3.1 局部麻醉药 局部麻醉药是在局部发生感觉(痛温觉)及运动(肌力)消失的效果,应用后对神经或肌肉无损伤,其麻醉范围小,不良反应少,较安全。实验选用的盐酸利多卡因和盐酸布比卡因具有一定的代表性。
目前局部麻醉药产生神经阻滞的确切机制尚不清楚,在表面电荷学说、膜膨胀学说和受体部位学说中,又以受体部位学说受重视。该学说认为局部麻醉药是通过对神经细胞膜钠通道的阻滞,使钠通道失活来阻滞神经传导。
颜光美[2]认为,在神经阻滞时痛觉先消失,然后是冷觉、温觉、触觉和压觉消失,最后为运动神经麻醉;麻醉消失时顺序相反。
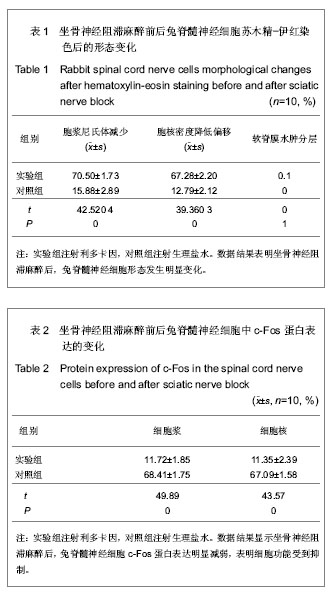
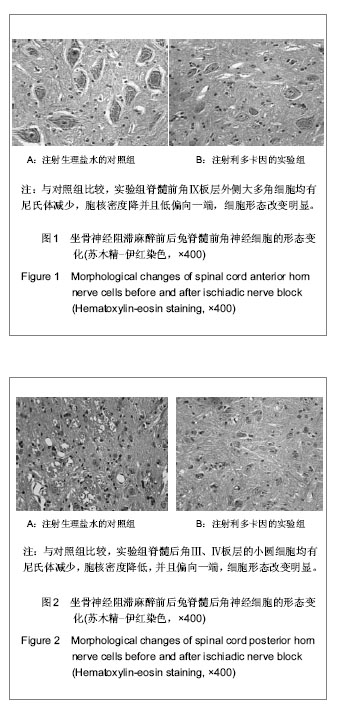
3.2 周围神经阻滞麻醉与尼氏体的关系 实验结果显示,坐骨神经阻滞麻醉,腰麻,硬膜外阻滞麻醉后,L5、L6、L7节段脊髓后角Ⅲ、Ⅳ板层小细胞,脊髓前角Ⅸ板层外侧大多角细胞胞浆尼氏体减少,向外周移位,细胞核密度减低,核偏向一端。对照组脊髓神经细胞胞浆尼氏体分布均匀,胞核密度均匀无偏移。
尼氏体光镜下呈嗜碱性的颗粒或小块状。不同神经元尼氏体的形状、数量和大小不一。一般大神经元,尤其是大运动神经元的尼氏体丰富而粗大,犹如虎皮斑纹样;小神经元的尼氏体则较小而少。电镜下尼氏体是由平行排列的粗面内质网和游离核糖体构成的。
当代谢功能出现障碍时尼氏小体的形态可发生变化。当神经元损伤、过度疲劳和衰老时均能引起尼氏体的减少、解体,甚至消失[3]。坐骨神经横断常致脊髓前角运动神经元发生轴突反应,形态上表现为尼氏体溶解,核偏位等改变[4]。所以实验中的神经细胞尼氏体向周围分布,细胞核偏向一端,说明细胞功能受到抑制。
尼氏体溶解时细胞受损,胞浆内成分水解,损害不重时可以完全恢复,因此它是神经元的急性可逆性变性过程[5]。因此,麻醉作用后神经细胞的尼氏体逐渐增加,向核周围分布[6]。所以,正常麻醉是一个可逆的过程,有待进一步研究。尼氏染色中尼氏体受染后呈块状(形如虎斑) 或颗粒状,核周围尼氏体颗粒较大,近边缘处较小而细长,如在生理情况下尼氏体大而数量多,反映神经细胞合成蛋白质的功能较强,在神经元受损时,尼氏体的数量可减少甚至消失。通过尼氏染色后对尼氏体的观察来了解神经元的损伤[7]。陈德英等[7]探讨了神经元尼氏染色法在外周神经损伤研究中的应用,实验建立坐骨神经切断损伤模型,脊髓L4-6腰膨大连续石蜡切片,焦油紫尼氏染色的方法。结果显示坐骨神经切断损伤后,脊髓L4-6腰膨大前角外侧大、中型神经元较正常对照组数量减少,存活率下降,细胞轮廓不清,尼氏体模糊,表明焦油紫染色显示尼氏体的方法适用于坐骨神经损伤时脊髓腰膨大前角神经元的形态学研究。
实验结果正说明外周神经阻滞麻醉后,脊髓神经细胞形态发生改变,细胞c-Fos蛋白表达减弱或消失,是脊髓神经细胞功能受到了抑制。此外,蛛网膜下腔阻滞麻醉后脊软膜有水肿,分层或断裂;对照组软脊膜无变化。局部麻醉药直接作用于脊髓软脊膜后有血管扩张,软脊膜不同程度的水肿,浓度太大时可能分层断裂,说明蛛网膜下腔阻滞麻醉对软脊膜刺激较大。
3.3 周围神经阻滞麻醉与c-Fos蛋白表达之间的关系 对照组脊髓神经细胞c-Fos阳性表达,显示染成棕黄色颗粒,大部分为胞浆着色,胞核也有着色;阻滞麻醉后的脊髓神经细胞c-Fos免疫组织化学表达不明显或阴性。
c-fos基因是即刻早期基因,正常生理情况下在多种细胞中均有低水平的表达,起到参与细胞的生长、分化、信息传导等生理功能,其特征为静止细胞在受到外界多种刺激时能快速、早期表达[8]。
多种麻醉药单纯给药均可引起中枢神经系统c-fos基因的表达,但表达的程度和部位有差异[9]。局部麻醉药可阻断神经冲动的传导,使c-fos基因表达减弱[10]。
资料已证实各种伤害性刺激(包括疼痛,创伤,精神心理因素等)均可诱导多种组织细胞中c-fos基因的表 达[11]。王贤裕等[9]观察星状神经节阻滞对甲醛致痛兔脊髓背角c-fos基因表达的影响,探讨其治疗疼痛的可能机制。实验在星状神经节阻滞模型建立1周后,19只日本大耳白兔随机分为假手术组5例、星状神经节阻滞组和对照组各7例:假手术组麻醉后灌注固定取脊髓C6-8,星状神经节阻滞组和对照组在皮下注射甲醛1 h后,星状神经节阻滞组经导管注入0.25%布比卡因0.5 mL,对照组用等量的生理盐水,观察1 h后灌注固定取脊髓;用免疫组织化学方法检测脊髓背角Fos含量的变化。结果显示星状神经节阻滞组和对照组刺激侧脊髓背角内可见大量的Fos阳性神经元,Fos阳性神经元主要集中分布于背角Ⅰ、Ⅱ层,但两组间Fos的A值无明显差别(P > 0.05);而对侧脊髓和假手术组内未见或偶见少量Fos阳性神经元,表明皮下注射甲醛可引起兔脊髓背角c-fos基因的表达,但星状神经节阻滞对其无明显影响。但在一定程度上c-fos基因被诱导的数量与所受刺激强度一致,而且c-fos基因表达的数量和时程随刺激强度、时间及性质而异。许多研究结果表明,在中枢神经系统中伤害性刺激诱导的c-fos表达多数情况下可被麻醉药所抑制[12]。实验结果说明神经阻滞麻醉可抑制脊髓神经细胞中c-Fos蛋白的表达。
目前认为c-fos基因产物Fos蛋白具有核内调节因子的功能,它可与其他核蛋白,如JUN蛋白通过LZ形成转录因子AP-1,与DNA结合以调控某些效应基因的表达。已有证据指出Fos蛋白调控脑啡肽、NGF、cck-8等基因表达。研究认为c-fos基因在神经网络的建立,神经递质或调质的合成与相互平衡方面具有重要作用[13]。周围神经阻滞麻醉后阻断了神经冲动的传导,减弱了转录因子AP-1与DNA结合,调控c-fos效应基因的表达。有学者利用c-fos技术对全麻药物的作用机制、疼痛机制、应激反应已进行了不同角度和深度的探讨[13]。
局部麻醉药是通过对神经细胞膜钠通道的阻滞,使钠通道失活来阻滞神经传导的[14]。实验中周围神经阻滞麻醉(坐骨神经阻滞麻醉、硬膜外神经阻滞麻醉和腰麻)后,神经细胞膜的钠通道被阻滞,神经兴奋的传导被抑制,细胞核c-fos基因接受的信号减少,表达的蛋白相应减少。这就进一步说明周围神经阻滞麻醉后,脊髓神经细胞的功能受到了抑制,但这种功能抑制到底对神经功能的影响有多大有待进一步探讨研究。
实验通过对标本苏木精-伊红染色观察脊髓灰质后角Ⅲ、Ⅳ板层小圆细胞,前角Ⅸ板层外侧大多角细胞的形态,免疫组织化学SP法检测c-Fos蛋白在上述神经细胞中的表达,从而探讨周围神经阻滞麻醉对脊髓节段的影响。现得出以下结论:兔坐骨神经阻滞麻醉、蛛网膜下腔阻滞麻醉、硬膜外阻滞麻醉后,相应节段脊髓后角Ⅲ、Ⅳ板层小圆细胞,前角Ⅸ板层外侧大多角细胞有变化,苏木精-伊红染色显示胞浆尼氏体减少,向外周分布,细胞核密度减低向一端移位。此外,蛛网膜下腔阻滞麻醉后脊软膜有水肿,分层或断裂。免疫组织化学显示,对照组c-Fos阳性表达细胞显示棕黄色颗粒,大部分为胞浆着色,胞核也有着色;阻滞麻醉后的细胞c-Fos表达有下降趋势。


.jpg)