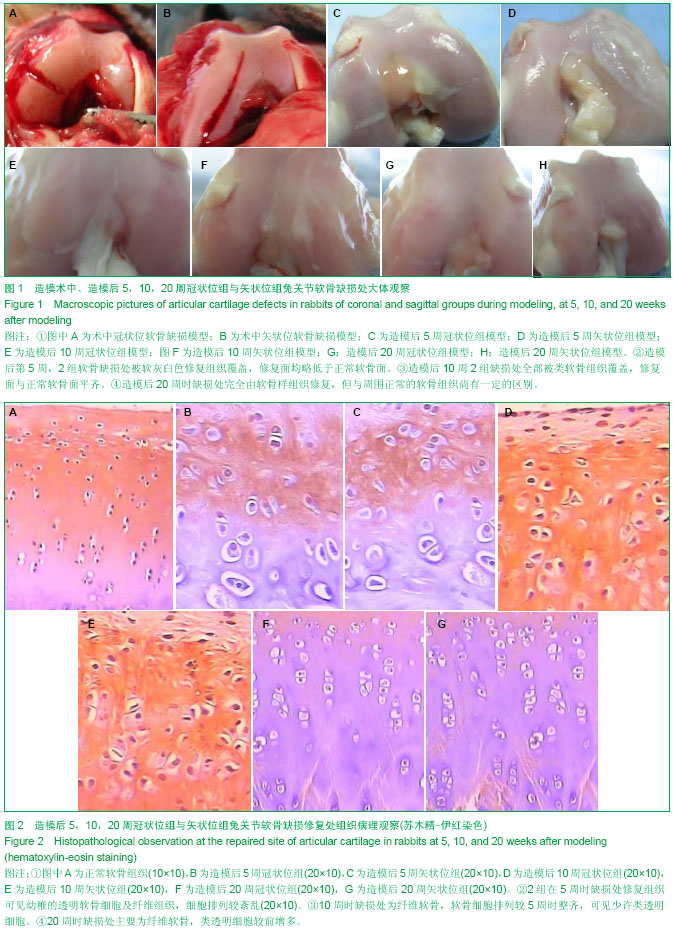
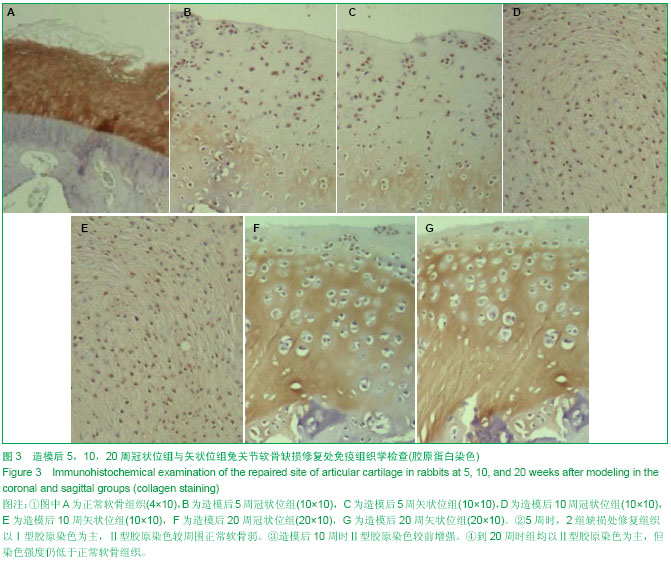
| [1] Li HP,Liu YJ,Wang ZG,et al. Arthroscopic microfrature for cartilage damage of knee. Orthop J Chin. 2007;15(10): 731-733.[2] Piasecki DP, Spindler KP, Warren T, et al. Intraarticular injuries associated with anterior cruciate ligament tear,findings at ligament reconstruction in high school and recreational athletes. Am J Sports Med. 2003;31:601-605.[3] Bálint L, Park SH, Bellyei A,et al. Repair of Steps and Gaps in Articular Fracture Models. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;(430): 208-218.[4] 李宝文, 高政, 刘丽梅, 等.兔关节内骨折错位关节软骨的自身修复[J].中国临床康复, 2003,7(2):220-221.[5] Zhang HB,Chen BC,Zhang HJ,et al. Experimental study of hepatocyte growth factor in repairing articular cartilage defects. Zhonghua Guke Zazhi(Chin J Orthop). 2000; 20(3): 181-184.[6] Redler LH, Caldwell JM, Schulz BM, et al. Management of articular cartilage defects of the knee. Phys Sports Med. 2012;40(1):20-35. [7] Ogawa T, Akazawa T, Tabata Y. In vitro proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow stem cells cultured with gelatin hydrogel microspheres for TGF-beta1 release.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2010;21:609-621.[8] Ivkovic A, Pascher A, Hudetz D, et al. Articular cartilage repair by genetically modified bone marrow aspirate in sheep. Gene Ther. 2010;17:779-789.[9] Qi BW, Yu AX, Zhu SB, et al, Chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel combined with Ad-hTGF-b1 transfected mesenchymal stem cells to repair rabbit articular cartilage defects. Exp Biol Med. 2013; 238:23-30.[10] 张远金,柯雯昙. 全层软骨缺损合并深部“微骨折”兔软骨修复情况[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(14): 2688- 2690.[11] 葛志强,冯传汉,吕厚山,等.孔数不同的软骨下骨钻孔术对兔软骨缺损修复的影响[J].中华骨科杂志,1997,17(6):389-391.[12] Steadman JR, Rodkey WG, Briggs KK. The microfracture techinic in the management of complete cartilage defects in the knee joint. Orthopade. 1999;28:26-32.[13] Williams RJ III, Harnly HW. Microfracture: indications, technique, and results. Instr Course Lect. 2007;56:419-428.[14] Knutsen G, Engebretsen L, Ludvigsen TC, et al. Autologous chondrocyte implantation compared with microfra cture in the knee. A randomi zed trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A: 455-464.[15] Ollat D, Lebel B, Thaunat M, et al. Mosaic osteochondral transplantations in the knee joint, midterm results of the SFA multicenter study. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2011;97(8 Suppl.):160-166.[16] Bentley G, Biant LC, Vijayan S, et al. Minimum ten-year results of a prospec tive randomised study of autologous chondrocyte implantation versus mosaicplasty for symp tomatic articular cartilage lesions of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94:504-509.[17] Aulin C, Jensen-Waern M, Ekman S, et al. Cartilage repair of experimentally 11 induced osteochondral defects in New Zealand White rabbits. Lab Anim. 2013;47:58-65.[18] Singh NK, Singh GR, Jeong DK, et al. Healing of full-thickness articular cartilage defects treated with cultured autologous chondrogenic satellite cells isolatedfrom chondral stem cell niche in rabbits. Knee. 2013;183(2):629-638. [19] 束志勇,查振刚,汪炬,等. PLGA-Ⅱ型胶原复合rhBMP-2/bFGF修复兔膝关节软骨的缺损[J]. 暨南大学学报:自然科学与医学版, 2009,30(2):180-184.[20] 李彬,陈华,温昱. Ⅱ型胶原BMP复合物对关节软骨缺损的修复作用[J].中华实用中西医杂志, 2005,18(9): 1357-1358.[21] 熊高鑫,查振刚,谭文成,等. PLGA复合Ⅱ型胶原和生长因子诱导组织工程软骨修复兔关节软骨缺损[J]. 中山大学学报:医学科学版,2010,31(3):315-320.[22] 李斯明,黄雪芳,叶惠贞,等. Ⅱ型胶原移植修复关节软骨缺损过程中抗体水平的动态变化[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志,2004,8(6):332-334.[23] 沈雁,唐毅,钟灿灿,等. 应用Ⅱ型胶原为载体的异种异体移植修复关节软骨缺损[J]. 中国临床康复,2005,9(14):209-211.[24] Balain B, Kerin C, Kanes G, et al. Effects of knee compartment, concomitant surgery and smoking on medium-term outcome of microfracture. Knee 2012;19:440 -444.[25] Knutsen G, Drogset JO, Engebretsen L, et al. A randomized trial comparing autologous chondrocyte implantation with microfracture. Findings at fi ve years. J Bone Join t Surg Am. 2007;89:2105-2112.[26] Lim HC, Bae JH, Song SH, et al. Current treatments of isolated artic-ular cartilage lesions of the knee achieve similar outcomes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470:2261-2267. |