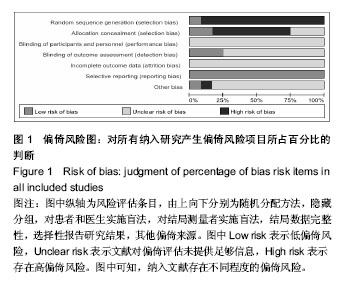
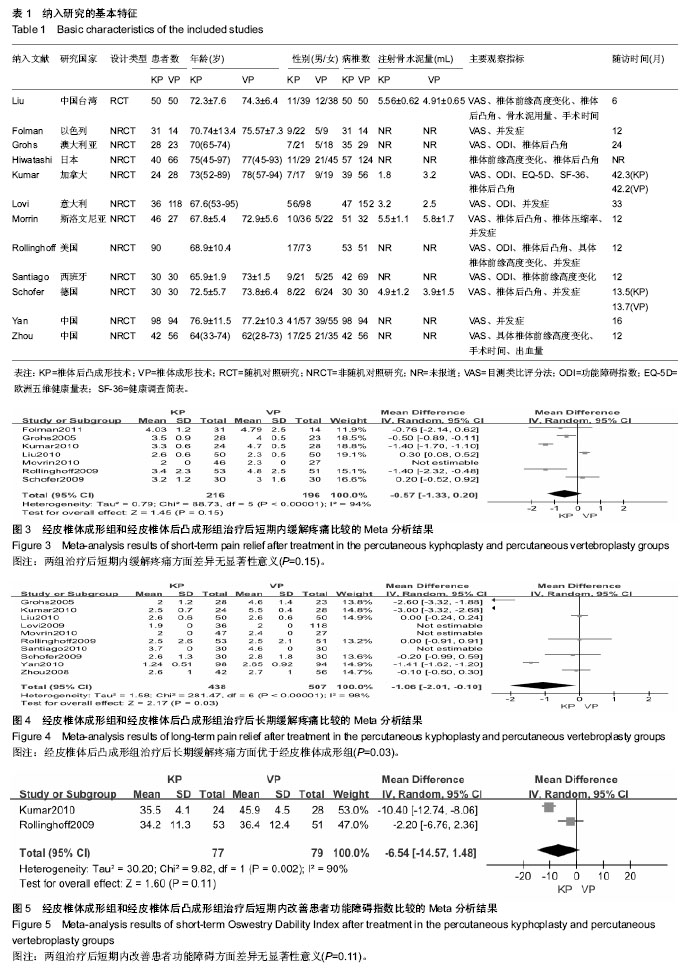
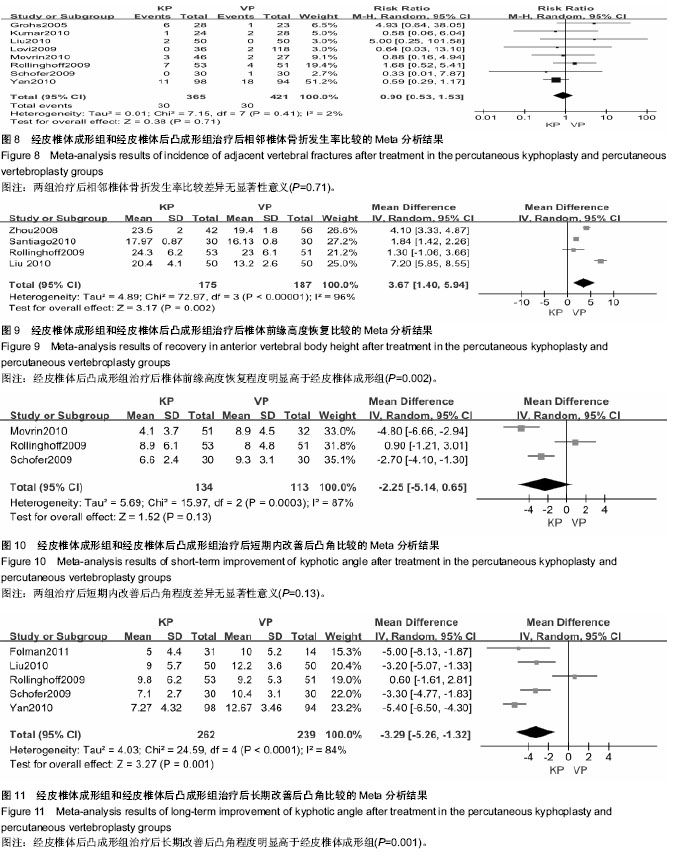
| [1] Warriner AH, Saag KG.Osteoporosis diagnosis and medical treatment.Orthop Clin North Am. 2013;44(2):125-135.
[2] Fenniri H.The Canadian Regenerative Medicine and Nanomedicine Enterprise (CARMENE).Int J Nanomedicine. 2006;1(3):225-227.
[3] Liu ZH, Zhao YL, Liu LN. Epidemiological investigation of peak bone density and the incidence of osteoporosis in China. J Bone Miner Res.1997;12:S245.
[4] Njeh CF, Boivin CM, Langton CM.The role of ultrasound in the assessment of osteoporosis: a review.Osteoporos Int. 1997; 7(1):7-22.
[5] Chen LH, Lai PL, Chen WJ.Current status of vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fracture.Chang Gung Med J. 2011;34(4):352-359.
[6] Silverman SL.The clinical consequences of vertebral compression fracture.Bone. 1992;13 Suppl 2:S27-31.
[7] Lee HM, Park SY, Lee SH,et al.Comparative analysis of clinical outcomes in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs): conservative treatment versus balloon kyphoplasty.Spine J. 2012;12(11):998-1005.
[8] Papaioannou A, Watts NB, Kendler DL,et al.Diagnosis and management of vertebral fractures in elderly adults.Am J Med. 2002;113(3):220-228.
[9] Black DM, Cummings SR, Karpf DB,et al.Randomised trial of effect of alendronate on risk of fracture in women with existing vertebral fractures. Fracture Intervention Trial Research Group.Lancet. 1996;348(9041):1535-1541.
[10] Galibert P, Deramond H, Rosat P,et al.Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty.Neurochirurgie. 1987;33(2):166-168.
[11] Yu SW, Yang SC, Kao YH,et al.Clinical evaluation of vertebroplasty for multiple-level osteoporotic spinal compression fracture in the elderly.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008;128(1):97-101.
[12] Zampini JM, White AP, McGuire KJ.Comparison of 5766 vertebral compression fractures treated with or without kyphoplasty.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(7):1773-1780.
[13] Zoarski GH, Snow P, Olan WJ,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fractures: quantitative prospective evaluation of long-term outcomes.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002;13(2 Pt 1):139-148.
[14] Lieberman I, Reinhardt MK.Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for osteolytic vertebral collapse.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; (415 Suppl):S176-186.
[15] Watts NB, Harris ST, Genant HK.Treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures with percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty.Osteoporos Int. 2001;12(6): 429-437.
[16] Evans AJ, Jensen ME, Kip KE, et al.Vertebral compression fractures: pain reduction and improvement in functional mobility after percutaneous polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty retrospective report of 245 cases.Radiology. 2003;226(2):366-372.
[17] Mathis JM, Barr JD, Belkoff SM,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty: a developing standard of care for vertebral compression fractures.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001;22(2): 373-381.
[18] Klazen CA, Lohle PN, de Vries J,et al.Vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (Vertos II): an open-label randomised trial.Lancet. 2010;376(9746):1085-1092.
[19] Wardlaw D, Cummings SR, Van Meirhaeghe J, et al.Efficacy and safety of balloon kyphoplasty compared with non-surgical care for vertebral compression fracture (FREE): a randomised controlled trial.Lancet. 2009;373(9668):1016-1024.
[20] Boonen S, Wahl DA, Nauroy L,et al.Balloon kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty in the management of vertebral compression fractures.Osteoporos Int. 2011;22(12):2915-2934.
[21] Liu JT, Liao WJ, Tan WC,et al.Balloon kyphoplasty versus vertebroplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a prospective, comparative, and randomized clinical study.Osteoporos Int. 2010;21(2): 359-364.
[22] Folman Y, Shabat S.A comparison of two new technologies for percutaneous vertebral augmentation: confidence vertebroplasty vs. sky kyphoplasty.Isr Med Assoc J. 2011; 13(7):394-397.
[23] Grohs JG, Matzner M, Trieb K,et al.Minimal invasive stabilization of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a prospective nonrandomized comparison of vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18(3):238-242.
[24] Hiwatashi A, Westesson PL, Yoshiura T,et al.Kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty produce the same degree of height restoration.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009;30(4):669-673.
[25] Kumar K, Nguyen R, Bishop S. A comparative analysis of the results of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Neurosurgery. 2010;67 (3 Suppl Operative):ons171-188.
[26] Lovi A, Teli M, Ortolina A,et al.Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: complementary techniques for the treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. A prospective non-randomised study on 154 patients.Eur Spine J. 2009;18 Suppl 1:95-101.
[27] Movrin I, Vengust R, Komadina R.Adjacent vertebral fractures after percutaneous vertebral augmentation of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a comparison of balloon kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010;130(9):1157-1166.
[28] Röllinghoff M, Siewe J, Zarghooni K,et al.Effectiveness, security and height restoration on fresh compression fractures--a comparative prospective study of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty.Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2009;52(5-6):233-237.
[29] Santiago FR, Abela AP, Alvarez LG,et al.Pain and functional outcome after vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. A comparative study.Eur J Radiol. 2010;75(2):e108-113.
[30] Schofer MD, Efe T, Timmesfeld N,et al.Comparison of kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty in the treatment of fresh vertebral compression fractures.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129(10):1391-1399.
[31] Yan D, Duan L, Li J,et al.Comparative study of percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(5):645-650.
[32] Zhou JL, Liu SQ, Ming JH,et al.Comparison of therapeutic effect between percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty on vertebral compression fracture.Chin J Traumatol. 2008; 11(1):42-44.
[33] Xing D, Ma JX, Ma XL,et al.A meta-analysis of balloon kyphoplasty compared to percutaneous vertebroplasty for treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.J Clin Neurosci. 2013;20(6):795-803.
[34] Belkoff SM, Mathis JM, Jasper LE,et al.The biomechanics of vertebroplasty. The effect of cement volume on mechanical behavior.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(14):1537-1541.
[35] Belkoff SM, Mathis JM, Deramond H,et al.An ex vivo biomechanical evaluation of a hydroxyapatite cement for use with kyphoplasty.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001;22(6): 1212-1216.
[36] Heini PF, Wälchli B, Berlemann U.Percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty with PMMA: operative technique and early results. A prospective study for the treatment of osteoporotic compression fractures.Eur Spine J. 2000;9(5):445-540.
[37] Togawa D, Bauer TW, Lieberman IH,et al.Histologic evaluation of human vertebral bodies after vertebral augmentation with polymethyl methacrylate.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(14):1521-1527.
[38] Hulme PA, Krebs J, Ferguson SJ,et al.Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: a systematic review of 69 clinical studies.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(17):1983-2001.
[39] Eck JC, Nachtigall D, Humphreys SC,et al.Comparison of vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty for treatment of vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis of the literature.Spine J. 2008;8(3):488-497.
[40] Berlemann U, Franz T, Orler R,et al.Kyphoplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a prospective non-randomized study.Eur Spine J. 2004;13(6):496-501. |