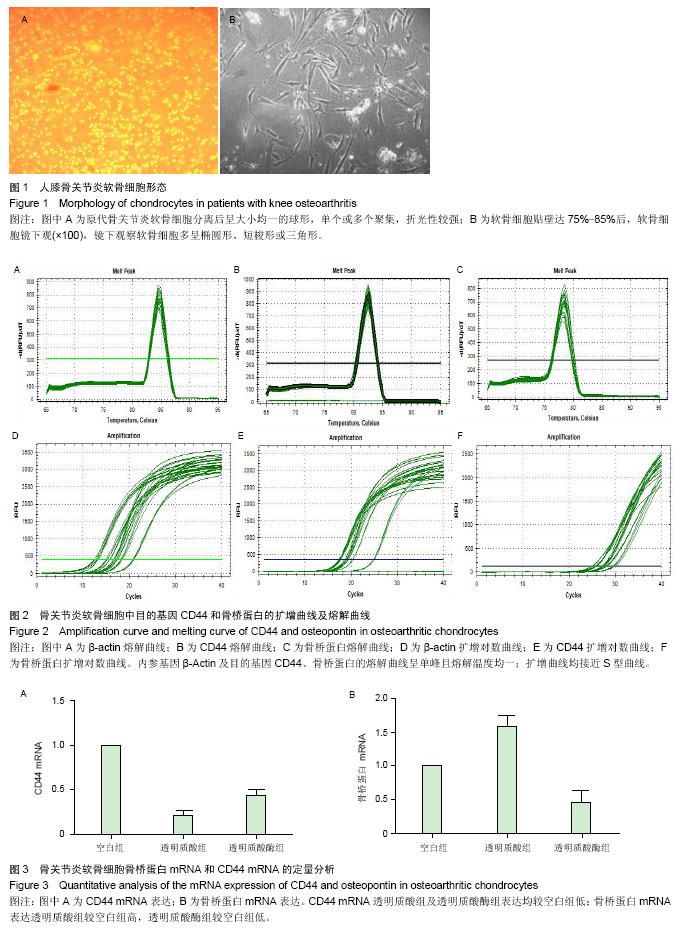
| [1] Pullig O,Pfander D,Swoboda B.[Molecular principles of induction and progression of arthrosis]. Orthopade. 2001; 30(11):825-833.
[2] Chen C, Tambe D T, Deng L, et al. Biomechanical properties and mechanobiology of the articular chondrocyte. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.2013;305(12):C1202-C1208.
[3] Laurent TC, Fraser JR. Hyaluronan. FASEB J.1992;6(7): 2397-2404.
[4] Felson DT, Lawrence RC, Dieppe PA, et al. Osteoarthritis: new insights. Part 1: the disease and its risk factors. Ann Intern Med. 2000;133(8):635-646.
[5] Fraser JR, Laurent TC, Laurent UB. Hyaluronan: its nature, distribution, functions and turnover. J Intern Med.1997;242(1): 27-33.
[6] Wells A F, Klareskog L, Lindblad S, et al.Correlation between increased hyaluronan localized in arthritic synovium and the presence of proliferating cells. A role for macrophage-derived factors. Arthritis Rheum.1992;35(4):391-396.
[7] Denhardt DT,Noda M.Osteopontin expression and function: role in bone remodeling. J Cell Biochem Suppl.1998;30-31: 92-102.
[8] Gravallese EM. Osteopontin: a bridge between bone and the immune system. J Clin Invest.2003;112(2):147-149.
[9] Balazs EA, Denlinger JL. Viscosupplementation: a new concept in the treatment of osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1993;39:3-9.
[10] Dahl LB, Dahl IM, Engstrom-Laurent A, et al. Concentration and molecular weight of sodium hyaluronate in synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other arthropathies. Ann Rheum Dis.1985;44(12):817-822.
[11] Burdo TH, Wood MR, Fox HS. Osteopontin prevents monocyte recirculation and apoptosis. J Leukoc Biol. 2007; 81(6):1504-1511.
[12] Lin YH, Yang-Yen HF. The osteopontin-CD44 survival signal involves activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway.J Biol Chem.2001;276(49):46024-46030.
[13] Screaton GR, Bell MV, Jackson DG, et al. Genomic structure of DNA encoding the lymphocyte homing receptor CD44 reveals at least 12 alternatively spliced exons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.1992;89(24):12160-12164.
[14] Naor D, Wallach-Dayan SB, Zahalka MA, et al. Involvement of CD44, a molecule with a thousand faces, in cancer dissemination. Semin Cancer Biol.2008;18(4):260-267.
[15] Bajorath J. Molecular organization, structural features, and ligand binding characteristics of CD44, a highly variable cell surface glycoprotein with multiple functions. Proteins. 2000; 39(2):103-111.
[16] Salter DM, Godolphin JL, Gourlay MS, et al.Analysis of human articular chondrocyte CD44 isoform expression and function in health and disease.J Pathol.1996;179(4):396-402.
[17] Zhang FJ, Luo W, Gao SG, et al. Expression of CD44 in articular cartilage is associated with disease severity in knee osteoarthritis.Mod Rheumatol.2013;23(6):1186-1191.
[18] Martinez-Sanz E, Ossipov DA, Hilborn J, et al. Bone reservoir: Injectable hyaluronic acid hydrogel for minimal invasive bone augmentation.J Control Release.2011;152(2):232-240.
[19] Mendes RM, Silva GA, Lima MF, et al. Sodium hyaluronate accelerates the healing process in tooth sockets of rats. Arch Oral Biol.2008;53(12):1155-1162.
[20] Kim J, Kim IS, Cho TH, et al. In vivo evaluation of MMP sensitive high-molecular weight HA-based hydrogels for bone tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;95(3): 673-681.
[21] Xu C, Wang Y, Yu X, et al. Evaluation of human mesenchymal stem cells response to biomimetic bioglass-collagen- hyaluronic acid-phosphatidylserine composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;88(1): 264-273.
[22] Gao C, Guo H, Downey L, et al. Osteopontin-dependent CD44v6 expression and cell adhesion in HepG2 cells. Carcinogenesis.2003;24(12):1871-1878.
[23] Zhang FJ, Gao SG, Cheng L, et al. The effect of hyaluronic acid on osteopontin and CD44 mRNA of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Rheumatol Int.2013;33(1):79-83.
[24] Chow G, Nietfeld JJ, Knudson CB, et al. Antisense inhibition of chondrocyte CD44 expression leading to cartilage chondrolysis.Arthritis Rheum.1998;41(8):1411-1419.
[25] Kim MS, Park MJ, Moon EJ, et al. Hyaluronic acid induces osteopontin via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway to enhance the motility of human glioma cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65(3):686-691.
[26] Brun P,Zavan B,Vindigni V,et al.In vitro response of osteoarthritic chondrocytes and fibroblast-like synoviocytes to a 500-730 kDa hyaluronan amide derivative. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2012;100(8):2073-2081.
[27] Julovi SM,Ito H,Nishitani K,et al.Hyaluronan inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-13 in human arthritic chondrocytes via CD44 and P38. J Orthop Res.2011;29(2):258-264.
[28] Hiraoka N, Takahashi KA, Arai Y, et al. Intra-articular injection of hyaluronan restores the aberrant expression of matrix metalloproteinase-13 in osteoarthritic subchondral bone. J Orthop Res.2011;29(3):354-360.
[29] Yasuda T. Comparison of hyaluronan effects among normal, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis cartilages stimulated with fibronectin fragment.Biomed Res.2010;31(1):63-69.
[30] Yatabe T, Mochizuki S, Takizawa M, et al. Hyaluronan inhibits expression of ADAMTS4 (aggrecanase-1) in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Ann Rheum Dis, 2009,68(6): 1051-1058.
[31] Dunn S, Kolomytkin OV, Waddell DD, et al. Hyaluronan- binding receptors: possible involvement in osteoarthritis. Mod Rheumatol.2009;19(2):151-155.
[32] Smith MM, Cake MA, Ghosh P, et al.Significant synovial pathology in a meniscectomy model of osteoarthritis: modification by intra-articular hyaluronan therapy. Rheumatology (Oxford).2008;47(8):1172-1178.
[33] Wang CT, Lin YT, Chiang BL, et al.High molecular weight hyaluronic acid down-regulates the gene expression of osteoarthritis-associated cytokines and enzymes in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with early osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2006;14(12): 1237-1247.
[34] Attur MG, Dave MN, Stuchin S, et al.Osteopontin: an intrinsic inhibitor of inflammation in cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 2001; 44(3):578-584.
[35] Matsui Y, Iwasaki N, Kon S, et al. Accelerated development of aging-associated and instability-induced osteoarthritis in osteopontin-deficient mice. Arthritis Rheum.2009;60(8): 2362-2371.
[36] Little CB, Barai A, Burkhardt D, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase 13-deficient mice are resistant to osteoarthritic cartilage erosion but not chondrocyte hypertrophy or osteophyte development. Arthritis Rheum.2009;60(12):3723-3733.
[37] Glasson SS, Askew R, Sheppard B, et al.Deletion of active ADAMTS5 prevents cartilage degradation in a murine model of osteoarthritis. Nature.2005;434(7033):644-648.
[38] Ashkar S, Weber GF, Panoutsakopoulou V, et al. Eta-1 (osteopontin): an early component of type-1 (cell-mediated) immunity. Science.2000;287(5454):860-864.
[39] O'Regan AW, Nau GJ, Chupp GL, et al. Osteopontin (Eta-1) in cell-mediated immunity: teaching an old dog new tricks. Immunol Today.2000;21(10):475-478.
[40] Smith MM, Russell AK, Schiavinato A, et al. A hexadecylamide-derivative of hyaluronan (HYMOVIS(R)) has superior beneficial effects on human osteoarthritic chondrocytes and synoviocytes than unmodified hyaluronan.J Inflamm (Lond).2013;10(1):26. |