| [1] Felson DT, Lawrence RC, Dieppe PA,et al.Osteoarthritis: new insights. Part 1: the disease and its risk factors.Ann Intern Med. 2000;133(8):635-646.
[2] Edgington SM.A new force in biotech: tissue engineering. Understanding how mechanical force combines with cytokines and other growth factors may help shape future biotech drugs.Biotechnology (N Y). 1994;12(4):361-364.
[3] Brittberg M, Peterson L, Sjögren-Jansson E, et al.Articular cartilage engineering with autologous chondrocyte transplantation. A review of recent developments.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A Suppl 3:109-115.
[4] Mandelbaum B, Browne JE, Fu F,et al.Treatment outcomes of autologous chondrocyte implantation for full-thickness articular cartilage defects of the trochlea.Am J Sports Med. 2007;35(6):915-921.
[5] Wang DW, Fermor B, Gimble JM,et al.Influence of oxygen on the proliferation and metabolism of adipose derived adult stem cells.J Cell Physiol. 2005;204(1):184-191.
[6] Levorson EJ, Santoro M, Kasper FK,et al.Direct and indirect co-culture of chondrocytes and mesenchymal stem cells for the generation of polymer/extracellular matrix hybrid constructs.Acta Biomater. 2014;10(5):1824-1835.
[7] Dahlin RL, Ni M, Meretoja VV,et al.TGF-β3-induced chondrogenesis in co-cultures of chondrocytes and mesenchymal stem cells on biodegradable scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2014;35(1):123-132.
[8] Portron S, Merceron C, Gauthier O,et al.Effects of in vitro low oxygen tension preconditioning of adipose stromal cells on their in vivo chondrogenic potential: application in cartilage tissue repair.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e62368.
[9] Wu SC, Chen CH, Chang JK,et al.Hyaluronan initiates chondrogenesis mainly via CD44 in human adipose-derived stem cells.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2013;114(11):1610-1618.
[10] Oni G, Lequeux C, Cho MJ,et al.Transdermal delivery of adipocyte-derived stem cells using a fractional ablative laser.Aesthet Surg J. 2013;33(1):109-116.
[11] Araña M, Peña E, Abizanda G,et al.Preparation and characterization of collagen-based ADSC-carrier sheets for cardiovascular application.Acta Biomater. 2013;9(4):6075- 6083.
[12] An C, Cheng Y, Yuan Q,et al.IGF-1 and BMP-2 induces differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells into chondrocytes-like cells.Ann Biomed Eng. 2010;38(4): 1647-1654.
[13] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.
[14] Xue D, Zheng Q, Zong C,et al.Osteochondral repair using porous poly(lactide-co-glycolide)/nano-hydroxyapatite hybrid scaffolds with undifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;94(1):259-270.
[15] Barbosa I, Garcia S, Barbier-Chassefière V,et al.Improved and simple micro assay for sulfated glycosaminoglycans quantification in biological extracts and its use in skin and muscle tissue studies.Glycobiology. 2003;13(9):647-653.
[16] Hwang NS, Varghese S, Puleo C,et al.Morphogenetic signals from chondrocytes promote chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.J Cell Physiol. 2007; 212(2):281-284.
[17] 尹航,张亚,王晓东,等.条件培养基诱导人骨髓间充质干细胞分化为软骨细胞的连续进行性特征[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(11):2170-2172,2181.
[18] Aung A, Gupta G, Majid G,et al.Osteoarthritic chondrocyte-secreted morphogens induce chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells.Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(1):148-158.
[19] Bian L, Zhai DY, Mauck RL,et al.Coculture of human mesenchymal stem cells and articular chondrocytes reduces hypertrophy and enhances functional properties of engineered cartilage.Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(7-8):1137- 1145.
[20] Wu L, Prins HJ, Helder MN,et al.Trophic effects of mesenchymal stem cells in chondrocyte co-cultures are independent of culture conditions and cell sources.Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(15-16):1542-1551.
[21] Fischer J, Dickhut A, Rickert M,et al.Human articular chondrocytes secrete parathyroid hormone-related protein and inhibit hypertrophy of mesenchymal stem cells in coculture during chondrogenesis.Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(9): 2696-2706.
[22] 吕晶,柯杰,王琳,等.与软骨细胞共培养和条件培养液诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(19):3421-3426.
[23] Egli RJ, Bastian JD, Ganz R,et al.Hypoxic expansion promotes the chondrogenic potential of articular chondrocytes. J Orthop Res. 2008;26(7):977-985.
[24] Foldager CB, Nielsen AB, Munir S,et al.Combined 3D and hypoxic culture improves cartilage-specific gene expression in human chondrocytes.Acta Orthop. 2011;82(2):234-240.
[25] Wei W, Yu XD.Hypoxia-inducible factors: crosstalk between their protein stability and protein degradation.Cancer Lett. 2007;257(2):145-156.
[26] Duval E, Baugé C, Andriamanalijaona R,et al.Molecular mechanism of hypoxia-induced chondrogenesis and its application in in vivo cartilage tissue engineering.Biomaterials. 2012;33(26):6042-6051.
[27] Lafont JE, Talma S, Hopfgarten C,et al.Hypoxia promotes the differentiated human articular chondrocyte phenotype through SOX9-dependent and -independent pathways.J Biol Chem. 2008;283(8):4778-4786.
[28] Müller J, Benz K, Ahlers M,et al.Hypoxic conditions during expansion culture prime human mesenchymal stromal precursor cells for chondrogenic differentiation in three-dimensional cultures.Cell Transplant. 2011;20(10): 1589-1602.
[29] Kanichai M, Ferguson D, Prendergast PJ,et al.Hypoxia promotes chondrogenesis in rat mesenchymal stem cells: a role for AKT and hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha.J Cell Physiol. 2008;216(3):708-715.
[30] Mandl EW, van der Veen SW, Verhaar JA,et al.Multiplication of human chondrocytes with low seeding densities accelerates cell yield without losing redifferentiation capacity. Tissue Eng. 2004;10(1-2):109-118. |
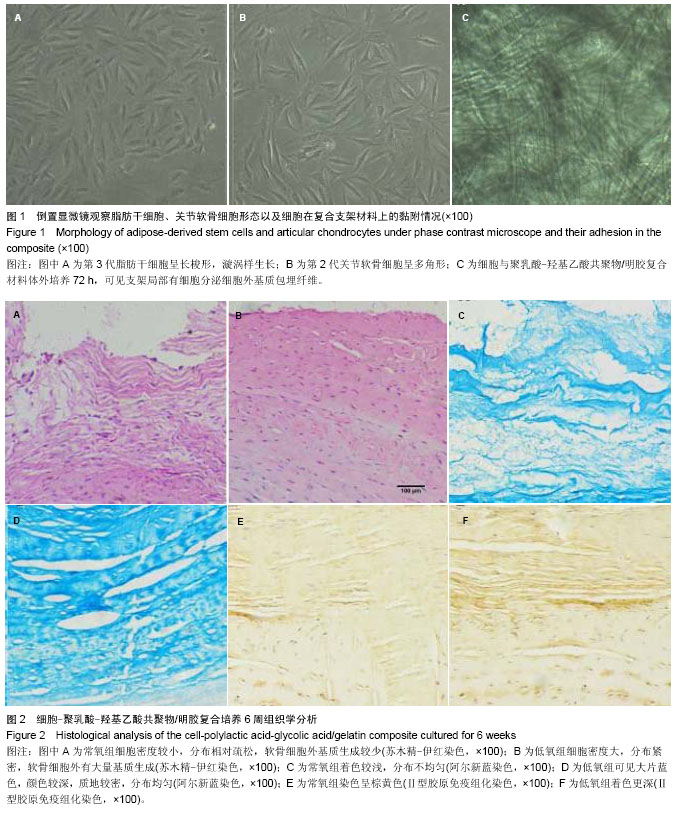
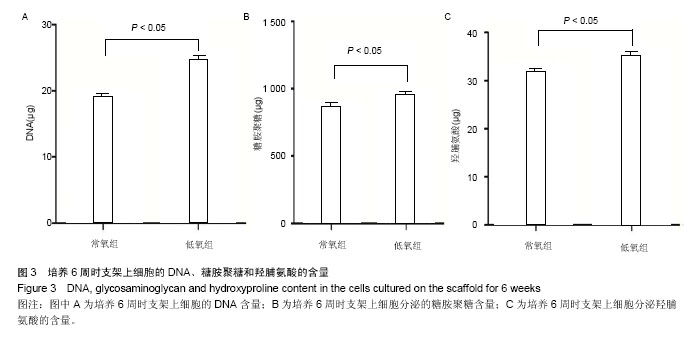
.jpg)