| [1]Lindvall O, Rehncrona S, Gustavii B, et al.Fetal dopamine rich mesence Phalic grafts in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet. 1988; 2(8626-8627):1483-1484.
[2]李耀宇,舒斯云,包新民,等.大鼠纹状体边缘区与杏仁核和终纹床核之间相互联系的免疫组织化学研究[J]. 神经解剖学杂志, 2000,16(3):265-268.
[3]李泽鸿,陶英楠,刘继阳,等. 6-羟基多巴胺致帕金森病大鼠模型的建立与评价[J]. 中国畜牧兽医,2012,39(12):162-165.
[4]冯飞阳,陈施艳,张志坚,等. TNF-α、IL-6在6-OHDA诱导帕金森病大鼠脑中的改变[J]. 福建医科大学学报,2012,46(5):315-318.
[5]朱红艳,吴凌燕,裴虓,等. 同步辐射显微红外光谱研究6-OHDA诱导帕金森病大鼠海马[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2012,32(1): 113-114.
[6]杨茂全,光奎,丁方香,等.帕金森病大鼠行为学模型实用性研究[J].山东医药,2011,51(49):21-22.
[7]丁宏娟,何建成,王文武. 左旋多巴对帕金森病大鼠神经行为学影响的动态研究[J]. 重庆医科大学学报,2011,36(11): 1281-1284.
[8]刘婷婷,孟涛,刘中海,等. 帕金森病大鼠模型纹状体中谷氨酸、γ-氨基丁酸与多巴胺之间的关系[J]. 神经解剖学杂志,2011, 27(3): 307-310.
[9]常晓赞,葛顺楠,杨晨,等. 6-OHDA帕金森病大鼠快动眼睡眠状态下皮层脑电及基底节场电位的异常变化[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2011,11(10):1813-1816
[10]丁宏娟,何建成,王文武. 不同剂量左旋多巴对帕金森病大鼠神经行为学的影响[J]. 西安交通大学学报:医学版,2011,32(1): 93-96,106.
[11]朱红灿,李倩倩,赵静,等. 左旋多巴对帕金森病大鼠结肠神经递质的影响[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2011, 21 (20):2365-2369.
[12]王爽,高捷,苏兴利,等. 帕金森病模型大鼠中缝中核5-羟色胺神经元电活动增强[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2011,31(5): 829-830
[13]王爽,高捷,苏兴利,等. 帕金森病模型大鼠内侧前额叶皮层中间神经元电活动的增强[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2011,31(11): 2016-2018
[14]秦晓凌,黄文娟,陈国芳,等. 单侧内侧前脑束注射6-羟基多巴建立帕金森病大鼠模型的实验研究[J]. 卒中与神经疾病,2011, 18(1): 34-37.
[15]宋璐,马雅萍,巴茂文,等.不同剂量左旋多巴对帕金森病运动并发症大鼠模型行为学的影响[J]. 中国临床神经科学,2011, 19(2): 131-135.
[16]周丽娜,王世民. 帕金森病模型大鼠丘脑底核神经元电生理活动的研究[J]. 继续医学教育,2011,25(6):67-71.
[17]王华,陈蕾. 5-HT对帕金森病模型大鼠丘脑底核神经元放电影响[J]. 青岛大学医学院学报,2011,47(1):8-10.
[18]盘晓荣,胡玉英,俸道荣,等. 单点注射6-羟基多巴胺成功建立帕金森病大鼠模型的实验研究[J]. 中国临床新医学,2010, 3(10): 933-937.
[19]王刚,郑静. 6-OHDA损毁帕金森大鼠模型和MPTP诱导帕金森小鼠模型的比较(综述)[J]. 南京医科大学学报:自然科学版, 2010,30(3):383.
[20]李敏,朱俊玲,石美祥,等. 6-OHDA帕金森病大鼠模型清醒静止状态下基底节-皮层环路振荡性电活动的特征[J]. 中国神经免疫学和神经病学杂志,2009,16(4):254-258.
[21]韩志桐. 纹状体内注射6-羟基多巴胺制备帕金森病大鼠模型的实验研究[J]. 内蒙古民族大学学报,2009,15(5):15-17.
[22]孙慧勤,陈先文,李芳,等. 左旋多巴诱发异动症大鼠模型的制作及其行为学研究[J]. 安徽医科大学学报,2009,44(3):355-358.
[23]张淑静,陈蕾. 苍白球微量注射5-HT对帕金森病模型大鼠旋转行为影响[J]. 青岛大学医学院学报,2009,45(4):319-321,324.
[24]王涛,纪超,黎青,等. 帕金森病模型大鼠纹状体内氧化应激与细胞凋亡蛋白的表达[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2009,15(5): 431-433.
[25]梅加明,牛朝诗,韩暄,等.单侧纹状体多靶点注射6-OHDA诱导帕金森病动物模型的实验研究[J].立体定向和功能性神经外科杂志,2013,26(2):1.
[26]陈刚,徐国政,段秋红,等. 一种帕金森病大鼠模型的建立及评价[J]. 中国临床神经外科杂志,2009,14(8):488-490.
[27]贾丛康,杨新玲,姜涛,等. 6-羟基多巴胺所致帕金森病大鼠模型稳定性的研究[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2009,29(5):521-524
[28]Litvan I, Halliday G, Hallett M, et al. The etiopathogenesis of Parkinson disease and suggestions for future research. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.2007;66(4):251-257.
[29]Przedborski S,Levivier M,Jiang H,et al.Dose-dependent lesions of the dopaminergic nigrostratal pathway induced by intrastriatal injection of 6-hydroxydropamine. Neuroscience. 1995;67:631-647.
[30]Schwarting RK,Huston JP.The unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine lesion model in behavioral brain research. Analysis of functional deficits, recovery and treatments. Prog Neurobiol. 1996;50(223):275 - 331.
[31]肖春苟,沈伟哉,郭国庆,等.帕金森病模型大鼠中脑腹侧被盖区酪氨酸羟化酶免疫阳性神经元的改变[J].解剖学研究,2009,31(5): 321-329.
[32]孙玉娟,侯琳,程秦,等. 6-OHDA所致帕金森病模型大鼠黑质FP1基因表达及启动子甲基化状态变化[J]. 青岛大学医学院学报, 2012,48(3): 214-217.
[33]谭雪锋,金国华,刘娟,等. PD模型大鼠黑质中Nurr1和TH的表达变化及其意义[J]. 神经解剖学杂志,2009,25(1):16-20
[34]吕娥,付文玉,庄宝祥,等. 6-羟多巴胺制备的帕金森病大鼠脑内神经递质的变化[J]. 解剖学杂志,2008,31(4):541-544.
[35]Reglódi D, Tamás A, Lengvári I, et al. Comparative Study of the Effects of PACAP in Young, Aging, and Castrated Males in a Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006; 1070:518-524.
[36]陆建明,周厚广.帕金森病大鼠模型的行为学及神经元形态学评价[J].中国临床康复,2004,16(8):3180-3182.
[37]邹志浩,张世忠,姜晓丹,等.6-羟基多巴定向注射建立帕金森病大鼠模型的实验研究[J].中华神经医学杂志,2006,5(3):87-89.
[38]Kirik D,Rosenblad C,Bjorklund A. Character of behavioral and neurodegenerative changes following partial lesions of the nigrostriatal dopamine system induced by intrastriatal 6-hydroxydopamine in the rat. Exp Neurol.1998;152(2):259–277. |

.jpg)
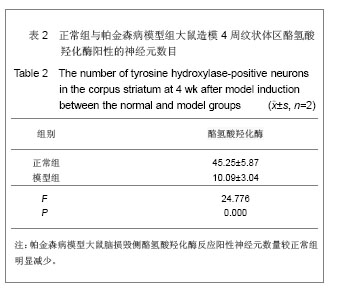
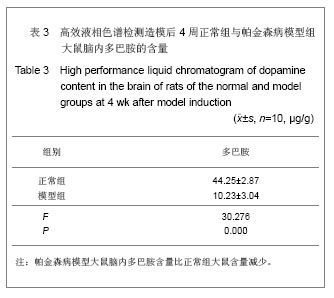
.jpg) 阿朴吗啡诱导造模大鼠的旋转行为目前已成为衡量6-羟基多巴胺损毁效果,模型成功与否的最常用方法[30] 。6-羟基多巴胺单侧损毁法制备帕金森病模型是目前很常用并且操作技术成熟的研究帕金森病的造模方法,成功的模型动物在病理、生化和行为学等方面都有与人类帕金森病有相似之处。酪氢酸羟化酶是多巴胺合成限速酶,故酪氢酸羟化酶免疫阳性细胞数可反映多巴胺能神经元的数量和功能状态[31] 。注射6-羟基多巴胺建立帕金森病模型大鼠脑部酪氨酸羟化酶阳性表达文献报道见表5。
阿朴吗啡诱导造模大鼠的旋转行为目前已成为衡量6-羟基多巴胺损毁效果,模型成功与否的最常用方法[30] 。6-羟基多巴胺单侧损毁法制备帕金森病模型是目前很常用并且操作技术成熟的研究帕金森病的造模方法,成功的模型动物在病理、生化和行为学等方面都有与人类帕金森病有相似之处。酪氢酸羟化酶是多巴胺合成限速酶,故酪氢酸羟化酶免疫阳性细胞数可反映多巴胺能神经元的数量和功能状态[31] 。注射6-羟基多巴胺建立帕金森病模型大鼠脑部酪氨酸羟化酶阳性表达文献报道见表5。.jpg) 实验在黑质致密部和中脑腹侧被盖区两点注射6-羟基多巴胺建立的帕金森病大鼠模型,表现出明显的黑质神经元损伤帕金森病症状,诱导后出现旋转行为。部分大鼠于术后2-24 h可出现头偏斜、行动迟缓、少动、尾僵、嗅探、躁动、激惹等现象,说明手术定位的准确性。对帕金森病大鼠黑质区、纹状体区进行酪氢酸羟化酶免疫组织化学染色,发现毁损侧酪氢酸羟化酶阳性细胞较对侧显著减少(P < 0.05)。同时模型鼠的脑内的多巴胺含量也明显减少,从检测模型鼠行为及病理3方面改变说明帕金森病大鼠模型制作成功。帕金森病大鼠模型的稳定建立也为后期进一步研究干预治疗帕金森病提供基础平台。
实验在黑质致密部和中脑腹侧被盖区两点注射6-羟基多巴胺建立的帕金森病大鼠模型,表现出明显的黑质神经元损伤帕金森病症状,诱导后出现旋转行为。部分大鼠于术后2-24 h可出现头偏斜、行动迟缓、少动、尾僵、嗅探、躁动、激惹等现象,说明手术定位的准确性。对帕金森病大鼠黑质区、纹状体区进行酪氢酸羟化酶免疫组织化学染色,发现毁损侧酪氢酸羟化酶阳性细胞较对侧显著减少(P < 0.05)。同时模型鼠的脑内的多巴胺含量也明显减少,从检测模型鼠行为及病理3方面改变说明帕金森病大鼠模型制作成功。帕金森病大鼠模型的稳定建立也为后期进一步研究干预治疗帕金森病提供基础平台。