| [1] Baccetti T, Franchi L, McNamara JA Jr. An improved version of the cervical vertebral maturation (CVM) method for the assessment of mandibular growth. Angle Orthod. 2002; 72(4): 316-323.[2] Kopecky GR, Fishman LS.Timing of cervical headgear treatment based on skeletal maturation.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1993;104(2):162-169.[3] Fishman LS.Radiographic evaluation of skeletal maturation. A clinically oriented method based on hand-wrist films.Angle Orthod. 1982;52(2):88-112. [4] Grave KC, Brown T. Skeletal ossification and the adolescentgrowth spurt. Am J Orthod. 1976;69(6):611- 619.[5] Fishman LS. Maturational patterns and prediction during adoles-cence. Angle Orthod. 1987;57(3):178- 193.[6] 张邵岩,邵伟东,杨仕增,等主编.中国人骨成熟度评价标准及应用(CHN记分法和骨龄标准图谱)[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,1995: 74-94.[7] 陈莉莉,许天民,林久祥.手腕骨骨龄在面部生长预测中的应用[J].口腔医学,2007, 27(11) :607-609.[8] 孙燕,陈荣敬,沈刚, 等.上海地区男性少年儿童颈椎骨骨龄的测量分析[J].中华口腔正畸学杂志,2011,18(3):155-157.[9] 苏莉, 吕婴, 王红梅,等. 青春发育期颈椎骨龄计算方法的探讨[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2006,41(12):728-729.[10] Grippaudo C, Garcovich D, Volpe G, etal.Comparative evaluation between cervical vertebral morphology and hand-wrist morphology for skeletal maturation assessment. Minerva Stomatol. 2006;55(5):271-280.[11] 高辉,肖丹娜,陈扬熙. 颈椎片判断青春快速生长发育期研究进展[J]. 国外医学:口腔医学分册,2003,30(2):160-164.[12] 孙燕,游清玲,刘泓虎.上海地区少年儿童颈椎骨成熟度与手腕骨成熟度的相关研究[J].上海口腔医学,2007,16(4):365-369.[13] 刘泓虎,钱玉芬,孙燕,等.上海地区208名儿童颈椎骨成熟度的研究[J].上海口腔医学,1998,7(3):167-169,175.[14] 张丹,戚琳.女性青少年颈椎骨龄与腕骨骨龄的相关性研究中国血液流变学杂志,2007;17(1)100-101.[15] 张咏梅, 王邦康. 北京地区儿童颈椎生长发育的观察与骨龄测定 [J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 1997,32(3):152- 154.[16] García-Fernandez P, Torre H, Flores L, et al. The cervical vertebrae as maturational indicators. J Clin Orthod. 1998; 32(4):221-225.[17] Chang HP, Liao CH, Yang YH,et al. Correlation of cervical vertebra maturation with hand-wrist maturation in children[J]. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2001;17(1):29–35.[18] Flores-Mir C, Burgess CA, Champney M, et al. Correlation of skeletal maturation stages determined by cervical vertebrae and hand-wrist evaluations. Angle Orthod. 2006; 76(1): 1-5.[19] Santiago RC, de Miranda Costa LF, Vitral RW, et al.Cervical vertebral maturation as a biologic indicator of skeletal maturity. Angle Orthod. 2012; 82(6):1123-1131.[20] Santos EC, Bertoz FA, Arantes F de M, et al. Skeletal maturation analysis by morphological evaluation of the cervical vertebrae. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2006; 30(3): 265-270.[21] 吴尽红,吕婴.腕骨骨龄与颈椎骨龄相关性的研究[J].北京口腔医学,2006; 14(2): 108-109. [22] 杨川,米丛波,祖青,等.乌鲁木齐地区汉族青少年腕骨成熟度和颈椎骨成熟度的相关性[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(35): 6641-6645.[23] Stahl F, Baccetti T, Franchi L, et al. Longitudinal growth changes in untreated subjects with Class II Division1 malocclusion.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.2008; 134(1): 125-137.[24] Baccetti T, Franchi L, McNamara JA Jr, et al. Early dentofacial features of Class II malocclusion: a longitudinal study from the deciduous through the mixed dentition. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.1997;111(5):502-509.[25] Bishara SE, Jakobsen JR, Vorhies B,et al. Changes in dentofacial structures in untreated Class II division 1 and normal subjects: a longitudinal study. Angle Orthod. 1997; 67(1):55-66.[26] Morris JM, Park JH. Correlation of dental maturity with skeletal maturity from radiographic assessment: a review. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2012; 36(3): 309-314.[27] Perinetti G, Contardo L, Gabrieli P,et al.Diagnostic performance of dental maturity for identification of skeletal maturation phase. Eur J Orthod. 2012; 34(4):487-492.[28] Hassel B, Farman AG. Skeletal maturation evaluation using cervical vertebrae. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1995; 107(1): 58-60.[29] Mito T, Sato K, Mitani H. Predicting mandibular growth potential with cervical vertebral bone age. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2003;124(2):173-177.[30] Gu Y, McNamara JA. Mandibular growth changes and cervical vertebral maturation. A cephalometric implant study.Angle Orthod.2007;77(6):947-953.[31] Zhao XG, Lin J, Jiang JH,et al.Validity and reliability of a method for assessment of cervical vertebral maturation.Angle Orthod.2012;82(2):229-234. [32] O′Reilly MT, Yanniello GJ.Mandibular growth changes and maturation of cervical vertebrae-a longitudinal cephalometric study.Angle Orthod.1988;58(2):179-184.[33] San Roman P, Palma JC, Oteo MD,et al. Skeletal maturation determined by cervical vertebrae development.Eur J Orthod. 2002;24(3):303-311.[34] Franchi L, Baccetti T, McNamara JA Jr.Mandibular growth as related to cervical vertebral maturation and body height.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.2000; 118(3):335-340.[35] Mito T, Sato K, Mitani H. Cervical vertebral bone age in girls. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2002;122(4):380–385.[36] Chen F, Terada K, Hanada K.A new method of predicting mandibular length increment on the basis of cervical vertebrae.Angle Orthod. 2004; 74(5): 630- 634.[37] 彭燕,杨连平,贺振华,等. 颈椎骨龄系统预测青春期女性下颌骨生长发育的研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2009;25(10):599-601.[38] Moore RN,Moyer BA,DuBois LM.Skeletal maturation and craniofacial growth. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.1990; 98(1):33-40.[39] Silveira AM,Fishman LS,Subtelny JD,et al.Facial growth during adolescence in early,average and late maturers.Angle Orthod.1992;62(3):185-190.[40] Formby WA,Nanda RS,Currier GF.Longitudinal changes in the adult facial profile. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1994; 105(5):464-476.[41] Baccetti T,Franchi L,Toth LR,et al.Treatment timing for Twin-block therapy. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2000; 118(2):159-170.[42] Baccetti T,Franchi L,Cameron CG,et al.Treatment timing for rapid maxillary expansion.Angle Orthod.2001;71(5):343-350. |
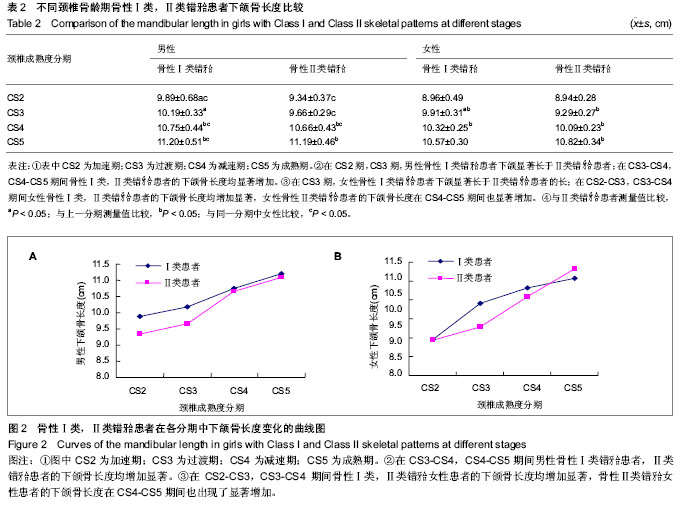
.jpg)