1 对象和方法 Subjects and methods
设计:对比观察临床试验。
时间及地点:于2011年1月至2014年4月在粤北人民医院完成。
对象:选择2011年1月至2014年4月粤北人民医院收治的老年胸腰痛患者,MR检查提示胸腰椎椎体新鲜压缩性骨折,双能骨密度仪检查提示骨质疏松或严重骨质疏松。入院后对患者详细讲解治疗方式,术前签署知情同意书并告知术后复查资料用于研究用途。
纳入标准:临床诊断骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折者;椎体无结核、化脓等感染性病变者;穿刺点周围或穿刺通道无感染者;无心肺、肝、肾功能衰竭或昏迷者;无凝血功能障碍或出血倾向者;椎体压缩程度≤80%者;体质良好,能较长时间俯卧而耐受手术者。
试验分组:纳入患者41例,共60个椎体,随机分为高黏度骨水泥治疗及低黏度骨水泥治疗,高黏度骨水泥组中患者根据经济情况自愿选择高黏度骨水泥椎体成形治疗或椎体后凸成形治疗。①高黏度骨水泥椎体成形组:共22例,其中男7例,女15例;年龄61-87岁,平均(74.14±8.86)岁;共33个椎体,其中T8 1个,T9 2个,T10 3个,T11 2个,T12 5个,L1 4个,L2 8个,L3 5个,L4 2个,L5 1个;13例为单节段压缩骨折,7例为双节段压缩骨折,2例为多节段压缩骨折;受伤到手术时间为3-180 d,平均(20.2±15.9) d;3例有既往椎体成形手术史,2次骨折相隔时间4-96周(60,96,4周),平均53.3周。②高黏度骨水泥椎体后凸成形组:共5例,其中男4例,女1例;年龄52-86岁,平均(72.80± 12.95)岁;共7个椎体,其中T10 1个,T12 3个,L1 1个,L2 1个,L4 1个;3例为单节段压缩骨折,2例为双节段压缩骨折;受伤到手术时间为3-180 d,平均为(79.0±65.2) d。③低黏度骨水泥椎体成形组:共14例,其中男3例,女10例;年龄56-86岁,平均(73.71±8.51)岁;共20个椎体,其中T8 2个,T9 1个,T12 5个,L1 4个,L2 3个,L3 3个,L4 1个,L5 1个;9例为单节段压缩骨折,4例为双节段压缩骨折,1例为多节段压缩骨折;受伤到手术时间为7-180 d,平均(51.25±56.68) d;2例有既往椎体成形手术史,2次骨折相隔时间22,86周,平均59周。
亚组设置:将高黏度骨水泥椎体成形组、低黏度骨水泥椎体成形组据骨水泥注射量分为:高剂量组(>3.0 mL)和低剂量组(≤3.0 mL);据骨折至手术时间分为新鲜组(<3周)、亚急性组(3-6周)、陈旧组(>6周);据术前椎体压缩程度参考Genant半定量法的椎体骨变形分度方 法[2],分为Ⅰ度组(压缩率<0.25)、Ⅱ度组(0.25-0.40)和Ⅲ度组(> 0.40)。
材料:高黏度骨水泥(规格型号:1220/I,产品标准编号:SPA01-2002<骨水泥>,骨水泥主要成分为聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯,骨水泥变硬的时候会释放一定的单体,具有一定的毒性,会引起生命体征的波动,极少有过敏者,变硬后无细胞毒性,无血液及组织相容性,不降解,注册证编号:国药管械(进)2003第3650329号(更),生产公司:意大利Tecres S.P.A公司);低黏度骨水泥,主要成分为聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯(规格型号:1230/I,产品标准编号:进口产品注册标准YZB/ITA0267,注册证编号:国食药监检(进)2010第3650613号(更),生产公司:意大利Tecres S.P.A公司);“龙冠”牌椎体成形成套手术器械(规格型号:20 mL,产品标准号:YZB/国 0313-2010,产品注册编号:国食药监械(准)字2010第3100560号);“麦瑞克”牌椎体后凸成形手术器械(规格型号:15 mL,产品标准编号:YZB/粤中0022-2010,产品注册编号:粤中食药监械(准)字2010第1100062号);飞利浦移动C臂X射线机(荷兰皇家飞利浦电子公司生产);GE64排128层高档螺旋CT(Lightspeed VCT,美国GE公司生产)。
方法:
椎体成形治疗方法:根据术前影像学检查及术中C臂透视下定位责任椎及拟穿刺的椎弓根,确定进针位置及角度。消毒、麻醉:患者取俯卧位,垫体位,常规术区消毒,用1%利多卡因在进针途径进行局部浸润麻醉。在椎弓根影的外上侧进针(左侧:椎弓根影10点位置,右侧:椎弓根影2点位置),钻入套管针,当针尖进入椎弓根、椎体中部及前部时,正位片显示穿刺针尖分别位于椎弓根影外侧壁、椎弓根影中线处及椎弓根影内侧缘,此时可继续钻入;侧位片显示针尖到达椎体前正中3/4处时,针尾略向头侧倾斜,针尖的斜面朝向椎体中线为理想位置。调制高黏度或低黏度骨水泥,装入旋转加压装置,在骨水泥拉丝期,C臂透视监视下旋转加压将骨水泥缓慢注入椎体,每旋转1圈注射量为0.30 mL,当椎体旁静脉丛显影或者骨水泥到达椎体后壁时,应立即停止注射,以防止骨水泥进入椎管或者血管内。通过填充器上的刻度读出骨水泥的注射量,待骨水泥将要凝结时旋转穿刺针,防止其被骨水泥黏牢而导致拔出困难,待骨水泥完全凝固后,拔出穿刺针;压迫止血,敷贴包扎伤口。手术过程中常规心电监护及吸氧。
椎体后凸成形治疗方法:确定穿刺点及穿刺方法同椎体成形治疗方法。用生理盐水将压力泵填充满,将压力泵连接管与骨水泥填充器后部相接,排出残留的空气;调制好骨水泥并装入骨水泥填充器;在骨水泥拉丝期,C臂透视监视下旋转加压将骨水泥缓慢注入椎体,每旋转1圈注射量为0.30 mL,当椎体旁静脉丛显影或者骨水泥到达椎体后壁时,应立即停止注射,以防止骨水泥进入椎管或者血管内。通过填充器上的刻度读出骨水泥的注射量,待骨水泥将要凝结时旋转穿刺针,防止其被骨水泥黏牢而导致拔出困难,待骨水泥完全凝固后,拔出穿刺针;压迫止血,敷贴包扎伤口。手术过程中常规心电监护及吸氧。
主要观察指标:术后所有患者均复查CT,通过CT的三维成像和容积再现功能,在影像工作站上清晰重现术后椎体及骨水泥等三维立体图像(CT扫描的层厚为0.625 mm),并利用工作站的相关功能对骨水泥及椎体进行测量。
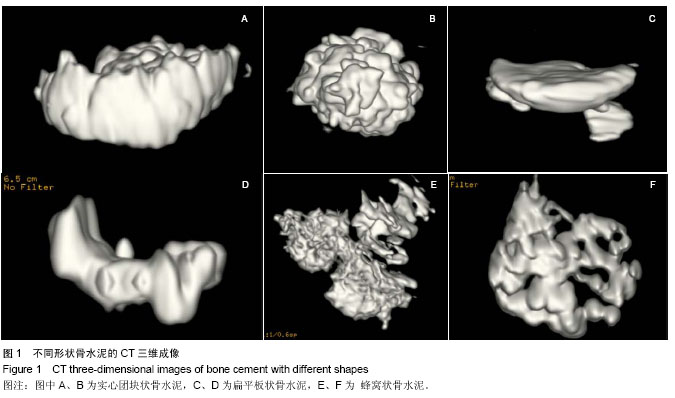
观察记录骨水泥在椎体内的分布特点:骨水泥在椎体内是否到达上下终板,在骨水泥中心平面是否越过椎体中线;进一步判断骨水泥在椎体内均匀分布或是偏心分布等,以及观察骨水泥的形状,具体分为实心团块状、扁平板状、蜂窝状(图1)。
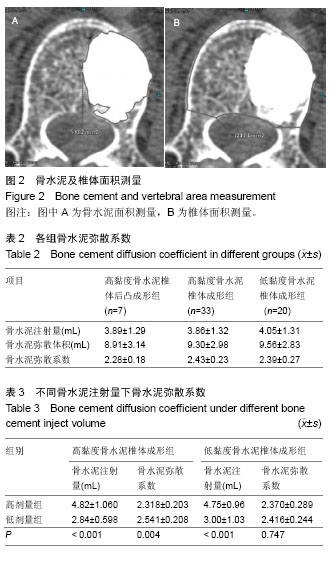
骨水泥中心平面弥散面积及所在平面椎体面积的测量:骨水泥中心平面弥散面积及所在平面椎体面积比值为骨水泥相对填充面积。在Adw 4.5影像工作站上,调出骨水泥中心平面所在的横切片,点击工作站自身所带的不规则形状面积测量的功能,用鼠标勾画骨水泥中心平面弥散的边缘及所在椎体平面的边缘,点击鼠标右键,即可得出相关面积(图2)。
椎体内骨水泥弥散体积及椎体体积测量:体内骨水泥弥散体积及椎体体积比值为骨水泥相对填充体积。其中骨水泥的弥散体积是指:骨水泥注入椎体后沿骨小梁间隙及骨折线弥散,黏合骨小梁及其包绕的空间,而形成的一种由骨水泥、骨小梁、骨小梁间隙共同构成的三维空间结构[3]。
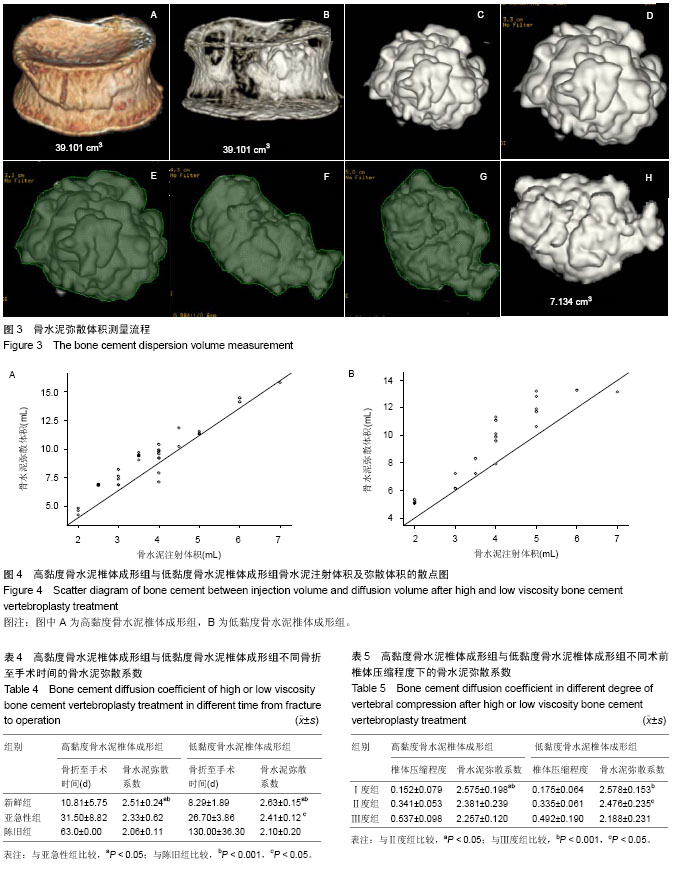
测量方法见图3所示:A:在Adw 4.5影像工作站上调出患者伤椎的VR图像→B:调节适合的CT值,清晰显现骨水泥三维立体图像,初步观察骨水泥在椎体内的分布情况 →C:继续调节窗值,完全显示骨水泥的形态→D:放大图像→E:点击Reformat软件包的切割功能键,用鼠标箭头在勾画出骨水泥弥散的边界,点击软件包上的“CUT OUTSIDE”键,切去骨水泥以外的组织→F:旋转调节至骨水泥的另一平面,余操作同E→G:继续旋转调节至骨水泥的另一平面,操作同E→经数次切割后通过调节CT窗值观察是否残留多余的椎体组织,若有,则调整适当的位置后,用鼠标箭头勾画出该多余部分,点击软件包上的“CUT INSIDE”将多余部分切除→H:切割完毕后,点击Reformat软件包的calculate 3D功能键,即可得出骨水泥的弥散体积。椎体体积的测量方法类似此流程。
骨水泥渗漏观察:观察Adw 4.5影像工作站上所重现的术后椎体及骨水泥等三维立体图像,记录和统计骨水泥渗漏情况(渗漏部位、渗漏量),分别计算出各组中骨水泥的渗漏率。
统计学分析:所得数据用SPSS 20.0统计软件进行统计学分析。①计算3组骨水泥注射体积、骨水泥弥散体积、骨水泥中心平面相对弥散面积、骨水泥相对弥散体积的均数及标准差,并对所得数据进行正态分布检验,计算各组骨水泥达到上下终板、中心平面过椎体中线、骨水泥各种形状所占比例。②用独立样本t 检验比较高黏度骨水泥椎体成形组与高黏度骨水泥椎体后凸成形组间、高黏度骨水泥椎体成形组与低黏度骨水泥椎体成形组间骨水泥弥散系数的差异。③利用Pearson相关性分析检验高黏度骨水泥椎体成形组、低黏度骨水泥椎体成形组骨水泥注射体积与骨水泥弥散体积的相关程度,行F显著性检验,如有差异,建立回归方程及绘制二者散点图;用独立样本t 检验比较分析高黏度骨水泥椎体成形组、低黏度骨水泥椎体成形组中骨水泥注射量对骨水泥弥散系数的影响。④用单因素方差分析比较分析高黏度骨水泥椎体成形组、低黏度骨水泥椎体成形组中不同骨折至手术时间、术前椎体压缩程度对骨水泥弥散系数的影响。⑤设定检验标准(α=0.05),定义P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义,P < 0.001为差异有非常显著性意义。