| [1]侯树勋.胸腰椎骨折的治疗[J].创伤外科杂志,2003,5(4): 41-243.
[2]张贵林,荣围威,丁占云.脊柱胸腰段骨折术后椎弓根螺钉断裂及弯曲松动的原因分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2000,20(8):470-472.
[3]洪全明,兰林,叶刚,等.短节段椎弓根螺钉治疗胸腰段脊柱爆裂骨折分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008,23(11):915-916.
[4]贺世武,韩伟杰,闫志强,等.椎弓根钉系统复位内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].医学信息(下月刊),2009,1(7):101.
[5]Korovessis P, Baikousis A, Zacharatos S, et al. Combined anterior plus posterior stabilization versus posterior short-segment instrumentation and fusion for mid-lumbar (L2-L4) burst fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(8): 59-868.
[6]李晶,吕国华,王冰,等.胸腰椎骨折脱位伤椎固定的可行性研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2005,25(5):293-295.
[7]杜心如,刘春生,刘忠金,等.经伤椎椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2007,9(23):659-661.
[8]潘勇,初同伟,郝勇,等.经伤椎与不经伤椎椎弓根螺钉复位固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的临床对比研究[J].中华创伤杂志,2009,25(8): 694-697.
[9]Guven O, Kocaoglu B, Bezer M, et al. The use of screw at the fracture level in the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2009;22(6):417-421.
[10]Shono Y, Kaneda K, Abumi K, et al. Stability of posterior spinal instrumentation and its effects on adjacent motion segments in the lumbosacral spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998;23(14):1550-1558.
[11]王新伟,陈德玉,鲍达,等.小牛胸腰椎解剖、生物力学研究及其临床意义[J].脊柱外科杂志,2003,1(4):223-225.
[12]王新伟,赵定麟,陈德玉,等.人工椎体植入位置的生物力学研究[J].中华创伤杂志,2004,20(2):93-96.
[13]王向阳,戴力扬,徐华梓,等.胸腰椎不同程度前中柱骨折内固定后的生物力学特征及前路重建的意义[J].中华创伤杂志,2006, 22(3):14-217.
[14]陈金传.穹顶形开窗减压术的生物力学评估[D].徐州:徐州医学院. 2006.
[15]吕夫新,黄勇,张强,等.椎弓根钉结合伤椎固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008,23(1):46-48.
[16]王树海,付国权,王桂华,等.后路短节段钉棒系统结合伤椎椎弓根固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2011,26(1):36-38.
[17]Krag MH, Van Hal ME, Beynnon BD. Placement of transpedicular vertebral screws close to anterior vertebral cortex. Description of methods. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1989; 14(8):879-883.
[18]Oner FC, Verlaan JJ, Verbout AJ, et al. Cement augmentation techniques in traumatic thoracolumbar spine fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(11 Suppl):S89-95; discussion S104.
[19]Abe E, Nickel T, Buttermann GR, et al. Lumbar intradiscal pressure after posterolateral fusion and pedicle screw fixation. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1998;186(4):243-253.
[20]昌耘冰,夏虹,王义生,等.伤椎置钉技术在治疗胸腰椎骨折中的即时复位作用[J].中华创伤杂志,2009,25(10):894-897.
[21]Lenarz CJ, Place HM, Lenke LG, et al. Comparative reliability of 3 thoracolumbar fracture classification systems. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2009;22(6):422-427.
[22]李熙雷,车武 ,董健,等.经伤椎单节段椎弓根螺钉固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折的生物力学研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2012,14(3): 225-227.
[23]Dick JC, Jones MP, Zdeblick TA, et al. A biomechanical comparison evaluating the use of intermediate screws and cross-linkage in lumbar pedicle fixation. J Spinal Disord. 1994; 7(5):402-407.
[24]昌耘冰,范志丹,夏虹,等.应用伤椎置钉技术治疗胸腰椎骨折的生物力学研究与临床应用[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2009,27(3): 347-350.
[25]Shen WJ, Liu TJ, Shen YS. Nonoperative treatment versus posterior fixation for thoracolumbar junction burst fractures without neurologic deficit. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(9): 1038-1045.
[26]吕夫新,黄勇,张强,等.胸腰椎骨折伤椎椎弓根内固定生物力学研究与临床应用[J].脊柱外科杂志,2008,6(4):229-233.
[27]Farrokhi MR, Razmkon A, Maghami Z, et al. Inclusion of the fracture level in short segment fixation of thoracolumbar fractures. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(10):1651-1656.
[28]肖斌.后路单侧伤椎椎弓根钉内固定的生物力学评价[D]:广州:广州医学院.2009.
[29]贾水淼,董胜利,张凯,等.伤椎单侧椎弓根固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的临床探讨[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(20):1595-1596.
[30]潘兵,宋舟锋,张志敬,等.经伤椎单侧椎弓根固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的初步临床研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2013,15(3):247-250.
[31]刘匆聪,镇万新,高国勇,等.经伤椎与跨伤椎短节段内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效比较[J].广东医学,2013,34(4):590-592.
[32]徐兆万,万青山,王炳武,等.相邻椎体单节段椎弓根内固定椎间植骨融合治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2007,23(3):182-184.
[33]刘春生,王长富,杜心如.经伤椎椎弓根螺钉撬拨恢复椎体前缘高度及生理弯曲的临床观察[J].解剖与临床,2010,6(15):179-182. |
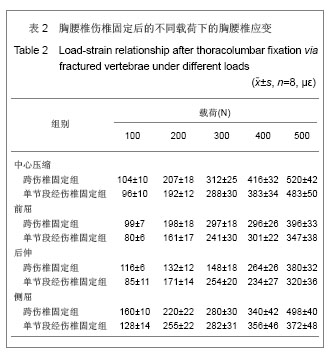
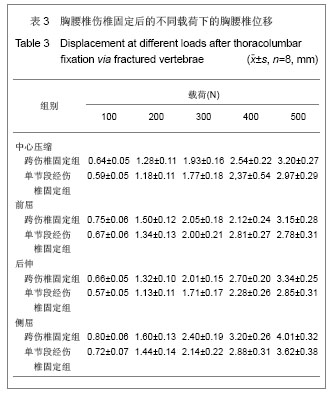
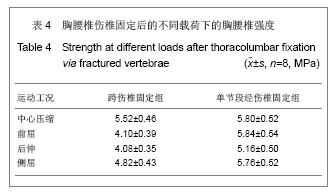
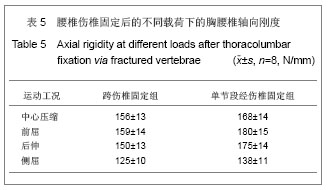
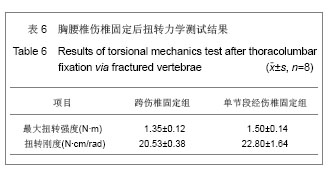
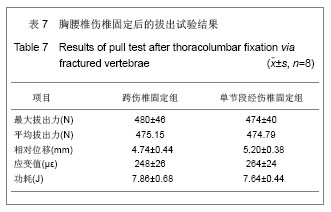
.jpg)
.jpg)
