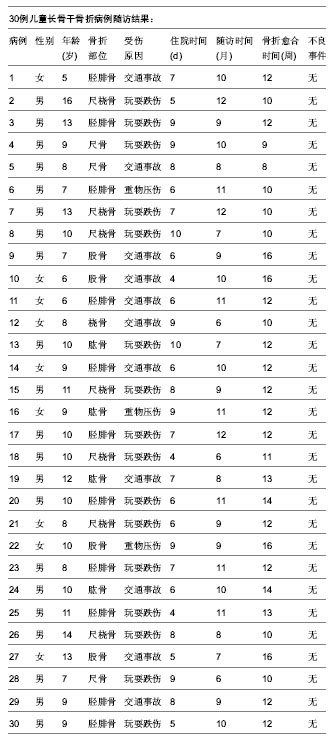
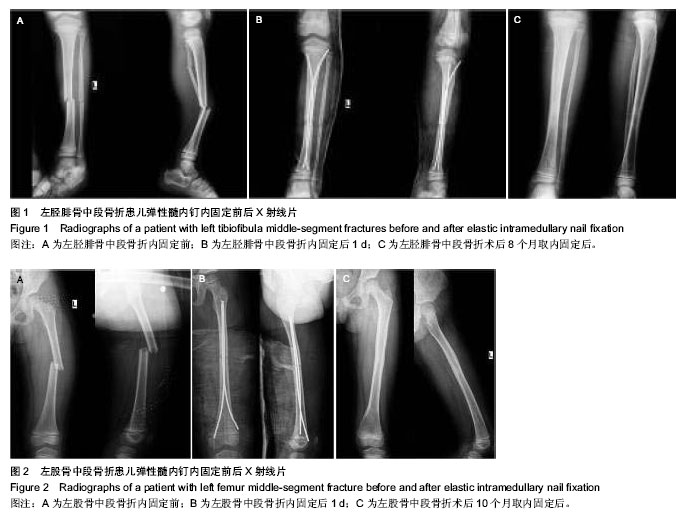
| [1] Ligier JN, Metaizeau JP, Prévot J,et al. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fractures in children. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1988;70(1):74-77.
[2] Fernandez FF, Eberhardt O, Wirth T. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing as alternative therapy for the management of paediatric humeral shaft fractures.Z Orthop Unfall. 2010;148 (1):49-53.
[3] Weinberg AM, Castellani C, Amerstorfer F. Elastic Stable Intramedullary Nailing (ESIN) of forearm fractures. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2008;(4-5):285-296.
[4] Maier M, Marzi I. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing of femur fractures in children. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2008; (4-5): 364-372.
[5] 吴素英.髓内钉置入治疗儿童股骨干骨折:来源于SCI数据库的文献分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(30):5670-5567.
[6] 王华明,陈志龙,李卫平,等.弹性髓内钉治疗儿童股骨干骨折钢板固定失效病例[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(26): 4819-4825.
[7] Flynn JM, Hresko T, Reynolds RA, et al. Tianium elastic nails for pediatric femur fractures: a multicenter study of early results with analysis of complications. J Pediatr Orthop. 2001; 21(1):4-8
[8] 陈博昌,王志刚,杨杰,等.弹性髓内针交叉固定治疗儿童长骨骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2003,11(9):598-601.
[9] Aktu?lu K, Ozkayin N. Long-term results of elastic intramedullary nailing in pediatric femoral shaft fractures. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2003;9(3):203-208.
[10] Nisar A, Bhosale A, Madan SS, et al. Complications of Elastic Stable Intramedullary Nailing for treating paediatric long bone fractures. J Orthop. 2013;10(1):17-24.
[11] Furlan D, Pogoreli? Z, Biotic M, et al. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing for pediatric long bone fractures: experience with 175 fractures. Scand J Surg. 2011;100(3): 208-215.
[12] Lu B, Liu P, Wang Y. Application of elastic intramedullary nail in the treatment of both ulna and radius fractures in children. Zhong Hua Yi Xue Za Zhi.2014;94(24):1882-1885.
[13] 刘国庆,王文己,时红萍,等.弹性髓内钉与钢板内固定修复前臂骨折疗效与安全性的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(26): 4248-4253.
[14] Lefèvre Y,Journeau P, Angelliaume A, et al. Proximal humerus fractures in children and adolescents. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100 (1 Suppl):S149-156.
[15] Antabak A, Luetic T, Ivo S, et al. Treatment outcomes of both-bone diaphyseal paediatric forearm fractures. Injury. 2013;44 (Suppl 3) S11-15.
[16] Kaiser MM, Zachert G, Wendlandt R, et al. Increasing stability by pre-bending the nails in elastic stable intramedullary nailing: a biomechanical analysis of a synthetic femoral spiral fracture model. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(5):713-718.
[17] Doser A,Helwig P, Konstantinidis L, et al. Does the extent of prebending affect the stability of femoral shaft fractures stabilized by titanium elastic nails? A biomechanical investigation on an adolescent femur model.J Pediatr Orthop. 2011;31 (8):834-838.
[18] Richter D, Ostermann PA, Ekkernkamp A, et al. Elastic intramedullary nailing: a minimally invasive concept in the treatment of unstable forearm fractures in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 1998;18(4):457-461.
[19] Perez A, Mahar A, Negus C, et al. A computational evaluation of the effect of intramedullary nail material properties on the stabilization of simulated femoral shaft fractures. Med Eng Phys. 2008;30(6):755-760.
[20] Sinikumpu JJ, Keränen J, Haltia AM, et al. A new mini-invasive technique in treating pediatric diaphyseal forearm fractures by bioabsorbable elastic stable intramedullary nailing: a preliminary technical report. Scand J Surg. 2013;102(4):258-264. |