2.1 关节软骨的结构特点、营养来源及其损伤修复特性
2.1.1 关节软骨的结构特点 人体正常的关节软骨呈白色、透明状,表面光滑,边缘规则整齐,其厚度为 2-7 mm,关节软骨的基本成分是软骨细胞和细胞外基质,其中软骨细胞只占1%,而细胞外基质占99%,基质中以Ⅱ型胶原纤维为主,约占50%,还有少量的Ⅵ型和Ⅺ型胶原。
成熟的软骨细胞多为2-8个成群分布于软骨陷窝内,这些软骨细胞由同一个母细胞分裂增殖而成,称为同源细胞群。软骨基质主要成分为水分、蛋白多糖和胶原纤维,它有10%-15%的蛋白多糖、10%-15%的胶原和70%-80%水分。
2.1.2 关节软骨的营养来源 关节软骨没有血液直接供应,其营养全部来源于滑膜分泌的滑液,其中的营养成分靠关节面之间的挤压作用进入软骨。所以关节软骨的营养供应不仅取决于滑膜正常分泌滑液,而且还取决于关节的适当运动。
关节的适当运动能把滑液中含有的营养成分挤压进软骨中。王宇泽等
[5]研究发现失去关节液的营养后,关节软骨表现出早期退变迹象,关节液营养对关节软骨有重要影响。
2.1.3 关节软骨的损伤与修复 研究表明关节缺乏活动和关节过度活动引起老损均可引起关节软骨的损 伤[6-7],其损伤后修复受年龄、关节运动及负重的影响。
目前治疗关节软骨损伤的方法包括:①刺激关节软骨修复与再生技术如微骨折技术。②关节软骨移植技术如自体软骨移植和同种异体软骨移植。③组织工程技术。近年来,细胞生物与生物材料学的迅速发展促进了组织工程的研究。由于软骨只有一种细胞成分,组织工程在软骨领域具有很大的优势。
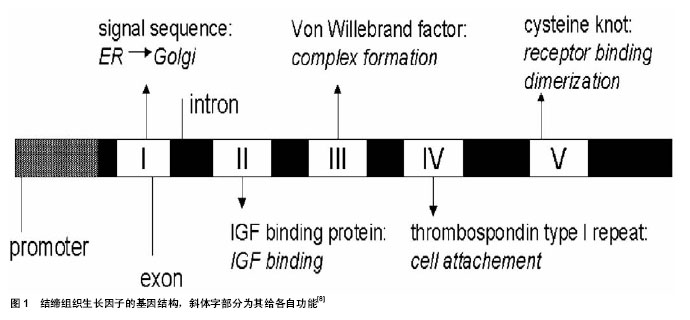
2.2 结缔组织生长因子的蛋白结构 结缔组织生长因子属于CCN蛋白家族,又称CCN2。人类结缔组织生长因子基因位于染色体6q23.1 区,含有5个外显子和4个内含子。其mRNA长2.4 kb,5端编码区由1个分泌肽和4个功能结构域组成,3端非编码区含有负性调节元件,可抑制结缔组织生长因子基因的转录后表达[2]。基于对氨基酸序列的研究,预测5个外显子编码一个信号肽和4个不同的结构域,这个结构域其他已知的相关蛋白具有高度相似性[8]。如图1。
结缔组织生长因子是一种富含半胱氨酸的分泌多肽,共包括4个结构区域:① IB区-结合胰岛素样生长因子蛋白结构域,该区含有的序列可以与胰岛素样生长因子特异结合。②VWC区-C型血管假性血友病因子结构域,与自身蛋白的寡聚化及二聚化有关。③TSP-1区-血小板反应蛋白1结构域。④cysteine-knot区-半胱氨酸羧基端结构域[9]。
 2.3 结缔组织生长因子与软骨细胞修复
2.3 结缔组织生长因子与软骨细胞修复 起初对结缔组织生长因子的大部分研究重点都放在了组织纤维化的方面,因为在多种组织纤维化过程中发现了转化生长因子β,而研究发现转化生长因子β又是诱导结缔组织生长因子基因表达的关键因子,并且研究还发现结缔组织生长因子促进了纤维母细胞的增殖、迁移及黏附。
生理状态下结缔组织生长因子在组织中表达程度低,病理状态下经高机械力病理负荷的刺激,在组织器官中的表达可明显上调。后来发现结缔组织生长因子同样存在于软骨细胞中,并由此开展了结缔组织生长因子研究的崭新领域,尤其在探索其生理功能方面。
2.3.1 结缔组织生长因子对关节软骨及其修复过程中的功能 研究发现正常关节软骨的各个阶段均可表达结缔组织生长因子[10],在正常人以及患有骨性关节炎患者的关节腔内均检测到结缔组织生长因子的表达,并且研究还表明结缔组织生长因子的表达与骨性关节炎患者关节软骨破坏处上的纤维组织发展有关。
Takigawa等[11]对初生小鼠的研究发现,在小鼠骨骼发育过程中软骨肥大带和钙化带软骨细胞可高水平表达结缔组织生长因子mRNA,并且在软骨下骨化过程中生成的结缔组织生长因子通过加速血管形成及软骨细胞的增殖和分化起到了关键作用。
Nishida等[12-13]通过研究体外培养的兔关节软骨细胞时重组人结缔组织生长因子产生的影响发现,重组人结缔组织生长因子可促进其分化及增殖,但不促进其矿化或肥大。
另外,早期骨骼发育过程中要获得软骨力学性能,需要结缔组织生长因子。
结缔组织生长因子mRNA在正常关节软骨细胞及处于休眠期的关节软骨细胞中几乎不表达或低水平表达,但在生长期或骨性关节炎软骨细胞中表现为强烈表达。其研究还发现单纯的用含有结缔组织生长因子的水溶液来修复用MIA制作的鼠膝关节骨性关节炎模型,效果并不理想,并分析可能的原因是在关节腔内,结缔组织生长因子发挥生物活性的半衰期短,于是他们将结缔组织生长因子固定在明胶水凝胶内,在修复MIA制作的鼠膝关节骨性关节炎模型时取得了理想效果,并且有效剂量每100 g体质量不小于1.5 μg。
Eguchi等[14]研究显示,在骨性关节炎早期结缔组织生长因子在软骨浅层的软骨细胞呈阳性表达,但是较为严重患者的软骨增殖区软骨细胞呈强阳性表达,在骨质增生患者的骨赘肥大区和增殖区均呈强阳性表达。
据有关报道显示,当小鼠结缔组织生长因子基因表达有缺陷时,在出生后不久便会死于软骨细胞分裂增殖异常及软骨基质的合成障碍[15],可以得出结缔组织生长因子对软骨损伤后具有再生作用的结论。
有关实验的结果显示,作为软骨细胞特异性基因表达产物的结缔组织生长因子,在软骨细胞的代谢过程中作用明显,能够保持机体软骨组织相对完整;结缔组织生长因子具有诱导并促进软骨细胞增殖与分化的功能,被视为软骨组织损伤后再修复发挥重要作用的因子之一。
骨性关节炎动物实验显示损伤、退变软骨细胞之结缔组织生长因子mRNA过度表达,给予重组结缔组织生长因子可诱导软骨细胞增殖和分化,促进Ⅱ型胶原和蛋白聚糖合成,因此结缔组织生长因子是软骨细胞生长、增殖、分化的关键生长因子之一,贯穿软骨修复整个过程。
Zhu等[16]在利用转染结缔组织生长因子基因骨髓间充质干细胞结合NaOH处理后的聚乳酸乙醇酸支架修复兔关节软骨的研究中发现,当骨髓间充质干细胞转染了表达结缔组织生长因子基因的腺病毒后,这些细胞会持续不断的表达结缔组织生长因子蛋白并且加速了骨髓间充质干细胞的分化,最终使糖胺聚糖和胶原的表达增加。这为结缔组织生长因子刺激诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化方面提供了明确的证据,但是该研究发现产生的结缔组织生长因子蛋白不能刺激骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖。
2.3.2 结缔组织生长因子在关节软骨修复过程中的信号通路 Cruzado等[17]研究发现,结缔组织生长因子可通过细胞外信号调节激酶及p38有丝分裂原蛋白激酶在促进关节软骨细胞分化和增殖方面发挥重要作用。
Yosimichi等[18]研究发现,氨基末端激酶(JUK)及大部分MAPK也参与结缔组织生长因子信号传导,通过研究信号传导上游激酶发现蛋白激酶A、蛋白激酶B、蛋白激酶C和磷脂酰肌醇激酶也在结缔组织生长因子促进人关节软骨细胞分化过程中的发挥信号转导的作用,其中蛋白激酶B主要在细胞核内参与调节结缔组织生长因子的表达。
作为蛋白激酶C的抑制剂,卡弗他丁(calphostin)C可抑制蛋白激酶C、调节激酶、p38有丝分裂原蛋白激酶的活性,从而影响结缔组织生长因子的作用。但是卡弗他丁C没有明显抑制JUK的活性的作用。
作为细胞表面表达受体的主要成员,整合素(integrin),结缔组织生长因子可结合关节软骨细胞的整合素α5β1从而加强整合素α5表达,说明结缔组织生长因子在其中的过程中发挥着配体的作用。在关节软骨细胞中结缔组织生长因子通过调节整合素α5的表达和细胞外基质的生成,激活整合素介导的信号通路而发挥作用。
Wnt信号传导通路参与传递生长刺激信号[19],Mercurio等[20]通过对非洲爪蟾蜍的胚胎的研究证实,通过自身CT结构域,结缔组织生长因子可与Wnt信号传导通路相互联系。相关实验证实在软骨内结缔组织生长因子在干细胞时期时核内转录因子T细胞因子(TCF)-淋巴细胞增强因子(IEF)-Sox9复合体,而在肥大软骨细胞阶段表现为TCF-LEF-β-连环蛋白(β-catenin)复合体。
因此Huang等[21]认为wnt信号通路通过调整复合体中Sox9和β-catenin来调整结缔组织生长因子水平。
Strassburg等[22]研究则发现,通过调节结缔组织生长因子可调节Sox9水平。此外,有研究表明软骨内Ras相关C3肉毒素底物1(Racl)和肌动蛋白信号通路也参与调节结缔组织生长因子表达[23]。
2.3.3 结缔组织生长因子与其他细胞因子及药物在关节软骨修复中的相互作用 前列腺素E2是重要的细胞因子之一,为花生四烯酸的代谢产物,当创伤后应激、炎症等情况发生时发挥重要作用。
Masuko等[24]进行了评估前列腺素E2是否与结缔组织生长因子在关节软骨中表达的调控有关的相关研究,结果显示,前列腺素E2和白细胞介素1β都抑制了人类关节软骨中结缔组织生长因子的表达,并且前列腺素E2这种抑制效果呈EP4受体依赖性。
氨基葡萄糖是人体内合成的物质,是形成软骨细胞的重要营养素,是健康关节软骨的天然组织成份。Ali等[25]研究发现氨基葡萄糖能增加结缔组织生长因子mRNA在肝脏、肾脏及关节软骨的表达,从而产生了对长期服用氨基葡萄糖安全性的担忧。
结缔组织生长因子为转化生长因子β1的下游调节区域[26],Arnott等[27-28]研究结果显示转化生长因子β1可诱导成骨细胞中结缔组织生长因子的表达,并且在转化生长因子β1诱导成骨细胞产生胞外基质的过程中,结缔组织生长因子为其重要的下游调节器。由此可知结缔组织生长因子和转化生长因子β1有着密切的关系,这二者对关节软骨而言意义重大。
骨形态发生蛋白同样属于转化生长因子β超家族成员之一,为酸性多肽。
目前对骨形态发生蛋白2在关节软骨修复过程中的作用研究显示,其具有促进关节软骨细胞分化、细胞外基质形成并抑制关节软骨细胞去分化、诱导间充质细胞向关节软骨细胞不可逆地分化的作用[29]。
Maeda等[30]研究发现结缔组织生长因子主要通过CT结构域和部分VWC结构域与骨形态发生蛋白2相互作用,关节软骨培养中将结缔组织生长因子和骨形态发生蛋白2联合应用可降低ERKl/2磷酸化,在刺激细胞生长上要低于结缔组织生长因子或骨形态发生蛋白2的单独作用,但能使关节软骨细胞表型基因和蛋白多糖合成增加,表现出细胞表型成熟化。所以认为结缔组织生长因子、骨形态发生蛋白2在关节软骨细胞分化和成熟方面具有协同作用。
血管内皮生长因子是血管内皮细胞特异性的肝素结合生长因子,可在体内诱导血管新生,具有促进血管生成的作用。研究关节软骨内骨化的过程中国发现结缔组织生长因子变异体增生部分软骨内骨化受限制,于此同时血管内皮生长因子表达相应减少,故认为结缔组织生长因子还具有促进关节软骨生长板内血管生成的作用[31]。
成纤维细胞生长因子由平滑肌细胞、内皮细胞、巨噬细胞分泌,可促进内皮细胞的游走和平滑肌细胞的增殖,不能使平滑肌细胞游走,能够促进新血管形成,修复损害的内皮细胞。
Abd EI Kader等[32]在尝试寻找结缔组织生长因子的功能协同的新的分子物时发现了成纤维细胞生长因子1。进一步研究发现,骨性关节炎患者的关节软骨细胞对成纤维细胞生长因子1和结缔组织生长因子表达呈现明显相关性增加。


