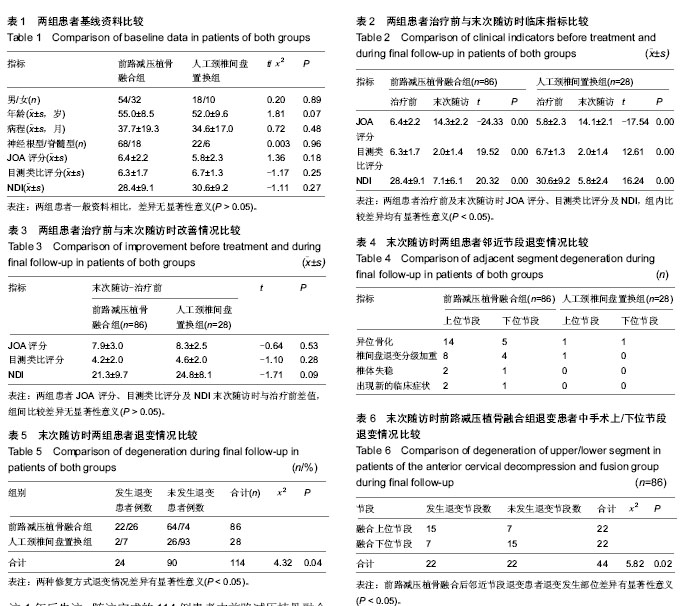
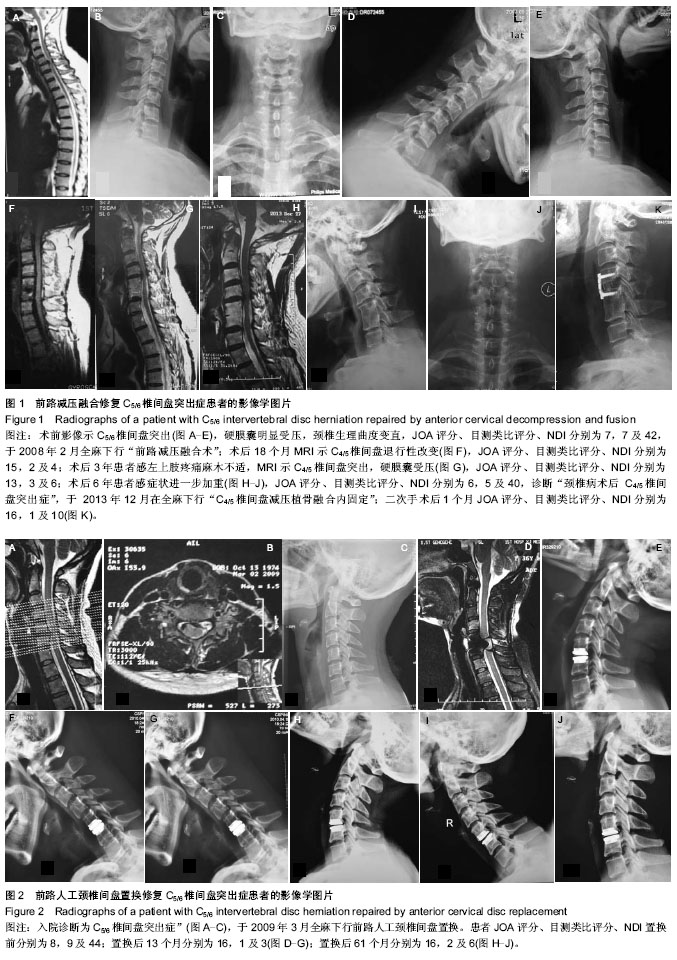
| [1] Takagi I,Eliyas JK,Stadlan N. Cervical spondylosis: an update on pathophysiology, clinical manifestation, and management strategies. Dis Mon.2011;57(10):583-591.
[2] Delamarter RB, Zigler J.Five-year reoperation rates, cervical total disc replacement versus fusion, results of a prospective randomized clinical trial.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(9): 711-717.
[3] 王岩,蔡斌,张雪松,等.Bryan人工颈椎间盘置换治疗单节段颈椎病的前瞻性临床研究[J].中华外科杂志,2008,46(5): 328-331.
[4] Vaccaro A, Beutler W,Peppelman W,et al. Clinical outcomes with selectively constrained SECURE-C cervical disc arthroplasty: two-year results from a prospective, randomized, controlled, multicenter investigational device exemption study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2013;38(26): 2227-2239.
[5] Demetriades AK,Ringel F,Meyer B.Cervical disc arthroplasty: a critical review and appraisal of the latest available evidence. Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg. 2014;41:107-129.
[6] Bin S, Xiangwang H, Sheng X. Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement for the Treatment of Adjacent Segment Disease after Anterior Cervical Decompression and Fusion.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014. [Epub ahead of print]
[7] Litrico S, Lonjon N, Riouallon G.Adjacent segment disease after anterior cervical interbody fusion. A multicenter retrospective study of 288 patients with long-term follow-up. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(6 Suppl):S305-309.
[8] 逢川,海涌,杨晋才,等.颈椎融合术后邻近节段退变的研究现状[J]. 脊柱外科杂志, 2013,11(2):112-114.
[9] Hilibrand AS, Carlson GD, Palumbo MA, et al.Radiculopathy and myelopathy at segments adjacent to the site of a previous anterior cervical arthrodesis. Bone Joint Surg Am.1999;81(4): 519-528.
[10] Sekhon LH.Cervical arthroplasty in the management of spondylotic myelopathy: 18-month results. Neurosurg Focus. 2004;17(3):E8.
[11] Caspar W, Geisler FH, Pitzen T, et al. Anterior cervical plate stabilization in one- and two-level degenerative disease: overtreatment or benefit? J Spinal Disord.1998;11(1):1-11.
[12] 刘忠军,党耕町.对颈椎人工椎间盘置换术现状的认识与思考[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2008,18(1):5-6.
[13] Bryan VE Jr.Cervical motion segment replacement. Eur Spine J. 2002;11 Suppl 2:S92-97.
[14] Wigfield CC, Gill SS, Nelson RJ. The new Frenchay artificial cervical joint: results from a two-year pilot study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(22):2446-2452.
[15] Cummins BH, Robertson JT,Gill SS.Surgical experience with an implanted artificial cervical joint.J Neurosurg.1998;88(6): 943-948.
[16] Wigfield CC,Skrzypiec D, Jackowski A,et al. Internal stress distribution in cervical intervertebral discs: the influence of an artificial cervical joint and simulated anterior interbody fusion.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2003;16(5):441-449.
[17] DiAngelo DJ, Roberston JT, Metcalf N.Biomechanical testing of an artificial cervical joint and an anterior cervical plate. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2003;16(4):314-323.
[18] Pointillart V.Cervical disc prosthesis in humans: first failure. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2001;26(5):E90-92.
[19] 盛斌,黄象望,向铁城,等.人工颈椎间盘置换治疗前路颈椎减压融合术后相邻节段病的中期随访观察[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013, 23(11):1050-1053.
[20] Bydon M, Xu R, Macki M, et al. Adjacent segment disease after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion in a large series. Neurosurgery. 2014;74(2)139-146.
[21] Chung JY,Kim SK,Jung ST,et al. Clinical adjacent-segment pathology after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: results after a minimum of 10-year follow-up.Spine J.2014; 14(10): 2290-2298.
[22] Phillips FM, Lee JY, Geisler FH,et al.A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Clinical Investigation Comparing PCM Cervical Disc Arthroplasty With Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2013;38(15): E907-918.
[23] Faldini C, Leonetti D, Nanni M,et al. Cervical disc herniation and cervical spondylosis surgically treated by Cloward procedure: a 10-year-minimum. J Orthopaed Raumatol. 2010;11(2): 99-103. |