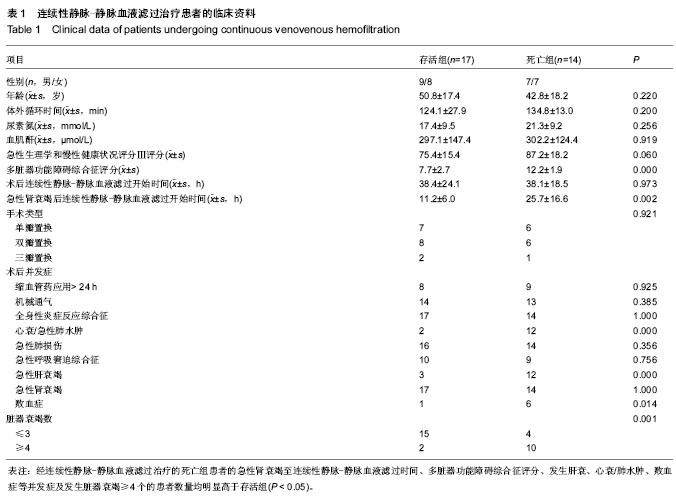
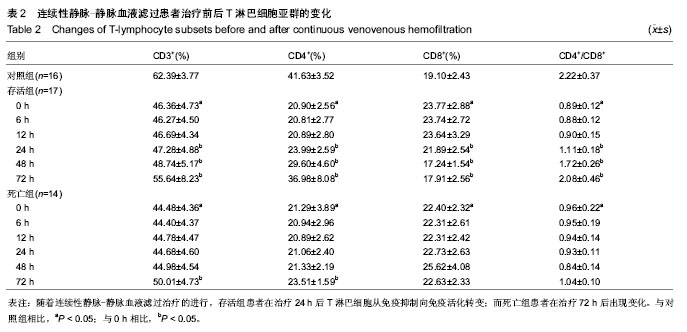
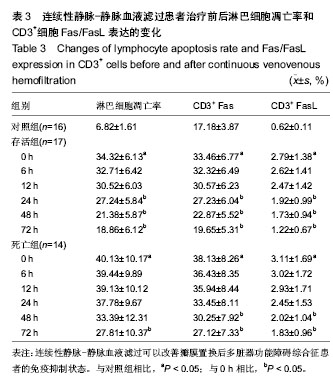
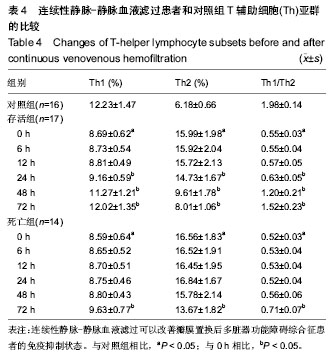
| [1] Tovey L, Dickie H, Gangi S, et al. Beyond the randomized clinical trial: citrate for continuous renal replacement therapy in clinical practice. Nephron Clin Pract. 2013;124(1-2): 119-123. [2] 张晓东,李小萍,宋洁,等.半永久双腔中心静脉导管维持性血液透析患者的微炎症状态[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(5): 913-919.[3] 吴道诩,徐岩.维持性血液透析患者的动脉粥样硬化[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(31):5666-5672.[4] 崔岩,魏丽丽,李琳,等.个体及集体干预对维持性血液透析患者生存质量的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(44):7815-7820.[5] 曹宁.肾移植前后未透析与透析效果及血液透析与腹膜透析的对比分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(18):3357-3364.[6] 曹宁.肾功能衰竭患者采用不同血液透析膜材料的生物相容性对比分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(25):4727-4734.[7] 王涛,张凡,魏萌,等.头孢他啶-肝素封管预防血液透析患者深静脉置管感染[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(31):5759-5762.[8] 沈蓓莉,曲青山,苗书斋,等.不同血液净化方式与移植肾功能的延迟恢复[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(31):5715-5719.[9] Franke A, Lante W, Kurig E, et al. Hyporesponsiveness of T cell subsets after cardiac surgery: a product of altered cell function or merely a result of absolute cell count changes in peripheral blood? Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2006;30(1):64-71. [10] 程光存,程明光,汤丹丹,等.改良心肌保护液在婴幼儿心内直视手术中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(31):5659-5665.[11] 李金友,李彤,于美丽,等.氧化海藻酸钠应用于体外循环管路[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(34):6159-6165.[12] 于广栋,李彤,高文卿,等.体外循环聚氯乙烯管路地塞米松涂层的性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(12):2177-2184.[13] 邵连彬,杨晓刚,杨海平,等.人工瓣膜置换体外循环过程中痰热清注射液的肺保护[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(5):843-850.[14] 周涛,何巍,谢晓勇.老年患者浅低温心脏不停跳瓣膜置换中的心肌保护[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(18):3259-3262.[15] 渠川铮,张瑞英,相开放.心脏瓣膜置换围手术期血糖控制对血乳酸水平的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(53):9955-9959.[16] 谢晓勇,何巍,郑宝石,等.浅低温体外循环心脏不停跳条件下瓣膜置换的肺保护[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(18):3267-3271.[17] Lugones F, Chiotti G, Carrier M, et al. Continuous renal replacement therapy after cardiac surgery. Review of 85 cases. Blood Purif. 2004;22(3):249-255. [18] Santiago MJ, López-Herce J, Urbano J, et al. Continuous renal replacement therapy in children after cardiac surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2013;146(2):448-454. [19] Morabito S, Pistolesi V, Tritapepe L, et al. Regional citrate anticoagulation in cardiac surgery patients at high risk of bleeding: a continuous veno-venous hemofiltration protocol with a low concentration citrate solution. Crit Care. 2012; 16(3):R111. [20] Miyamoto T, Yoshimoto A, Tatsu K, et al. Zero mortality of continuous veno-venous hemodiafiltration with PMMA hemofilter after pediatric cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;17(4):352-355.[21] 王今达,王宝恩.多脏器功能失常综合征(MODS)病情分期诊断及严重程度评分标准[J].中国危重病急救医学,1995,7(6):346-349.[22] Knaus WA, Wagner DP, Draper EA, et al. The APACHE III prognostic system. Risk prediction of hospital mortality for critically ill hospitalized adults. Chest. 1991;100(6):1619- 1636.[23] Clermont G, Vergely C, Jazayeri S, et al. Systemic free radical activation is a major event involved in myocardial oxidative stress related to cardiopulmonary bypass. Anesthesiology. 2002;96(1):80-87.[24] 刘宏宝,王汉民,李振江,等.连续性血液净化对心脏术后多器官功能障碍综合征存活者与死亡者血浆炎性介质的影响[J].中国急救医学,2005,25(7):475-478.[25] 王汉民,连耀国,刘宏宝,等.连续性血液净化对心脏术后多脏器功能障碍综合征患者炎性介质和氧化应激的影响[J].中国血液净化,2006,5(11):769-772.[26] 刘宏宝,王汉民,李振江,等.连续性肾脏替代治疗在心脏术后MODS合并ARF中的应用[J].中国血液净化,2005,4(4):201-204.[27] von Dossow V, Baehr N, Moshirzadeh M, et al. Clonidine attenuated early proinflammatory response in T-cell subsets after cardiac surgery. Anesth Analg. 2006;103(4):809-814.[28] Zedler S, Bone RC, Baue AE, et al. T-cell reactivity and its predictive role in immunosuppression after burns. Crit Care Med. 1999;27(1):66-72.[29] Brod SA, Nelson LD, Khan M, et al. Increased in vitro induced CD4+ and CD8+ T cell IFN-gamma and CD4+ T cell IL-10 production in stable relapsing multiple sclerosis. Int J Neurosci. 1997;90(3-4):187-202. [30] Rink L, Seyfarth M. Characteristics of immunologic test values in the elderly. Z Gerontol Geriatr. 1997;30(3):220-225. [31] Barlow Y. T lymphocytes and immunosuppression in the burned patient: a review. Burns. 1994;20(6):487-490.[32] Brunner M, Krenn C, Roth G, et al. Increased levels of soluble ST2 protein and IgG1 production in patients with sepsis and trauma. Intensive Care Med. 2004;30(7):1468-1473. [33] Schmidt DD, Schmidt PM, Crabtree BF, et al. The temporal relationship of psychosocial stress to cellular immunity and herpes labialis recurrences. Fam Med. 1991;23(8):594-599. [34] O'Sullivan ST, O'Connor TP. Immunosuppression following thermal injury: the pathogenesis of immunodysfunction. Br J Plast Surg. 1997;50(8):615-623.[35] Brunner M, Krenn C, Roth G, et al. Increased levels of soluble ST2 protein and IgG1 production in patients with sepsis and trauma. Intensive Care Med. 2004;30(7):1468-1473. [36] 刘宏宝,王汉民,李振江,等.连续性血液净化防治心脏术后患者多器官功能障碍综合征效果的评价[J].肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志, 2004,13(5):414-418. |
.jpg)