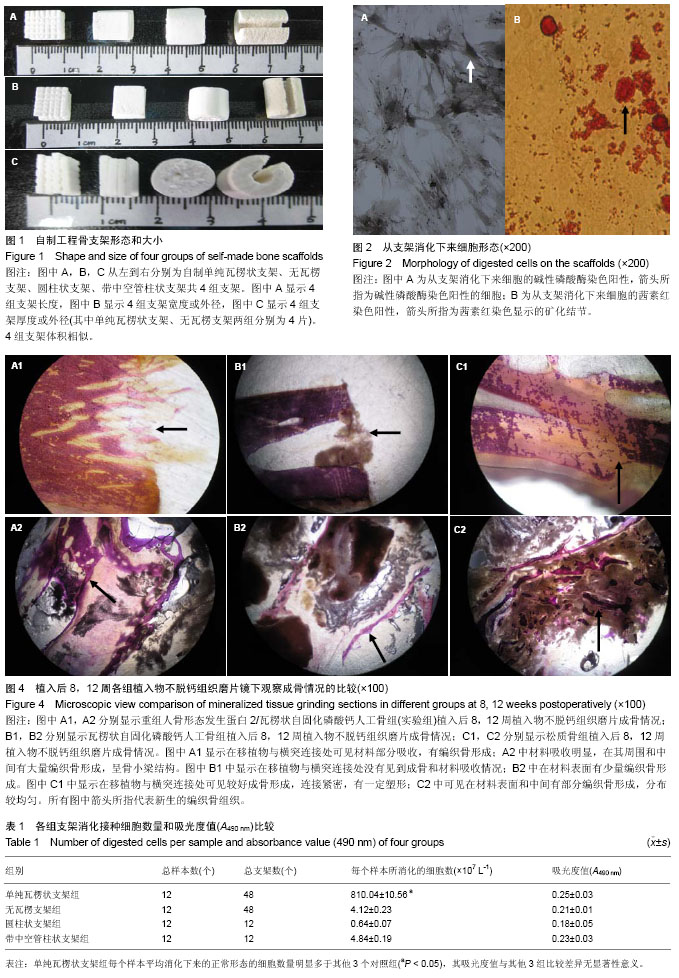
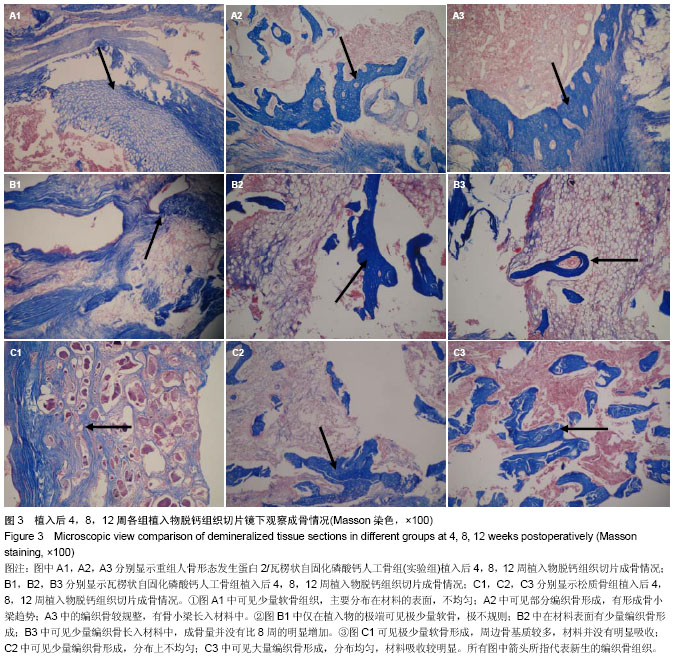
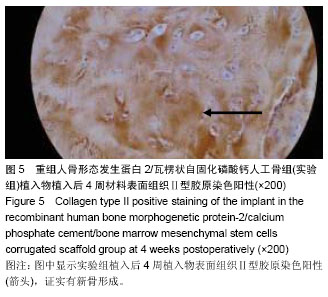
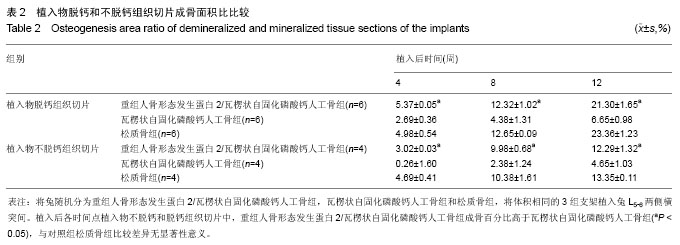
| [1] Harley BA, Lynn AK, Wissner-Gross Z, et al. Design of a multiphase osteochondral scaffold III: Fabrication of layered scaffolds with continuous interfaces. J Biomed Mater Res A 2010;92(3):1078-1093.
[2] Razi H, Checa S, Schaser KD, et al. Shaping scaffold structures in rapid manufacturing implants: a modeling approach toward mechano-biologically optimized configurations for large bone defect. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2012;100(7):1736-1745.
[3] Buma P, Schreurs W, Verdonschot N. Skeletal tissue engineering-from in vitro studies to large animal models. Biomaterials. 2004;25(9):1487-1495.
[4] Viateau V, Guillemin G, Bousson V, et al. Long-bone critical-size defects treated with tissue-engineered grafts: a study on sheep. J Orthop Res. 2007;25(6):741-749.
[5] Harris JS, Bemenderfer TB, Wessel AR, et al. A review of mouse critical size defect models in weight bearing bones. Bone. 2013;55(1):241-247.
[6] Guda T, Walker JA, Pollot BE, et al. In vivo performance of bilayer hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone tissue regeneration in the rabbit radius. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2011;22(3): 647-656.
[7] Papenburg BJ, Liu J, Higuera GA, et al. Development and analysis of multi-layer scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2009;30(31):6228-6239.
[8] Cipitria A, Lange C, Schell H, et al. Porous scaffold architecture guides tissue formation. J Bone Miner Res. 2012; 27(6):1275-1288.
[9] Vitacolonna M, Belharazem D, Hohenberger P, et al. Effect of static seeding methods on the distribution of fibroblasts within human acellular dermis. Biomed Eng Online. 2013;12:55.
[10] Li X, Bian W, Li D, et al. Fabrication of porous beta-tricalcium phosphate with microchannel and customized geometry based on gel-casting and rapid prototyping. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2011;225(3):315-323.
[11] Li LJ, Liu N, Shi JG, et al. Osteogenic scaffolds for bone reconstruction. Biores Open Access. 2012;1(3):137-144.
[12] Hoekstra JW, Ma J, Plachokova AS, et al. The in vivo performance of CaP/PLGA composites with varied PLGA microsphere sizes and inorganic compositions. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(7):7518-7526.
[13] Rentsch B, Bernhardt R, Scharnweber D, et al. Embroidered and surface coated polycaprolactone-co-lactide scaffolds: a potential graft for bone tissue engineering. Biomatter. 2012; 2(3):158-165.
[14] Roohani-Esfahani SI, Dunstan CR, Li JJ, et al. Unique microstructural design of ceramic scaffolds for bone regeneration under load. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(6): 7014-7024.
[15] Wieding J, Souffrant R, Mittelmeier W, et al. Finite element analysis on the biomechanical stability of open porous titanium scaffolds for large segmental bonedefects under physiological load conditions. Med Eng Phys. 2013;35(4): 422-432.
[16] Smith MR, Atkinson P, White D, et al. Design and assessment of a wrapped cylindrical Ca-P AZ31 Mg alloy for critical-size ulna defect repair. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2012; 100(1):206-216.
[17] Warnke PH, Seitz H, Warnke F, et al. Ceramic scaffolds produced by computer-assisted 3D printing and sintering: characterization and biocompatibility investigations. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2010;93(1):212-217.
[18] Andriano KP, Tabata Y, Ikada Y, et al. In vitro and in vivo comparison of bulk and surface hydrolysis in absorbable polymer scaffolds for tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999;48(5):602-612.
[19] Nukavarapu SP, Dorcemus DL. Osteochondral tissue engineering: current strategies and challenges. Biotechnol Adv. 2013;31(5):706-721.
[20] Howk D, Chu TM. Design variables for mechanical properties of bone tissue scaffolds. Biomed Sci Instrum. 2006;42: 278-283.
[21] Seitz H, Rieder W, Irsen S, et al. Three-dimensional printing of porous ceramic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2005;74(2):782-788.
[22] Lickorish D, Guan L, Davies JE. A three-phase, fully resorbable, polyester/calcium phosphate scaffold for bone tissue engineering: evolution of scaffold design. Biomaterials 2007;28(8):1495-1502.
[23] Mastrogiacomo M, Muraglia A, Komlev V, et al. Tissue engineering of bone: search for a better scaffold. Orthod Craniofac Res 2005;8(4):277-284.
[24] Vaquette C, Cooper-White J. A simple method for fabricating 3-D multilayered composite scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2013; 9(1):4599-4608.
[25] Melchels FP, Barradas AM, van Blitterswijk CA, et al. Effects of the architecture of tissue engineering scaffolds on cell seeding and culturing. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(11):4208-4217.
[26] DeConde AS, Sidell D, Lee M, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-2-impregnated biomimetic scaffolds successfully induce bone healing in a marginal mandibular defect. Laryngoscope. 2013;123(5):1149-1155.
[27] Bae JH, Song HR, Kim HJ, et al. Discontinuous release of bone morphogenetic protein-2 loaded within interconnected pores of honeycomb-like polycaprolactone scaffold promotes bone healing in a large bone defect of rabbit ulna. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(19-20):2389-2397.
[28] Fujita N, Matsushita T, Ishida K, et al. An analysis of bone regeneration at a segmental bone defect by controlled release of bone morphogenetic protein 2 from a biodegradable sponge composed of gelatin and β-tricalcium phosphate. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2012;6(4):291-298.
[29] Desai SC, Sclaroff A, Nussenbaum B. Use of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 for mandible reconstruction. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2013;15(3):204-209.
[30] Cheng G, Chen X, Li Z, et al. Comparison of three inoculation methods for bone tissue engineering. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012;27(6):1340-1350. |