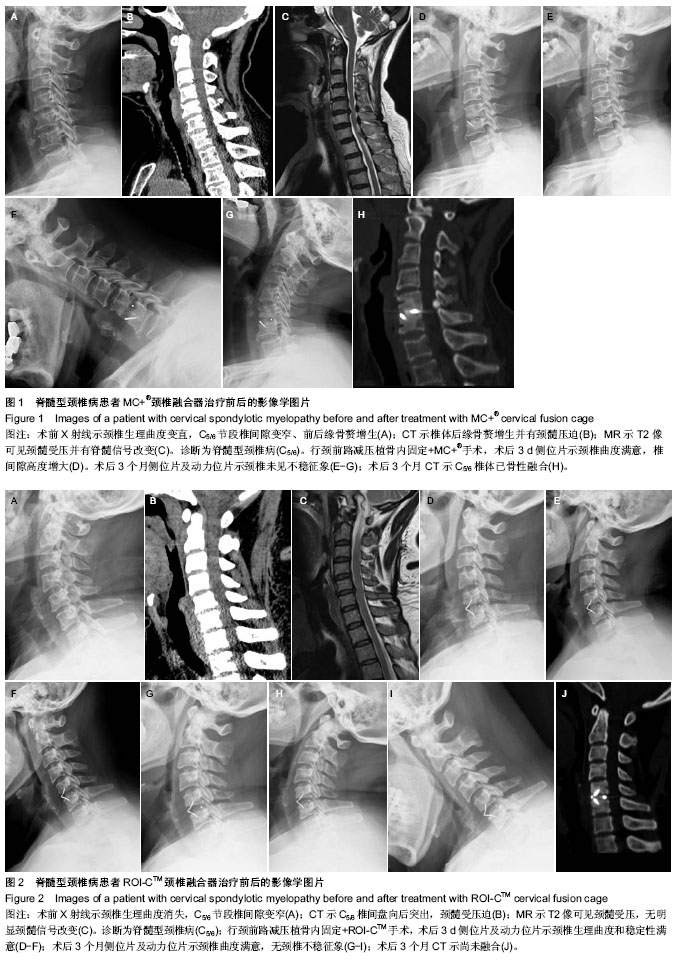
| [1] Jankowitz BT, Gerszten PC. Decompression for cervical myelopathy. Spine J. 2006;11(6):317-322.
[2] Gok B, Sciubba DM, McLoughlin GS, et al.Surgical treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy with anterior compression:a review of 67 cases. Neurosurg Spine. 2008; 9(2):152-157.
[3] Dean CL, Gabriel TP, Cassinelli EH, et al.Degengerative spondylolisthesis of the cervical spine:analysis of 58 patients treatment with anterior cervical decompression and fusion. Spine. 2009;9(6): 439-446.
[4] Katsuura A, Hukuda S, Saruhashi Y, et al. Kyphotic malalignment after anterior cervical fusion is one of the factors promoting the degenerative process in adjacent intervertebral levels. Eur Spine J. 2001;10(4):320-324.
[5] Hilibrand AS, Carlson GD, Palumbo MA, et al. Radiculopathy and myelopathy at segments adjacent tothe site of a previous anterior cervical arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81: 519-528.
[6] Yue WM, Brodner W, Highland TR. Persistent swallowing and voice problems after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion . Eur Spine J. 2005;7:677-682.
[7] 王少波,王圣林.颈椎前路手术后吞咽困难的原因分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,12(14):913-916.
[8] 祁敏,梁磊,新伟,等.颈前路多节段融合术后吞咽困难的原因分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2013,33(5):467-472.
[9] Goffin J, Casey A,Kehr P, et al. Prelimiary clinical experience with theBryancervical disc prosthesis.Neurosurg. 2002;51(3): 840-847.
[10] Fountas KN, Kapsalaki EZ, Nikolakakos LG, et al. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Associated Complications. Spine. 2007;(21):2310-2317.
[11] Pickett GE, Sekhon LH, Sears WR, et al.Complications with cervical arthroplasty. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006 ;4(2):98-105.
[12] Coric D, Finger F, Boltes P. Prospective randomized controlled study of the Bryan Cervical Disc: early clinical results from a single investigational site. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006;4(1):31-35.
[13] Leung C, Casey AT, Goffin J, et al. Clinical significance of heterotopic ossificationin cervical disc replacement: a prospective multicenter clinical trial. Neurosurgery. 2005;57: 759-763.
[14] Heidecke V, Burkert W, Brucke M, et al. Intervertebral disc replacement for cervical degenerative disease- clinical results and functional outcome at two yearsin patients implanted with the Bryan+ cervical disc prosthesis. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2008;150:453-459.
[15] Wang ZD, Zhu RF, Yang HL, et al. The application of a zero-profile implant in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. J Clin Neurosci. 2013;8 (13):00429-00433E.
[16] Kulkarni AG, Hee HT, Wong HK. Solis cage (PEEK) for anterior cervical fusion: preliminary radiological results with emphasis on fusion and subsidence. Spine J. 2007;7(2): 205-209.
[17] 华江,刘福存,王玮. ROI椎间融合器行前路颈椎间盘切除融合术治疗颈椎退行性病变早期临床结果[J].浙江中医药大学学报, 2013,37(7):877-880.
[18] 徐广辉,贾连顺.颈前路减压融合术后植骨融合的影像学评价方法及标准[J].中华外科杂志,2009,12(23):1824-1825.
[19] Lin CN, Wu YC, Wang NP, et al. Preliminary experience with anterior interbody titanium cage fusion for treatment of cervical disc disease. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2003; 19(5): 208-216.
[20] Morgan JP, Asfora WT. Extreme multi-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. S D Med. 2013;66(7):271-279.
[21] 祁敏,陈华江,杨立利.采用新型Zero-p颈椎椎间融合器置入治疗颈椎病的近期疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(24): 2232-2236.
[22] 贾龙,郑燕平,刘新宇. 颈前路减压cage融合术与自体髂骨块植骨钛板内固定术治疗脊髓型颈椎病的中期疗效[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011;21(1):28-32.
[23] Katsumi Y, Honma T, Nakamura T. Analysis of cervical instability resulting from laminectomies for removal of spine cord tumor. Spine. 1989; 14(11): 1171-1176.
[24] Lowery GL, McDonough RF. The significance of hardware failure in anterior cervical plate fixation. Patients with 2- to 7-year. Spine.1998;23(2):181-186.
[25] Geisler FH, Caspar W, Pitzen T. Reoperation in patients after anterior cervical plate stabilization in degenerative diseas. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998;23(8):911-920.
[26] Niu CC, Liao JC, Chen WJ, et al. Outcomes of Interbody Fusion Cages Used in 1 and 2-levels Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion: Titanium Cages Versus Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) Cages. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010;23(5):310-316. |