实验按照陈维华报道的方法,将10
2 CFU/mL的金黄色葡萄球菌注入犬的腰椎间盘,引导出犬的脊柱感染模型
[4]。实验成功的建立了发光基因标记金黄色葡萄球菌Xen29诱导的动物急性脊柱化脓性感染模型,感染模型成功率82.7%(24/29),再次证实了犬腰椎间隙注入细菌可稳定并安全的引导出犬的脊柱感染模型。本试验制作的脊柱感染模型与人的脊柱感染有很多相似之处,这种动物模型可以用来研究各种针对脊柱感染的各种预防和治疗措施。作者评估了应用一期清创、植骨和内固定的方法治疗化脓性感染术后感染的可能性, 研究了在内固定后不同时期在内植物上及附近组织是否有细菌存在,以及证明内固定后内植物附着细菌与内固定前脊柱所感染的细菌是否具有同源性。通过对以往相关文献的回顾,未发现有类似的动物实验。
3.1 抗生素的应用 应用抗生素预防感染目前还是减少内植物术后感染的最有效的一种方法。在涉及骨组织的手术中,一代或者二代头孢菌素例如,头孢唑啉、头孢孟多或头孢呋新可以作为一线药物
[7]。体外实验表明头孢孟多对于抗苯唑西林葡萄球菌更加有效,但是临床研究中发现以上头孢菌素并没有任何区别。实验应用的Xen29的药敏结果显示,它对青霉素不敏感而对庆大霉素敏感,实验中就是采用了头孢唑啉联合庆大霉素作为抗菌药物。作者采用头孢唑啉和庆大霉素联合抗感染还有一个原因是头孢唑啉为繁殖期杀菌药,庆大霉素为静止期杀菌药;前者破坏细胞壁的完整性,有助于后者进入细胞内作用于抗菌靶位。故两者联用可获得协同作用。抗生素应用的时机对于术后感染的预防也很重要。为了达到预防感染的目的,必须在从皮肤切开到手术结束的整个手术过程中保持药物在组织中的有效抑菌浓度
[8]。在一项动物实验中研究人员发现,抗生素的预防效果只能持续3 h。在另一项涉及2 847个手术的大型回顾性研究也证实了以上观点。研究表明抗生素应用太早(早于术前2 h)或太晚(晚于术后3 h),术后的切口感染率要增加6倍
[9]。实验采用了内固定前30 min肌注的方法应用抗生素,严格遵循了以上的抗菌素应用原则,有效地预防了内固定后感染。抗生素的应用是脊柱感染的治疗中必须的。但其应用的剂量、途经以及持续时间等方面还没有共识
[10]。本课题中,采用头孢唑啉1.0 g、庆大霉素8万单位肌肉注射,2次/d,连续应用4周抗生素抗感染治疗。
3.2 细菌的鉴定 以往对于细菌菌种和菌型的鉴定主要是依赖传统的细菌培养的方法,这种传统的方法有着一些难以克服的缺点,在某些情况下这种方法的假阴性率可以高达30%。随着科技的进步,越来越多的更加先进的技术被应用到细菌鉴定领域,其中包括PCR技术以及免疫组织化学技术等等。
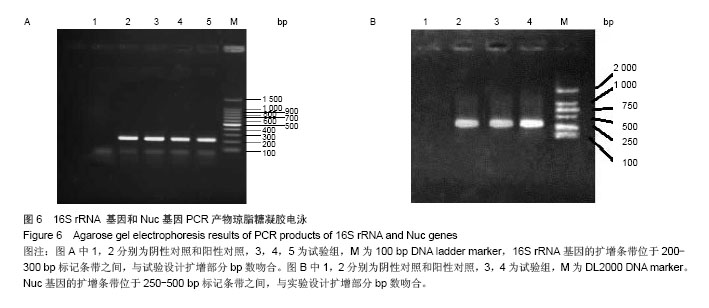
实验应用了PCR技术完成了对于生长在钛板以及附近骨组织的细菌检测。应用PCR技术可以对细菌进行定性以及定量检测。虽然近年来感染的PCR检测的技术,由于其较高的假阳性率而备受诟病。但本实验中有严格的阴性对照,以及采用细菌16S rRNA基因的PCR以及金葡菌的特异性基因nuc基因的PCR相结合的检测方法,可以显著提高检测结果的特异性。细菌的DNA基因中有一种被称为16S rRNA 基因,各种细菌的DNA中都存在这种基因并且这种基因的序列在各种细菌中高度保守。
作者将钛板以及周围骨组织的DNA提取出来,应用PCR技术对16S rRNA基因进行特异性扩增,如果这种16S rRNA基因存在,则说明有细菌生长
[11]。同时也对Nuc基因进行PCR检测。金黄色葡萄球菌产生的耐热核酸酶,由Nuc基因编码。Nuc基因为金黄色葡萄球菌特有的基因,且
在不同菌株之间高度保守
[6]。如果有Nuc基因存在,说明有金黄色葡萄球菌生长
[12]。
Kobayashi在一项实验中应用了PCR技术对45个临床可疑感染患者或没有感染患者的组织标本或者内植物进行了细菌检测,发现这些组织或内植物的细菌检测的阳性率高达40%,而应用传统细菌培养的方法的阳性率仅为31%
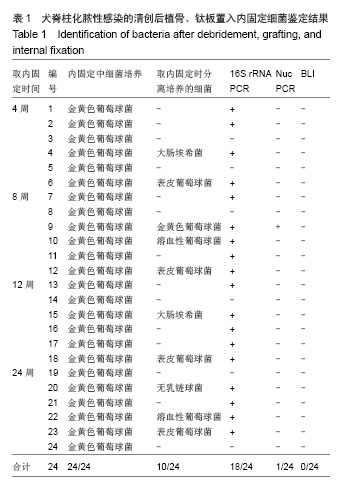
[11]。在本实验中传统细菌培养方法的细菌检出率仅为41.7%,这个检出效率远远低于应用PCR技术的分子学水平的检出率(75%)。说明应用PCR技术的检测方法的敏感性要优于传统的细菌培养的方法。同时也验证术后内植物表面细菌附着是一种普遍现象。
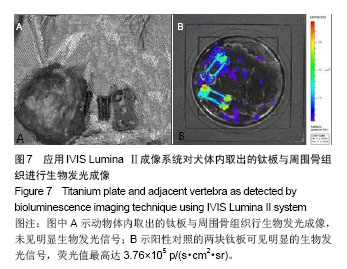
3.3 生物发光成像 生物发光成像技术是一门新兴的能够检测活体内基因表达的光学成像技术
[13]。目前已应用于感染性疾病、肿瘤等相关方面的细胞学研究
[14]。将基因标记生物发光细菌Xen29用于脊柱化脓性感染模型的建立尚属首次。采用BLI技术检测内植物和周围组织中存在的细菌是否为脊柱清创术前所感染的细菌(XEN29),从而确定二者是否具有同源性。金黄色葡萄球菌Xen29源自ATCC (American Type Culture Collection)12600。Xen29是将Lux操纵子(Lux ABCDE)通过分子克隆技术插入到金黄色葡萄球菌染色体上。所以Xen29能持续稳定的表达Lux ABCDE,能够自行产生荧光素酶及其底物合成酶,从而产生持续发光信号,不需要外源性底物。生物发光的原理为荧光素酶和底物结合产生发光信号,且特异性强。由于动物体内组织本身及钛板无自发光源,所以生物发光具有极低的背景,极高的信噪比,成像质量较高。
生物发光的主要特点就在于发光信号的高度可测性。每一次荧光素酶催化反应释放一个光子并发光,光的强度与标记细胞的数目线性相关。这种生物发光是肉眼无法观察到的,需要使用特殊的仪器观测并记录。如IVIS成像系统,
它通过一个超低温高灵敏的慢速扫描CCD相机及严格密闭的成像暗箱可以捕捉到此光子信号,经计算机和数据处理软件可对采集到的光子量进行处理,将光信号进行整体成像,从动物组织体表的信号水平得出发光细胞的数量。这样可以对生物发光成像进行定性分析及简单的定量计算。文献报道光学成像对于少到100多个生物发光细胞即可检测到发光信号
[15]。生物发光成像可得到一彩色图像,以颜色的变化表示光强度的变化,其中红色表示最强烈的发光,蓝色代表最弱的发光。发光信号的强度以荧光值(photons per second per cm2 per steradian,p/s/cm
2/sr)来表示。
光在动物组织内传播时小部分会被散射和吸收,光子遇到细胞膜和细胞质时会发生折射,而且不同类型的细胞和组织吸收光子的特性也不尽相同,同时体外检测体内发出的信号受体内发光源位置及深度影响。所以生物发光成像技术对发光细菌并不能绝对地定量。
3.4 假体周围感染的来源 对于内植物感染或假体周围的感染源问题,一直都存在很多的争论。主要的论点认为感染菌的来源有3个:一种观点认为内植物的感染是血源性感
染,是机体其他病灶的细菌经过血管传播而来。另一种观点认为内植物的感染是由于手术操作时污染的病源菌一直寄存在内植物及其周围组织,在适当时机时病源菌会繁殖,有可能造成临床感染[16]。而大多数的血源性感染被认为是由于表皮感染而引起的一过性的菌血症而造成,因为大多数血源性感染的病源菌都是来自表皮的正常寄生菌——葡萄球菌属的细菌。其他略少见的原因可以是细菌性尿道炎、肺炎、拔牙、肠道手术以及其他手术操作。
研究表明链球菌的感染可以占到假体周围感染的15%,而一般的肠道寄生菌感染如大肠埃希菌和绿脓杆菌感染可以占到21%
[16]。手术操作时污染的病源菌一般也认为来自表皮的正常寄生菌为主。假体周围感染的另一重要
机制是肠道寄生菌的细菌易位。也就是这些革兰染色阴性杆菌通过肠道内壁入血传播的过程[17]。已经发现的可以引起细菌易位的因素有很多种,例如:全胃肠外营养、年龄、应用抗生素、肿瘤以及免疫抑制、维生素A缺乏、失血性休克、严重的热损伤和内毒素以及腹膜内植物等因素
[18]。在本实验中治疗的创伤、围手术期抗生素的应用都可以是细菌易位的诱因,而造成细菌易位
[19]。从Bornside 描述的犬肠道内各种菌群分布频率可以看到,大肠杆菌属细菌是一种普遍存在于犬肠道中的细菌,不存在于犬的皮毛上;而葡萄球菌属是广泛寄生于人皮肤和犬的皮毛的细菌,很少出现在肠道中
[20]。所以从作者分离的主要细菌(既有大肠肝菌属,也有葡萄球菌属细菌)可以推断出钛板上寄生病菌的来源可能与血缘性传播、手术操作时的污染和肠道寄生菌的易位都有关系。
细菌在上亿年的自然选择和进化的过程中已经具备了在各种恶劣环境中生存的能力。细菌已经具备了在各种物体表面附着和生存的能力,医用内植物的表面当然也不例外。在内植物植入体内后,在各种诱因下,可能有几种病菌可以接触钛板表面,但只有一种或少数的几种细菌可以在这种特殊的条件下附着生长并形成生物膜,成为优势病菌。
表皮葡萄球菌是广泛存在于皮肤表面的条件致病菌,随着抗生素的广泛应用,医疗技术的进步,该菌已成为免疫缺陷者医院内感染(包括伤口感染和插管感染)的常见致病菌。实验中有4只动物标本培养出表皮葡萄球菌,占所有分离出来的细菌的40%(4/10)。可见表皮葡萄球菌是寄生于钛板及周围骨组织的重要病菌。在临床上由凝固酶阴性葡萄球菌引起的感染中,溶血性葡萄球菌普遍性仅次于表皮葡萄球菌。溶血性葡萄球菌为人体皮肤及黏膜正常寄生菌群,它是引起新生儿菌血症的常见病菌,并且是引起免疫抑制等免疫力低下患者以及假体周围感染的常见病菌
[21]。实验中有2只动物标本培养出溶血性葡萄球菌,占所有分离出来的细菌的20%(2/10)。大肠埃希菌也是本实验中分离培养的重要细菌,占到所有分离出来的细菌的20%(2/10)。在一项前瞻性研究中,Ahn从72例有各种症状患者体内取出的139个假体,而
E. coli的占所有分离出来的细菌的1.5%,是占到第3位的病菌,前两位分别是短小棒状杆菌(57.5%)和表皮葡萄球菌(41%),但细菌的分离阳性率与患者的症状并没有任何相关性
[22]。
实验采用了一期清创植骨内固定方法治疗化脓性脊柱感染,治疗后脊柱标本大体观察证实手术是成功的,观察期间没有发生临床可见的表皮感染或者窦道形成、脓液流出等情况,并且MRI检查未见异常。也就是说没有临床可见的感染发生。但是应用PCR技术发现细菌寄生于钛板上的情况非常普遍,阳性率可以达到75%(18/24),虽然发现的细菌大部分为低毒力细菌,但这也许是术后假体周围迟发性感染发生的隐患。最后虽然发现了钛板普遍存在细菌寄生的现象,但是作者认为这种感染在大多数情况下都没有什么临床症状,是一种亚临床感染状态,其危害不是很大。另外,即使发生了临床可见的术后假体周围感染,其他学者临床回顾研究指出脊柱假体周围感染的术后疗效满意,感染的控制很少需要取出假体,不会造成像人工关节术后感染的那些关节周围组织挛缩、关节丧失活动能力等严重后果
[23]。
结论:①在有效的抗生素治疗前提下,应用脊柱前路一期清创植骨内固定的方法治疗犬脊柱化脓性感染是一种安全、有效的方法,没有临床可见的感染发生。内固定的使用不是感染复发或持续性慢性感染的主要原因。②脊柱内固定术后,细菌在内植物上的寄生是一种相对普遍的现象,但并不足以引起临床可见感染的发生,是一种亚临床感染状态。且根据本实验表明这种细菌不是由术前脊柱所感染的细菌繁衍而来。
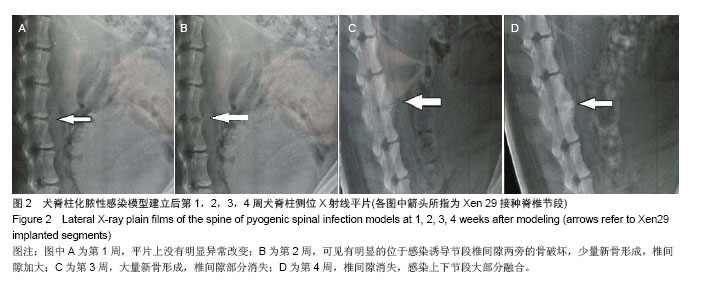
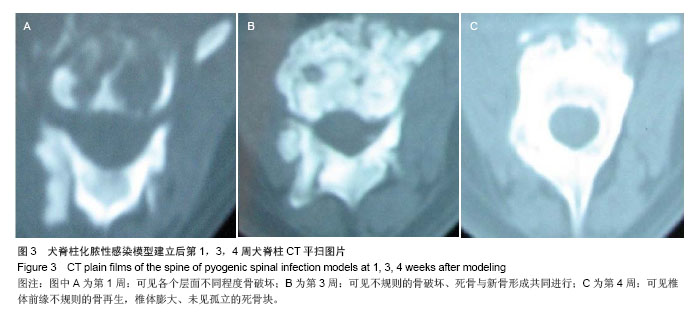
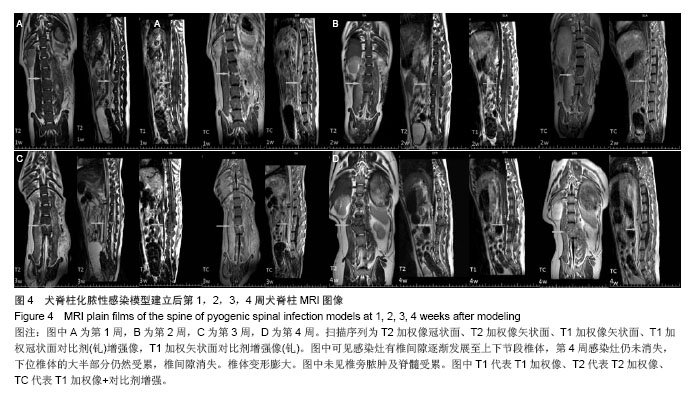
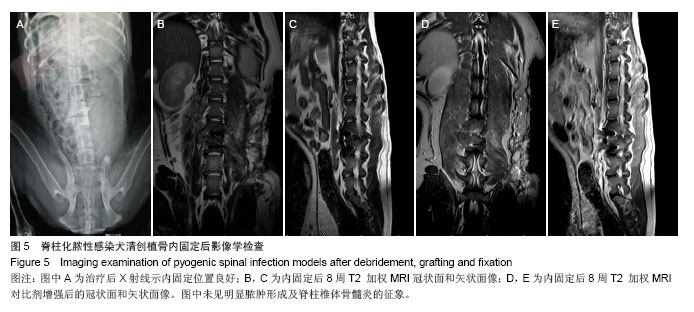
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)