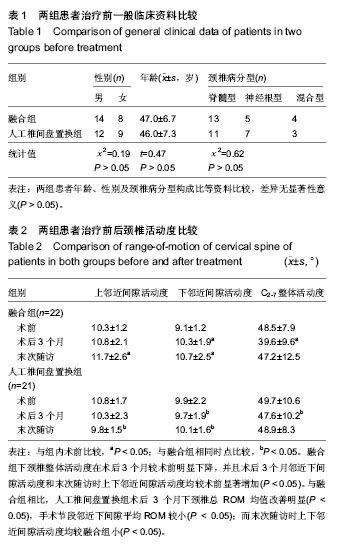
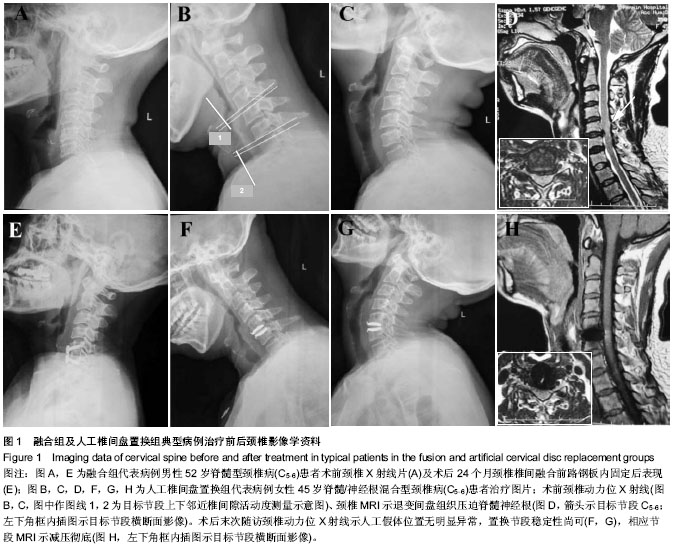
| [1] Cloward RB. Cervical diskography; technique, indications and use in diagnosis of ruptured cervical disks. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1958;79:563-574.
[2] Bose B. Anterior cervical fusion using Caspar plating:analysis of results and review of the literature. Surg Neurol. 1998;49:25-31.
[3] Goffin J, Geusens E, Vantomme N, et al. Long-term follow-up after interbody fusion of the cervical spine. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2004;17:79-85.
[4] Saavedra-Pozo FM, Deusdara RA, Benzel EC. Adjacent Segment Disease Perspective and Review of the Literature. Ochsner J. 2014;14(1):78-83.
[5] Lazaro BC , Yucesoy K , Yuksel KZ , et al. Effect of arthroplasty design on cervical spine kinematics: analysis of the Bryan Disc,ProDisc-C, and Synergy disc. Neurosurg Focus. 2010; 28: E6.
[6] Duggal N, Bertagnoli R, Rabin D, et al. ProDisc-C: an in vivo kinematic study. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2011;24:334-339.
[7] Park DK, Lin EL, Phillips FM. Index and adjacent level kinematics after cervical disc replacement and anterior fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(9): 721-730.
[8] Jaumard NV, Bauman JA, Guarino BB, et al. ProDisc cervical arthroplasty does not alter facet joint contact pressure during lateral bending or axial torsion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(2):E84-93.
[9] Nandyala SV, Marquez-Lara A, Fineberg SJ, et al. Comparison between cervical total disc replacement and anterior cervical discectomy and fusion of 1 to 2 levels from 2002 to 2009. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(1):53-57.
[10] 胥少汀.实用骨科学[M]. 4版.北京:人民军医出版社,2012: 1986-1990.
[11] Nikaido T, Kikuchi S, Yabuki S, et al. Surgical treatment assessment using the Japanese orthopedic association cervical myelopathy evaluation questionnaire in patients with cervical myelopathy: a new outcome measure for cervical myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34(23):2568-2572.
[12] Pietrobon R, Coeytaux R, Carey T, et al. Standard scales for measurement of functional outcome for cervical pain or dysfunction. Spine. 2002;27:515-522.
[13] Wu S, Ma C, Mai M, et al. Translation and validation study of Chinese versions of the neck disability index and theneck pain and disability scale. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010; 35(16): 1575-1579.
[14] Matz PG, Pritchard PR, Hadley MN. Anterior cervical approach for the treatment of cervical myelopathy. Neurosurgery. 2007;60(1 Supp1 1):S64-S70.
[15] Lopez-Espina CG, Amirouche F, Havalad V. Multilevel cervical fusion and its effect on disc degeneration and osteophyte formation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(9):972-978.
[16] Singh K, Phillips FM, Park DK, et al. Factors affecting reoperations after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion within and outside of a Federal Drug Administration investigational device exemption cervical disc replacement trial. Spine J. 2012;12(5):3372-3788.
[17] Barrey C, Campana S, Persohn S, et al. Cervical disc prosthesis versus arthrodesis using one-level, hybrid and two-level constructs: an in vitro investigation. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(3):432-442.
[18] Zigler JE, Delamarter R, Murrey D, et al. ProDisc-C and anterior cervical discectomy and fusion as surgical treatment for singlelevel cervical symptomatic degenerative disc disease:five-year results of a Food and Drug Administration study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(3):203-209.
[19] Wu JC, Huang WC, Tu TH, et al. Differences between soft-disc herniation and spondylosis in cervical arthroplasty: CT-documented heterotopic ossification with minimum 2 years of follow-up. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;16(2):163-171.
[20] Barbagallo GM, Assietti R, Corbino L, et al. Early results and review of the literature of a novel hybrid surgical technique combining cervical arthrodesis and disc arthroplasty for treating multilevel degenerative disc disease:opposite or complementary techniques? Eur Spine J. 2009;18 Suppl 1: 29-39.
[21] Salari B, MeAfee PC. CervicaI total disk replacement: complications and avoidance. Orthop Clin North Am. 2012; 43(1):97-107.
[22] de Beer N, Scheffer C. Reducing subsidence risk by using rapid manufactured patient specific intervertebral disc implants. Spine J. 2012;12(11):1060-1066.
[23] Bauman JA, Jaumard NV, Guarino BB,et al. Facet joint contact pressure is not significantly affected by ProDisc cervical disc arthroplasty in sagittal bending: a single-level cadaveric study. Spine J. 2012;12(10):949-959.
[24] Jaumard NV, Bauman JA, Guarino BB, et al. ProDisc cervical arthroplasty does not alter facet joint contact pressure during lateral bending or axial torsion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38(2):E84-93. |