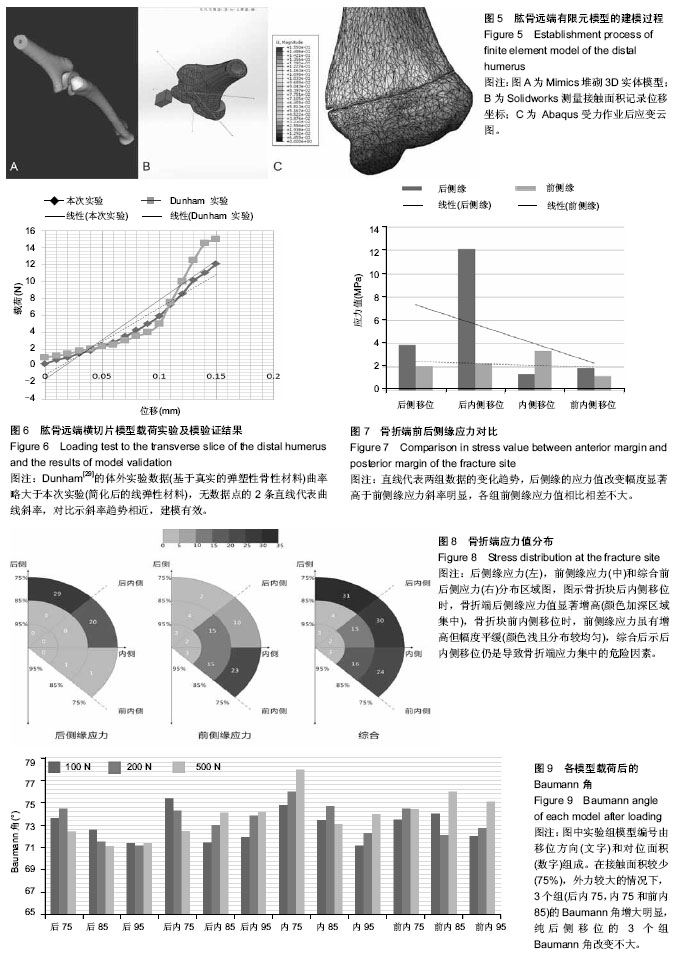
| [1] 陆春.儿童肱骨髁上骨折的内固定治疗[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2007,15(20):1550-1552.
[2] Mulpuri K, Wilkins K. The treatment of displaced supracondylar humerus fractures: evidence-based guideline. J PediatrOrthop. 2012;32Suppl 2:S143-152.
[3] 廖世杰,赵劲民,丁晓飞.儿童肱骨髁上骨折的分型与治疗进展[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(8):714-716.
[4] Omid R, Choi PD, Skaggs DL. Supracondylar humeral fractures in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(5): 1121-1132.
[5] Young S, Fevang JM, Gullaksen G, et al. Deformity and functional outcome after treatment for supracondylar humerus fractures in children: a 5- to 10-year follow-up of 139 supracondylar humerus fractures treated by plaster cast, skeletal traction or crossed wire fixation. J Child Orthop. 2010;4(5):445-453.
[6] Ababneh M, Shannak A, Agabi S, et al. The treatment of displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. A comparison of three methods. Int Orthop. 1998;22(4): 263-265.
[7] Tschopp O, Rombouts JJ. Complications of supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. Acta Orthop Belg. 1996; 62(Suppl1):51-57.
[8] Farnworth CL, Smith PD, Mubarak SJ. Etiology of supracondylar humerusfracture. J Pediatr Orthop. 1998; 18:38-42.
[9] 王建伟,马勇,诸方受,等.肱骨髁上骨折并发肘内翻的生物力学机制研究概况[J].北京中医药大学学报,1998,39(4):58-60.
[10] D'Ambrosia RD. Supracondylar fractures of humerus- prevention of cubitusvarus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1972; 54(1):60-66.
[11] ArinoVL, Lluch EE, Ramirez AM, et al. Percutaneous fixation of supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1977;59(7):914-916.
[12] 徐华梓,李也白,池永龙,等.儿童肱骨髁上骨折切开复位术后肘内翻畸形[J].中华小儿外科杂志,1995,16(1):28-29.
[13] 侯德光.肱骨髁上骨折并发肘内翻的探讨[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,1989,2:28-29.
[14] 李海波,田心义.儿童肱骨髁上骨折的治疗及肘内翻机理研究进展[J]. 中医药导报,2006,12(2):78-82.
[15] Flynn JC, Matthews JG, Benoit RL. Blind pinning of displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. Sixteen years' experience with long-term follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974;56(2):263-272.
[16] Smith L. Deformity following supracondylar fractures of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1965;47(8):1668.
[17] 霍力为,王广伟,庾伟中,等.黄氏手法配合小夹板治疗儿童Gartland Ⅲ型肱骨髁上骨折临床观察[J].新中医,2011, 43(11): 65-66.
[18] 宋冰,刘建科,张伟.手法整复小夹板治疗儿童伸直型肱骨髁上骨折[J].陕西中医学院学报,2008,31(5):37-38.
[19] 陈执平,齐振熙,周金水.应用三维有限元分析探讨髓芯减压术后产生的空洞对股骨头应力的影响[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2009,3(5):49-52.
[20] 魏秋实,何伟.有限元分析在股骨头坏死领域中的应用研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(19):1611-1614.
[21] Bonnick SL. Noninvasive assessments of bone strength.Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes.2007;14(6): 451-457.
[22] Keaveny TM. Biomechanical computed tomography-noninvasive bone strength analysis using clinical computed tomography scans. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1192: 57-65.
[23] Rice JC, Cowin SC, Bowman JA. On the dependence of the elasticity and strength of cancellous bone on apparent density. J Biomech. 1988;21(2):155-168.
[24] Morgan EF, Bayraktar HH, Keaveny TM. Trabecular bone modulus-density relationships depend on anatomic site. J Biomech. 2003;36(7):897-904.
[25] Rho JY, Hobatho MC, Ashman RB, et al. Relations of mechanical properties to density and CT numbers in human bone. Med Eng Phys.1995;17:347-355.
[26] Bahk MS, Srikumaran U, Ain MC, et al. Patterns of pediatric supracondylar humerusfractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 2008;28(5):493-499.
[27] Shockey JS, von Fraunhofer JA, Seligson D. A measurement of the coefficient of static friction of human long bones. Surf Tech. 1985;25(2):167-173.
[28] Schuster I, Korner J, Arzdorf M, et al. Mechanical comparison in cadaver specimens of three different 90-degree double-plate osteosyntheses for simulated C2-type distal humerus fractures with varying bone densities.J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(2):113-120.
[29] Dunham CE, Takaki SE, Johnson JA, et al. Mechanical properties of cancellous bone of the distal humerus. ClinBiomech (Bristol, Avon). 2005;20(8):834-838.
[30] 徐华梓,林焱,陈跃忠,等. Baumann角测量预测肱骨髁上骨折肘内翻的研究[J].温州医学院学报,1999,40(1):6-8.
[31] Williamson DM, Coates CJ, Miller RK, et al. Normal characteristics of the Baumann (humerocapitellar) angle: an aid in assessment of supracondylar fractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 1992;12(5):636-639.
[32] Worlock P. Supracondylar fractures of the humerus. Assessment of cubitusvarus by the Baumann angle. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1986;68(5):755-757.
[33] 庄志强,林乔龄,洪嘉志,等.基于Baumann角测定在预测儿童肱骨髁上骨折并发肘内翻的发生率的临床意义[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2012,32(2):27-28.
[34] 刘飞,楼跃,唐凯,等.儿童肱骨远端有限元模型的建立及力学分析[J]. 热带医学杂志,2011,11(5):527-528.
[35] 王亚斌,周小建,任亚军,等.肱骨远端三维有限元模型的建立及生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(22): 4002-4005.
[36] 刘剑,黄潮桐,陈隆福,等.肱骨髁上部位局部三维构建及有限元分析[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2012,4(6):427-431.
[37] Lamdan R, Liebergall M, Gefen A, et al. Pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures: effect of bone-implant interface conditions on fracture stability. J Child Orthop. 2013;7(6):565-569.
[38] Sabalic S, Kodvanj J, Pavic A. Comparative study of three models of extra-articular distal humerus fracture osteosynthesis using the finite element method on an osteoporotic computational model. Injury. 2013;44Suppl 3:S56-61.
[39] Worlock P. Supracondylar fractures of the humerus. Assessment of cubitusvarus by the Baumann angle. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1986;68(5):755-757.
[40] Silva M, Pandarinath R, Farng E, et al. Inter- and intra-observer reliability of the Baumann angle of the humerus in children with supracondylar humeral fractures. Int Orthop. 2010;34(4):553-557.
[41] 左大鹏.闭合治疗儿童肱骨髁上骨折[J].贵阳中医学院学报, 2008, 30(4):48-50.
[42] 郭源,王承武,范源,等.儿童“不可复性”肱骨髁上骨折的治疗[J]. 中华小儿外科杂志,1998,19(2):5-7.
[43] 凌长敦, 庞国栋. 儿童肱骨髁上移位骨折致肘内翻畸形的探讨与预防[J].广西中医药, 2007,30(4): 50.
[44] 刘献祥,林木南,符臣学,等. 肱骨髁上骨折并发症98例临床分析[J]. 中国骨伤,2001,14(4):8-9.
[45] 王国平,张玉柱,王人彦,等.屈肘前臂旋前位整复固定治疗肱骨髁上骨折120例[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2002,17(2):150-151.
[46] 高光明,杜成高. 肱骨髁上骨折后肘内翻畸形的原因探讨[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,1997,5(6):51-52. |