| [1]Horowitz MC, Xi Y, Wilson K, et al. Control of osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption by members of the TNF family of receptors and ligands. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2001;12(1):9-18.[2]Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Akatsu T, et al. Origin of osteoclasts: mature monocytes and macrophages are capable of differentiating into osteoclasts under a suitable microenvironment prepared by bone marrow-derived stromal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.1990;87(18): 7260-7264.[3]刘波,于世凤,庞淑珍.新伐他汀体外对破骨细胞性骨吸收及大鼠骨代谢的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2005,11(3): 351-355.[4]邱君思,陈靖. 无动力型骨病发病机制的新进展[J].中国血液净化,2007,6(11):614-617.[5]邢联平,张倩,姚振强. 破骨细胞介导炎症性骨丢失的研究进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2006,8(7):671-674.[6]胡永成,王志强,孙世荃,等. 同种异体骨移植后的病理组织学观察[J].中华骨科杂志,2004,24(10):597-603.[7]Nakashima T, Hayashi M, Takayanagi H. New insights into osteoclastogenic signaling mechanisms. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012;23(11):582-590.[8]Hughes A, Kleine-Albers J, Helfrich MH, et al. A class III semaphorin (Sema3e) inhibits mouse osteoblast migration and decreases osteoclast formation in vitro. Calcif Tissue Int. 2012;90(2):151-162.[9]Zheng K, Chen DS, Wu YQ, et al. MicroRNA expression profile in RAW264.7 cells in response to Brucella melitensis infection. Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(7):1013-1022.[10]张庆鸿,梁星,刘梦桃. 体外培养鼠破骨细胞对牙体硬组织的吸收实验[J]. 口腔医学,2007,27(9):452-454.[11]朱振康,骆峪潇,李陶冶,等.破骨细胞体外培养的影响因素[J]. 浙江临床医学,2011,13(5):559-562.[12]许多荣,余学清,方荸荠.甲状旁腺激素在体外对破骨细胞分化及骨重吸收能力的影响[J].中华肾脏病杂志,2005,21(4):186-190.[13]Takeshita S, Kaji K, Kudo A. Identification and characterization of the new osteoclast progenitor with macrophage phenotypes being able to differentiate into mature osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Res. 2000;15(8): 1477-1488.[14]Dempster DW, Hughes-Begos CE, Plavetic-Chee K, et al. Normal human osteoclasts formed from peripheral blood monocytes express PTH type 1 receptors and are stimulated by PTH in the absence of osteoblasts. J Cell Biochem. 2005; 95(1):139-148.[15]戴闽,程明,张斌,等. RAW264.7细胞在体外分化成破骨细胞的研究[J]. 天津医药,2010, 38(7):596-598.[16]肖新华,周后德,王运林,等. RANKL诱导小鼠单核细胞RAW264.7分化成成熟破骨细胞[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2005, 11(2):151-155.[17]Rahman MM, Bhattacharya A, Fernandes G. Conjugated linoleic acid inhibits osteoclast differentiation of RAW264.7 cells by modulating RANKL signaling. J Lipid Res. 2006;47(8):1739-1748.[18]Kudo O, Sabokbar A, Pocock A, et al. Isolation of human osteoclasts formed in vitro: hormonal effects on the bone-resorbing activity of human osteoclasts. Calcif Tissue Int. 2002;71(6):539-546.[19]Mochizuki A, Takami M, Miyamoto Y, et al. Cell adhesion signaling regulates RANK expression in osteoclast precursors. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48795.[20]Xu D, Shi Z, Mcdonald J, et al. Development of a chimaeric receptor approach to study signalling by tumour necrosis factor receptor family members. Biochem J. 2004;383(Pt 2): 219-225.[21]Liu Y, Song L, Wang Y, et al. Osteoclast differentiation and function in aquaglyceroporin AQP9-null mice. Biol Cell. 2009; 101(3):133-140.[22]毛英杰,谷志远,赵鹃.不同细胞接种密度及饥饿对RAW264.7诱导分化的影响[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2009,14(2):124-125.[23]Tomomura M, Hasegawa H, Suda N, et al. Serum calcium-decreasing factor, caldecrin, inhibits receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL)-mediated Ca2+ signaling and actin ring formation in mature osteoclasts via suppression of Src signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 2012;287 (22):17963-17974.[24]Ikeda F, Matsubara T, Tsurukai T, et al. JNK/c-Jun signaling mediates an anti-apoptotic effect of RANKL in osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Res. 2008;23(6):907-914.[25]Wu SH, Zhong ZM, Chen JT. Low-magnitude high-frequency vibration inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation of RAW264.7 cells. Int J Med Sci. 2012;9(9):801-807.[26]Hodge JM, Collier FM, Pavlos NJ, et al. M-CSF potently augments RANKL-induced resorption activation in mature human osteoclasts. PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21462.[27]Makihira S, Mine Y, Kosaka E, et al. Titanium surface roughness accelerates RANKL-dependent differentiation in the osteoclast precursor cell line, RAW264.7. Dent Mater J. 2007;26(5):739-745.[28]董伟,于静,戚孟春,等. M-CSF、RANKL浓度及M-CSF预诱导对破骨细胞生成影响的研究[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志,2010, 27(6): 1336-1340.[29]包洪卫,孙继芾,王青. 巨噬细胞集落刺激因子/核因子κB受体激活物配体体外诱导培养高纯度破骨细胞:最佳剂量探讨[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(2):191-195.[30]Raju R, Balakrishnan L, Nanjappa V, et al. A comprehensive manually curated reaction map of RANKL/RANK-signaling pathway. Database (Oxford).2011;2011:r21.[31]周怡,刘丽,张庆鸿. 鼠破骨细胞培养过程中凋亡现象的观察研究[J]. 口腔医学,2010, 30(2):90-92.[32]Lamothe B, Lai Y, Xie M, et al. TAK1 is essential for osteoclast differentiation and is an important modulator of cell death by apoptosis and necroptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 2013;33(3):582-595.[33]Christofferson DE, Yuan J. Necroptosis as an alternative form of programmed cell death. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010;22(2): 263-268.[34]Bharti AC, Aggarwal BB. Ranking the role of RANK ligand in apoptosis. Apoptosis. 2004;9(6):677-690.[35]Sugatani T, Hruska KA. Akt1/Akt2 and mammalian target of rapamycin/Bim play critical roles in osteoclast differentiation and survival, respectively, whereas Akt is dispensable for cell survival in isolated osteoclast precursors. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280(5):3583-3589.[36]Glantschnig H, Fisher JE, Wesolowski G, et al. M-CSF, TNFalpha and RANK ligand promote osteoclast survival by signaling through mTOR/S6 kinase. Cell Death Differ. 2003; 10(10):1165-1177.[37]Sankar U, Patel K, Rosol TJ, et al. RANKL coordinates cell cycle withdrawal and differentiation in osteoclasts through the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p27KIP1 and p21CIP1. J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19(8):1339-1348.[38]Lutter AH, Hempel U, Wolf-Brandstetter C, et al. A novel resorption assay for osteoclast functionality based on an osteoblast-derived native extracellular matrix. J Cell Biochem. 2010;109(5):1025-1032.[39]Okui T, Shimo T, Fukazawa T, et al. Antitumor effect of temsirolimus against oral squamous cell carcinoma associated with bone destruction. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010; 9(11):2960-2969.[40]Tang CH, Hsu TL, Lin WW, et al. Attenuation of bone mass and increase of osteoclast formation in decoy receptor 3 transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(4):2346-2354. |

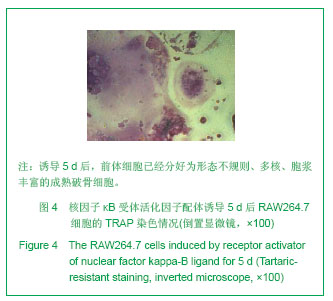
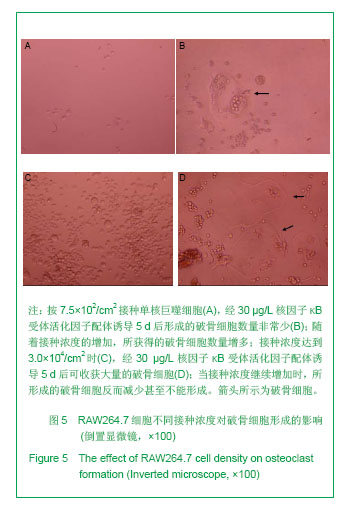
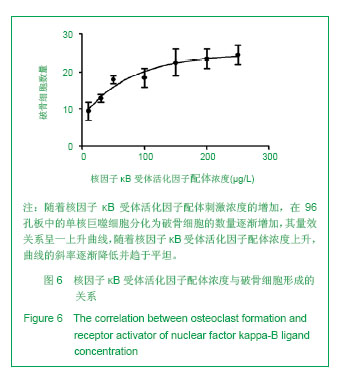
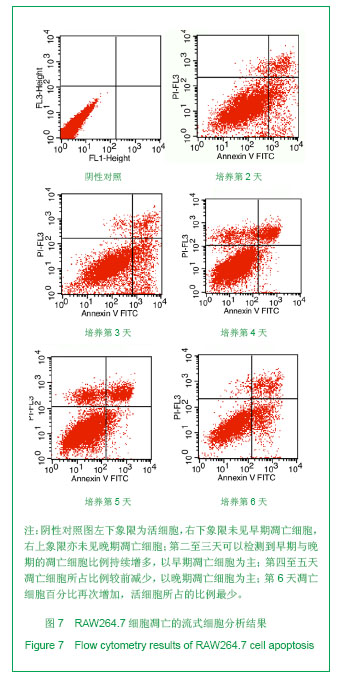
.jpg)